The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models
... and protein disulfide isomerases (PDI) [37]. Together, these findings suggest that PrPC organizes its molecular environment by binding adhesion molecules, which in turn recognize oligomannose-bearing membrane proteins. 4. Polymorphisms and Mutations in the PRNP Gene ORF More than 30 mutations in the ...
... and protein disulfide isomerases (PDI) [37]. Together, these findings suggest that PrPC organizes its molecular environment by binding adhesion molecules, which in turn recognize oligomannose-bearing membrane proteins. 4. Polymorphisms and Mutations in the PRNP Gene ORF More than 30 mutations in the ...
Dairy 17 - Milk Urea Nitrogen
... • Breakdown of excess amino acids in the liver. Excessive production of urea is associated with inefficient use of protein in dairy cow diets and has been implicated with reductions in dairy herd fertility in some situations. Most of the urea produced is removed via urine but some passes into the mi ...
... • Breakdown of excess amino acids in the liver. Excessive production of urea is associated with inefficient use of protein in dairy cow diets and has been implicated with reductions in dairy herd fertility in some situations. Most of the urea produced is removed via urine but some passes into the mi ...
chemistry 1000 - U of L Class Index
... On March 15, 2007, the US FDA learned that some brands of pet food were making animals very ill – even killing some! This was traced to vegetable proteins imported from China which were found to contain melamine. There was a large-scale recall of pet food and the responsible individuals were indicte ...
... On March 15, 2007, the US FDA learned that some brands of pet food were making animals very ill – even killing some! This was traced to vegetable proteins imported from China which were found to contain melamine. There was a large-scale recall of pet food and the responsible individuals were indicte ...
Supplemental figure legends13092010HM
... (Topf et al, 2008). The fitting procedure for the apo exosome improved the crosscorrelation coefficient between the cryo-EM map and the pseudo-atomic model from 0.54 for a rigid body fit of the crystal structures to 0.62 for the final model after flexible fitting. Fitting of the RNA-bound exosome wa ...
... (Topf et al, 2008). The fitting procedure for the apo exosome improved the crosscorrelation coefficient between the cryo-EM map and the pseudo-atomic model from 0.54 for a rigid body fit of the crystal structures to 0.62 for the final model after flexible fitting. Fitting of the RNA-bound exosome wa ...
Docking of B-cell epitope antigen to specific hepatitis B antibody
... algorithm which use a large cartesian grid to perform the Fourier transforms to accommodate all possible translations of the antigen about the stationary antibody. The default value in steric scan was used to improve the resolution in docking correlation. With suitable scaling factors, this docking ...
... algorithm which use a large cartesian grid to perform the Fourier transforms to accommodate all possible translations of the antigen about the stationary antibody. The default value in steric scan was used to improve the resolution in docking correlation. With suitable scaling factors, this docking ...
BLAST Homepage and Selected Search Pages
... page (pg.3). The main difference is that the database pull-down menu contains a smaller list of protein databases (J). Program Selection Four different programs (K and Table 1) are K available to satisfy various search needs. The default blastp is a general purpose protein alignment program for iden ...
... page (pg.3). The main difference is that the database pull-down menu contains a smaller list of protein databases (J). Program Selection Four different programs (K and Table 1) are K available to satisfy various search needs. The default blastp is a general purpose protein alignment program for iden ...
A model for mis-sense error in protein synthesis: mis
... referred to as anti-codon, matches perfectly, by complementary base pairing, with the codon on the template mRNA. In contrast, increasing degree of mismatch makes the tRNA near-cognate or non-cognate. However, because of the intrinsic stochasticity of aminoacylation, and occasional failure of the ed ...
... referred to as anti-codon, matches perfectly, by complementary base pairing, with the codon on the template mRNA. In contrast, increasing degree of mismatch makes the tRNA near-cognate or non-cognate. However, because of the intrinsic stochasticity of aminoacylation, and occasional failure of the ed ...
