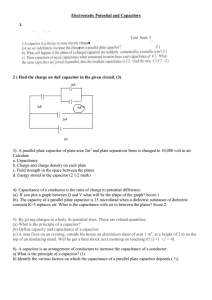
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
Scott Foresman Science
... This created an electric current. Faraday invented a device called a dynamo. A dynamo has a magnet inside a coil of wire. When the magnet moves back and forth, the dynamo produces electricity. When the magnet stops moving, the electric current stops. This shows that electric current and magnetic fie ...
... This created an electric current. Faraday invented a device called a dynamo. A dynamo has a magnet inside a coil of wire. When the magnet moves back and forth, the dynamo produces electricity. When the magnet stops moving, the electric current stops. This shows that electric current and magnetic fie ...
Resonant Frequencies in the Open Microstrip Structures
... An example of the elliptic structure is a microstrip rectangular patch of dimensions L = 3 cm and W = 4 cm located on a single dielectric substrate with a relative permittivity εr1 = 2.32 and thickness h = 0.795 mm covering the elliptical metal core of dimensions amax = 5 cm and amin ∈ (0.3, 0.999)a ...
... An example of the elliptic structure is a microstrip rectangular patch of dimensions L = 3 cm and W = 4 cm located on a single dielectric substrate with a relative permittivity εr1 = 2.32 and thickness h = 0.795 mm covering the elliptical metal core of dimensions amax = 5 cm and amin ∈ (0.3, 0.999)a ...
Lecture
... Flux through the surface due to ALL the charges this charge contributes ZERO FLUX as every field line from it that enters the surface at one point, leaves at another ...
... Flux through the surface due to ALL the charges this charge contributes ZERO FLUX as every field line from it that enters the surface at one point, leaves at another ...
Dielectric
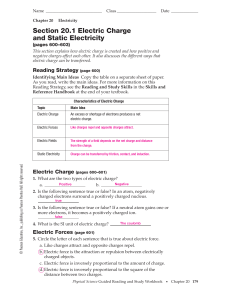
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.