Standard for the presentation of nucleotide and amino acid
... sequences which are included are any unbranched sequences of four or more amino acids or unbranched sequences of ten or more nucleotides. Branched sequences, sequences with fewer than four specifically defined nucleotides or amino acids as well as sequences comprising nucleotides or amino acids othe ...
... sequences which are included are any unbranched sequences of four or more amino acids or unbranched sequences of ten or more nucleotides. Branched sequences, sequences with fewer than four specifically defined nucleotides or amino acids as well as sequences comprising nucleotides or amino acids othe ...
Needleman Wunsch sequence alignment
... aligned_seq1 = "" aligned_seq2 = "" i = len(seq1) j = len(seq2) while(i !=0 or j != 0): if(T[i][j] == “L”): aligned_seq1 = “-” + aligned_seq1 aligned_seq2 = seq2[j-1] + aligned_seq2 j = j - 1 elif(T[i][j] == "U"): aligned_seq2 = "-" + aligned_seq2 aligned_seq1 = seq1[i-1] + aligned_seq1 i = i - 1 el ...
... aligned_seq1 = "" aligned_seq2 = "" i = len(seq1) j = len(seq2) while(i !=0 or j != 0): if(T[i][j] == “L”): aligned_seq1 = “-” + aligned_seq1 aligned_seq2 = seq2[j-1] + aligned_seq2 j = j - 1 elif(T[i][j] == "U"): aligned_seq2 = "-" + aligned_seq2 aligned_seq1 = seq1[i-1] + aligned_seq1 i = i - 1 el ...
the elastin gene
... significance of "acidic" and "basic" keratins in this respect? 6. What are the main crosslinks in keratin? How can they be broken to partially solubilise the protein? How does increased crosslinking affect keratin's properties? 7. Keratin is the main component of hair. How are individual keratin mol ...
... significance of "acidic" and "basic" keratins in this respect? 6. What are the main crosslinks in keratin? How can they be broken to partially solubilise the protein? How does increased crosslinking affect keratin's properties? 7. Keratin is the main component of hair. How are individual keratin mol ...
structural basis for thermal stability of thermophilic trmd proteins
... few decades, scientists have been examining various extremophile genomes in an attempt to unravel structural conformations and sequences that lead to heat stability. There are two broad categories of thermophilic bacteria, including those which grow optimally at 50oC – 80oC and others that grow betw ...
... few decades, scientists have been examining various extremophile genomes in an attempt to unravel structural conformations and sequences that lead to heat stability. There are two broad categories of thermophilic bacteria, including those which grow optimally at 50oC – 80oC and others that grow betw ...
Strain in Protein Structures as Viewed Through Nonrotameric Side
... freedom to attain multiple rotamers, because a part of its side chain forms the backbone. By using data from 19 well-refined crystallographic structures, Ponder and Richards6 assembled a library of rotamers for each amino acid type based on clustering techniques. They observed that most side chains ...
... freedom to attain multiple rotamers, because a part of its side chain forms the backbone. By using data from 19 well-refined crystallographic structures, Ponder and Richards6 assembled a library of rotamers for each amino acid type based on clustering techniques. They observed that most side chains ...
Cuvier meets Watson and Crick: the utility of molecules as classical
... collagen triple helix. Note the location of glycine residues in the core of the collagen helix. (Modified from Piez, 1984.) ...
... collagen triple helix. Note the location of glycine residues in the core of the collagen helix. (Modified from Piez, 1984.) ...
Modeling Cell Proliferation Activity of Human Interleukin
... • IL-3 promotes the growth of many hematopoietic cell lines • Theoretically, there are 19 × 112 = 2128 possible IL-3 mutants via single residue substitutions at all positions in the structure • Experimental dataset: 630 of these IL-3 mutants were synthesized, representing substitutions at all but 12 ...
... • IL-3 promotes the growth of many hematopoietic cell lines • Theoretically, there are 19 × 112 = 2128 possible IL-3 mutants via single residue substitutions at all positions in the structure • Experimental dataset: 630 of these IL-3 mutants were synthesized, representing substitutions at all but 12 ...