Characterization of Proteins Structurally Related to Human N
... association of each isoenzyme with the respective fraction was confirmed by Cellogel electrophoresis as described by Braidman et al. (1974). The recovery of protein was 75-77% of that applied (range from three experiments). Under these conditions the serologically unrelated hexosaminidase C is not r ...
... association of each isoenzyme with the respective fraction was confirmed by Cellogel electrophoresis as described by Braidman et al. (1974). The recovery of protein was 75-77% of that applied (range from three experiments). Under these conditions the serologically unrelated hexosaminidase C is not r ...
GI Endoscopic Procedures Operative Sequence - A
... Total Thyroidectomy may be done for malignancies – patient will have to take thyroid hormones for the rest of their life. Hyperthyroidism may be treated with a subtotal ...
... Total Thyroidectomy may be done for malignancies – patient will have to take thyroid hormones for the rest of their life. Hyperthyroidism may be treated with a subtotal ...
Overview of Urea and Creatinine
... rate (GFR.) Creatinine is produced endogenously within the body and is freely filtered by the glomerulus. These characteristics make creatinine a useful endogenous marker for creatinine clearance. If the GFR is decreased, as is in renal disease, creatinine clearance via the renal system is compromis ...
... rate (GFR.) Creatinine is produced endogenously within the body and is freely filtered by the glomerulus. These characteristics make creatinine a useful endogenous marker for creatinine clearance. If the GFR is decreased, as is in renal disease, creatinine clearance via the renal system is compromis ...
Supplementary Figure 2. Further examples of large differences
... scores assigned to predictions of binding site residues. Blue sticks represent the observed residues, red sticks represent incorrectly predicted residues, green sticks represent correctly predicted residues, yellow sticks represent neutral residues (ambiguous residues defined in CASP8 that were cons ...
... scores assigned to predictions of binding site residues. Blue sticks represent the observed residues, red sticks represent incorrectly predicted residues, green sticks represent correctly predicted residues, yellow sticks represent neutral residues (ambiguous residues defined in CASP8 that were cons ...
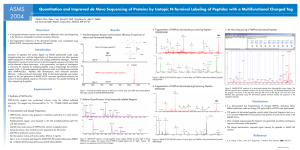
ASMS 2004 de Novo
... • It is demonstrated that fragmentations of charged TMPP-Ac derivatives follow different pathways under low energy CID performed in a Q-TOF mass spectrometer. ...
... • It is demonstrated that fragmentations of charged TMPP-Ac derivatives follow different pathways under low energy CID performed in a Q-TOF mass spectrometer. ...
to this tutorial as a PDF
... Each amino acid in a polypeptide chain is assigned a sequential number. You can use these number identifiers to select individual amino acids or ranges of amino acids. Note that there can be more than one amino acid with a given number, if there are more than one polypeptide chains in a structure fi ...
... Each amino acid in a polypeptide chain is assigned a sequential number. You can use these number identifiers to select individual amino acids or ranges of amino acids. Note that there can be more than one amino acid with a given number, if there are more than one polypeptide chains in a structure fi ...
Analytical Ultracentrifugation for Protein Analytical
... method includes using more precisely manufactured centerpieces, more consistent alignment control, and more accurate data fitting approaches (Gabrielson, J.P., et al., (2009). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 98(1). p. 50-62.) ...
... method includes using more precisely manufactured centerpieces, more consistent alignment control, and more accurate data fitting approaches (Gabrielson, J.P., et al., (2009). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 98(1). p. 50-62.) ...
Protein Structure and Interactions
... Chaperones are generally viewed as proteins that facilitate proper folding of other proteins often by preventing aggregation of folding intermediates. Another important class of chaperones is ribonucleic acid (RNA) chaperones. RNA chaperones are proteins that facilitate conformational changes of RNA ...
