Physics - Agra Public School
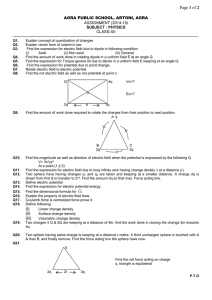
... Find the expression for electric field due to long infinity wire having change density λ at a distance [r]. Two sphere have having changes q1 and q2 are taken and keeping at a smaller distance. A charge dq is drawn from first & to transfer to 2nd. Find the amount dq so that max. Force acting b/w. De ...
... Find the expression for electric field due to long infinity wire having change density λ at a distance [r]. Two sphere have having changes q1 and q2 are taken and keeping at a smaller distance. A charge dq is drawn from first & to transfer to 2nd. Find the amount dq so that max. Force acting b/w. De ...
On Faraday`s Lines of Force
... "...that one body may act upon another at a distance through a vacuum without the mediation of anything else, by and through which their action and force may be conveyed from one to another, is to me so great an absurdity that, I believe no man, who has in philosophic matters a competent faculty of ...
... "...that one body may act upon another at a distance through a vacuum without the mediation of anything else, by and through which their action and force may be conveyed from one to another, is to me so great an absurdity that, I believe no man, who has in philosophic matters a competent faculty of ...
Gauss` Law
... Let us consider a uniform electric field which crosses some plane surface in space. For simplicity, let this electric field be perpendicular to the surface, so we can look at this as if the field flows through the surface and introduce the concept of electric flux. Remember that the density of elect ...
... Let us consider a uniform electric field which crosses some plane surface in space. For simplicity, let this electric field be perpendicular to the surface, so we can look at this as if the field flows through the surface and introduce the concept of electric flux. Remember that the density of elect ...
Electric Potential Energy
... ► 1 eV = the amount of energy gained by one electron moving through 1 Volt of potential difference ► 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
... ► 1 eV = the amount of energy gained by one electron moving through 1 Volt of potential difference ► 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.