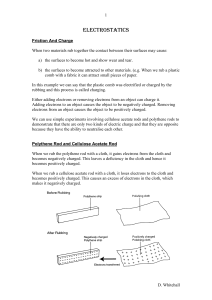
The 4 Maxwell`s Equations Facts on EM waves Quick Quiz on EM
... When a battery is connected to a circuit the current does not jump instantaneously from 0 to the final value !/R because there is an induced emf opposing to battery action. By calculating the work done in a solenoid against induced emf arising from increasing B-flux as current goes from 0 to I we ca ...
... When a battery is connected to a circuit the current does not jump instantaneously from 0 to the final value !/R because there is an induced emf opposing to battery action. By calculating the work done in a solenoid against induced emf arising from increasing B-flux as current goes from 0 to I we ca ...
Physics 417G : Solutions for Problem set 3
... Let us also consider the same thick spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b, which now carries a different polarization vector P~ (~r) = kr r̂, where k is a constant and ~r is the vector from the center. We add a metal sphere with radius a inside the inner shell with the same origin of ...
... Let us also consider the same thick spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b, which now carries a different polarization vector P~ (~r) = kr r̂, where k is a constant and ~r is the vector from the center. We add a metal sphere with radius a inside the inner shell with the same origin of ...
Study Guide - Chapter 33-1
... distance < from a displacement current M. is given by the formula F œ ...
... distance < from a displacement current M. is given by the formula F œ ...
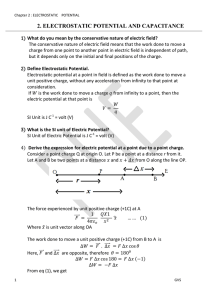
2. electrostatic potential and capacitance
... 26) What are Dielectrics? Mention the types of Dielectrics. Dielectrics are non-conducting substances. They have no charge carriers. There are two types of Dielectrics, polar Dielectrics and non-polar Dielectrics. 27) What are non-polar Dielectrics? Give examples. The non-polar Dielectrics are those ...
... 26) What are Dielectrics? Mention the types of Dielectrics. Dielectrics are non-conducting substances. They have no charge carriers. There are two types of Dielectrics, polar Dielectrics and non-polar Dielectrics. 27) What are non-polar Dielectrics? Give examples. The non-polar Dielectrics are those ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.