... Chaperones are generally viewed as proteins that facilitate proper folding of other proteins often by preventing aggregation of folding intermediates. Another important class of chaperones is ribonucleic acid (RNA) chaperones. RNA chaperones are proteins that facilitate conformational changes of RNA ...
4. Characterisation of novel proteins
... No differences of biological significance were observed between corn line 5307 and the nearisogenic line used as a comparator. A small number of statistical differences in some analytes were noted, but these occurred randomly across trial sites. Differences such as these simply reflect the fact that ...
... No differences of biological significance were observed between corn line 5307 and the nearisogenic line used as a comparator. A small number of statistical differences in some analytes were noted, but these occurred randomly across trial sites. Differences such as these simply reflect the fact that ...
BEL β-trefoil: A novel lectin with antineoplastic properties in king
... where x can be any residue, has been identified in the three subdomains of many lectins with the β-trefoil fold (Hazes 1996). In the case of BEL β-trefoil, it is present only in the third subdomain, amino acids 139–141, QLW and has been highlighted in Figure 1A. A sequence similarity search in the Ex ...
... where x can be any residue, has been identified in the three subdomains of many lectins with the β-trefoil fold (Hazes 1996). In the case of BEL β-trefoil, it is present only in the third subdomain, amino acids 139–141, QLW and has been highlighted in Figure 1A. A sequence similarity search in the Ex ...
Structure, function, and evolution of phosphoglycerate mutases
... In contrast to dPGMs, the iPGM enzymes are monomers and are signi®cantly larger than dPGMs or bPGMs, with a molecular weight of 050 kDa per monomer (Chander et al., 1999). The sequence similarity among iPGMs, even from dierent kingdoms, is very high suggesting their structural and functional simila ...
... In contrast to dPGMs, the iPGM enzymes are monomers and are signi®cantly larger than dPGMs or bPGMs, with a molecular weight of 050 kDa per monomer (Chander et al., 1999). The sequence similarity among iPGMs, even from dierent kingdoms, is very high suggesting their structural and functional simila ...
Supplementary Online Materials
... HeliQuest programme. Some of the polar and charged amino acids in the membrane-spanning helices enable an intramolecular interaction between TM1 and other semihydrophobic and/or amphipathic -helices folded by other regions within the NHB1-CNC factor (below), as has been described for other transmem ...
... HeliQuest programme. Some of the polar and charged amino acids in the membrane-spanning helices enable an intramolecular interaction between TM1 and other semihydrophobic and/or amphipathic -helices folded by other regions within the NHB1-CNC factor (below), as has been described for other transmem ...
Plastics_and_Reconstructive_Procedures
... other breast, where the same procedure is followed. Once the second side is temporarily closed, the patient is once again sat up to compare both breasts and t determine if further work is needed. If the MD is satisfied, the patient is returned to the supine position and ...
... other breast, where the same procedure is followed. Once the second side is temporarily closed, the patient is once again sat up to compare both breasts and t determine if further work is needed. If the MD is satisfied, the patient is returned to the supine position and ...
E.Coli Biological Background of Translation Initiation and
... to the 5´ end of the mRNA molecule. However, this does not happen in all cases. ...
... to the 5´ end of the mRNA molecule. However, this does not happen in all cases. ...
Neighbor-Dependent Ramachandran Probability Distributions of
... etc.); 2) filtering of suspect conformations and outliers using B-factors or other features; 3) secondary structure of input data (e.g., whether helix and sheet are included; whether beta turns are included); 4) the method used for determining probability densities ranging from simple histograms to ...
... etc.); 2) filtering of suspect conformations and outliers using B-factors or other features; 3) secondary structure of input data (e.g., whether helix and sheet are included; whether beta turns are included); 4) the method used for determining probability densities ranging from simple histograms to ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.


![[7] Semisynthesis of Proteins Containing Selenocysteine](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004768810_1-d08ecd7536246bbf8b4baa16bb630c93-300x300.png)