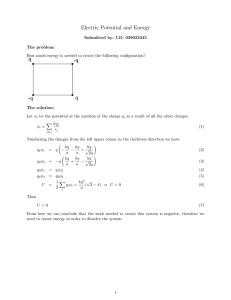
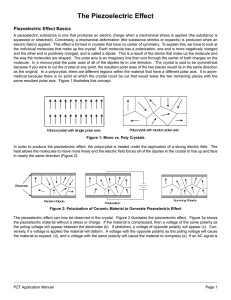
Electricity and Magnetism
... Energy is a word used to describe some kinds of energy. When you did the experiment with the balloons you produced one kind of electricity. Rubbing the two balloons together caused a change. They either pulled toward each other or pushed away from each other. These two results come from a single ...
... Energy is a word used to describe some kinds of energy. When you did the experiment with the balloons you produced one kind of electricity. Rubbing the two balloons together caused a change. They either pulled toward each other or pushed away from each other. These two results come from a single ...
PH262 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... 10. Calculate the electric field for various charge distributions from Coulomb's Law. 11. Apply Gauss' Law in the calculation of the electric field due to several charge symmetries. 12. Apply the concepts of electrical energy, potential at a point, and potential difference to various charge distribu ...
... 10. Calculate the electric field for various charge distributions from Coulomb's Law. 11. Apply Gauss' Law in the calculation of the electric field due to several charge symmetries. 12. Apply the concepts of electrical energy, potential at a point, and potential difference to various charge distribu ...
Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... plates separated by a distance. Examine how the electric field strength at a point varies according to the inverse square of the distance between two charges Solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law including electrostatic equilibrium in one-and two-dimensions. Represent magnetic fields using magneti ...
... plates separated by a distance. Examine how the electric field strength at a point varies according to the inverse square of the distance between two charges Solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law including electrostatic equilibrium in one-and two-dimensions. Represent magnetic fields using magneti ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.