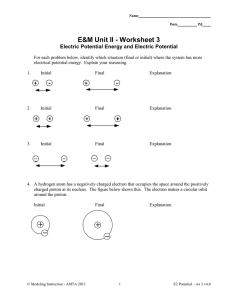
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... to one point charge is E, what is the value due to the 4 point charges? If the value of the electric potential at P due to one positive point charge is V, what is the value due to the 4 point charges? +Q -Q ...
... to one point charge is E, what is the value due to the 4 point charges? If the value of the electric potential at P due to one positive point charge is V, what is the value due to the 4 point charges? +Q -Q ...
Misconception Problems
... 1) charges are equal and positive 2) charges are equal and negative 3) charges are equal and opposite 4) charges are equal, but sign is undetermined 5) charges cannot be equal y ...
... 1) charges are equal and positive 2) charges are equal and negative 3) charges are equal and opposite 4) charges are equal, but sign is undetermined 5) charges cannot be equal y ...
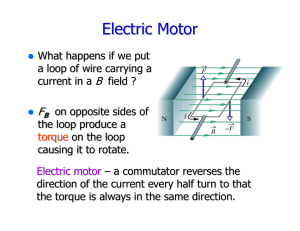
Global Circuit Overview
... Interaction of two point charges, electrostatic attraction between two point charges (of opposite sign) ...
... Interaction of two point charges, electrostatic attraction between two point charges (of opposite sign) ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.