1 –Electrostatics
... space at all its points, not only at those points where they are placed. The result of this modification is that when a test charge q0 is put at any point r then the force F = q0E(r) is acting on it. Elecric field of a point charge q follows from the Coulomb´s law and it is given by ...
... space at all its points, not only at those points where they are placed. The result of this modification is that when a test charge q0 is put at any point r then the force F = q0E(r) is acting on it. Elecric field of a point charge q follows from the Coulomb´s law and it is given by ...
General Physics for Engineering II PHYS 191
... LO 4 Draw the equipotential lines of electric potential for various simple charge configurations. Define and calculate the basic physical quantities of Magnetostatics for the case of simple steady LO 5 current distribution; namely magnetic force, magnetic field, and magnetic dipole moment. LO 6 Desc ...
... LO 4 Draw the equipotential lines of electric potential for various simple charge configurations. Define and calculate the basic physical quantities of Magnetostatics for the case of simple steady LO 5 current distribution; namely magnetic force, magnetic field, and magnetic dipole moment. LO 6 Desc ...
Answer ONE question from each unit
... Derive the expression for magnetic field intensity due to a infinite straight conductor placed along z axis which carries a uniform line current I amps. 6M Derive the expression for magnetic field infinite steel sheet of current using Ampere’s circuit law. 6M ...
... Derive the expression for magnetic field intensity due to a infinite straight conductor placed along z axis which carries a uniform line current I amps. 6M Derive the expression for magnetic field infinite steel sheet of current using Ampere’s circuit law. 6M ...
E_Field_2015feb_2702
... "...that one body may act upon another at a distance through a vacuum without the mediation of anything else, by and through which their action and force may be conveyed from one to another, is to me so great an absurdity that, I believe no man, who has in philosophic matters a competent faculty of ...
... "...that one body may act upon another at a distance through a vacuum without the mediation of anything else, by and through which their action and force may be conveyed from one to another, is to me so great an absurdity that, I believe no man, who has in philosophic matters a competent faculty of ...
.divxbhpi` ici lr dcyd z` aygp kdq d ~ E =
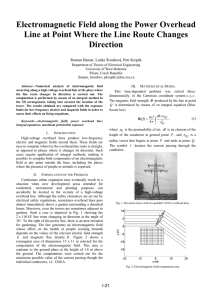
... What is the electrical field in the middle of the circle? The solution: The simple solution is to use superposition. The electric field in the middle of a complete ring is, of course, zero. Now we’ll sum up the field of a complete ring with the field of a very small wire of the same size and shape a ...
... What is the electrical field in the middle of the circle? The solution: The simple solution is to use superposition. The electric field in the middle of a complete ring is, of course, zero. Now we’ll sum up the field of a complete ring with the field of a very small wire of the same size and shape a ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.