A standard nomenclature for von Willebrand factor gene mutations
... For intronic changes, where nt close to the intron/exon boundary are numbered, it is simple to use the cDNA numbering with a + or - sign to designate distance into the intron. For alterations deeper into the intron, the full VWF genomic DNA sequence should be used once it is readily available, until ...
... For intronic changes, where nt close to the intron/exon boundary are numbered, it is simple to use the cDNA numbering with a + or - sign to designate distance into the intron. For alterations deeper into the intron, the full VWF genomic DNA sequence should be used once it is readily available, until ...
Characterization of the unique intron
... HI LHCPIIs can not be classified as type I or II based on amino acid sequence and their genes often contain multiple introns. Euglena gracilis, a unicellular protist, has a LHCPII precursor (pLHCPII) that is a polyprotein containing multiple copies of LHCPII covalently joined by a conserved decapept ...
... HI LHCPIIs can not be classified as type I or II based on amino acid sequence and their genes often contain multiple introns. Euglena gracilis, a unicellular protist, has a LHCPII precursor (pLHCPII) that is a polyprotein containing multiple copies of LHCPII covalently joined by a conserved decapept ...
Poster
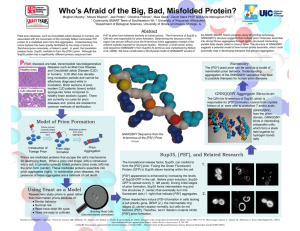
... The translational release factor, Sup35, can misfold to form the [PSI+] prion. Fusing the Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) to Sup35 allows tracking within the cell. [PSI+] appearance is enhanced by increasing the levels of Sup35-GFP in the cell. Before prion induction, Sup35GFP is spread evenly (1. l ...
... The translational release factor, Sup35, can misfold to form the [PSI+] prion. Fusing the Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) to Sup35 allows tracking within the cell. [PSI+] appearance is enhanced by increasing the levels of Sup35-GFP in the cell. Before prion induction, Sup35GFP is spread evenly (1. l ...
The integrity of a cholesterol-binding pocket in Niemann–Pick C2
... The 3D-PSSM web-based homology server (16, 17) identified the Der p 2 dust mite allergen as an excellent template for modeling the NPC2 protein structure (E value 7.14e-13) based on multiple sequence alignment, secondary structure prediction, and solvation potential. The Der p 2 structure is a  san ...
... The 3D-PSSM web-based homology server (16, 17) identified the Der p 2 dust mite allergen as an excellent template for modeling the NPC2 protein structure (E value 7.14e-13) based on multiple sequence alignment, secondary structure prediction, and solvation potential. The Der p 2 structure is a  san ...
Tertiary base pair interactions in slipped loop-DNA
... sequences (5). Ivanov and co-workers have proposed a threedimensional scheme for such an interaction, according to which the slipped loops form a secondary miniduplex (7,8). For the experimental study of base pair interactions in the SLS, they designed a sequence (SLS-1, figure 2a) that can potentia ...
... sequences (5). Ivanov and co-workers have proposed a threedimensional scheme for such an interaction, according to which the slipped loops form a secondary miniduplex (7,8). For the experimental study of base pair interactions in the SLS, they designed a sequence (SLS-1, figure 2a) that can potentia ...
No Slide Title
... • The [trp] determines the [trp-tRNA]. • The [trp-tRNA] determines whether a translating ribosome will add trp to the leader peptide. • If trp is added: – The ribosome moves on to the translation stop codon. – This places the attenuator in a secondary structure that causes termination of transcripti ...
... • The [trp] determines the [trp-tRNA]. • The [trp-tRNA] determines whether a translating ribosome will add trp to the leader peptide. • If trp is added: – The ribosome moves on to the translation stop codon. – This places the attenuator in a secondary structure that causes termination of transcripti ...
Structure based hypothesis of a mitochondrial
... of Ser-195 to glycine in mtRF1, most likely to accommodate the inserted threonine side chain. It should be noted that this is also one of the identified critical changes between mtRF1 and mtRF1a that we identified. The altered loop conformation that results from the RTinsert seems to completely bloc ...
... of Ser-195 to glycine in mtRF1, most likely to accommodate the inserted threonine side chain. It should be noted that this is also one of the identified critical changes between mtRF1 and mtRF1a that we identified. The altered loop conformation that results from the RTinsert seems to completely bloc ...
PRIONS THE INFECTIOUS PROTEINS
... What are Calpains? They generate a C-terminal fragment(C2) which has molecular weight of 27-30 kDs. ...
... What are Calpains? They generate a C-terminal fragment(C2) which has molecular weight of 27-30 kDs. ...
"Genetic Methods of Polymer Synthesis". In: Encyclopedia of
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
PDF - University of California, San Francisco
... structure and membrane orientation of 3-hydroxy-3methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, the glycoprotein of the endoplasmic reticulum that controls the rate of cholesterol biosynthesis. This model is derived from proteolysis experiments that separate the 97-kilodalton enzyme into two domains, an NHz-t ...
... structure and membrane orientation of 3-hydroxy-3methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, the glycoprotein of the endoplasmic reticulum that controls the rate of cholesterol biosynthesis. This model is derived from proteolysis experiments that separate the 97-kilodalton enzyme into two domains, an NHz-t ...
Computational and genetic evidence that different structural
... 2012), a process that remains poorly understood in plants. Seed plants contain a CESA protein family with six distinct types of isoforms, including three required for the synthesis of each of the major types of cell walls. For example, in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, AtCESA1, 3, and 6 are a ...
... 2012), a process that remains poorly understood in plants. Seed plants contain a CESA protein family with six distinct types of isoforms, including three required for the synthesis of each of the major types of cell walls. For example, in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, AtCESA1, 3, and 6 are a ...
collagen - MBBS Students Club
... It is the most abundant protein in the body. It is long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides are wound around one another in a rope like fashion. These polypeptides are called α-helix. ...
... It is the most abundant protein in the body. It is long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides are wound around one another in a rope like fashion. These polypeptides are called α-helix. ...
COLLAGEN - Rihs.com.pk
... It is the most abundant protein in the body. It is long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides are wound around one another in a rope like fashion. These polypeptides are called α-helix. ...
... It is the most abundant protein in the body. It is long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides are wound around one another in a rope like fashion. These polypeptides are called α-helix. ...
Steven`s project - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Using the downloaded software The downloaded software is much more difficult to use and does not contain user friendly GU interfaces. Whenever possible a novice user should opt for the on line version as described above. However, if you intend to repack proteins quite regularly, or need to repack i ...
... Using the downloaded software The downloaded software is much more difficult to use and does not contain user friendly GU interfaces. Whenever possible a novice user should opt for the on line version as described above. However, if you intend to repack proteins quite regularly, or need to repack i ...
Supplements - Haiyuan Yu
... web server. In defining these paths, we have attempted to avoid spurious results by minimizing the number of steps in each traversal, avoiding descending and climbing the graph in a single traversal, and minimizing the number of databases used. For instance, when converting from Ensembl Gene to RefS ...
... web server. In defining these paths, we have attempted to avoid spurious results by minimizing the number of steps in each traversal, avoiding descending and climbing the graph in a single traversal, and minimizing the number of databases used. For instance, when converting from Ensembl Gene to RefS ...
Protein Function and Classification (Cont.) - EMBL-EBI
... InterPro provides functional analysis of proteins by classifying them into families and predicting the presence of important domains and sites. It does this by combining predictive models known as protein signatures from a number of different databases (referred to as member databases) into a single ...
... InterPro provides functional analysis of proteins by classifying them into families and predicting the presence of important domains and sites. It does this by combining predictive models known as protein signatures from a number of different databases (referred to as member databases) into a single ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.