Align sequence to structure - Computational Bioscience Program
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
Quiz on Proteins (2.4) - Peoria Public Schools
... A structural change of a protein that results in the loss of its biological properties ...
... A structural change of a protein that results in the loss of its biological properties ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... 3.6 residues/turn - by far the most common helix 4.1 residues/turn - very rare ...
... 3.6 residues/turn - by far the most common helix 4.1 residues/turn - very rare ...
Chemistry 160 Protein Structure Homework
... 2. What are prosthetic groups? 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? 4. Describe the 4 levels of protein structure. 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 8. A small protein was ...
... 2. What are prosthetic groups? 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? 4. Describe the 4 levels of protein structure. 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 8. A small protein was ...
Protein Domains
... query sequence that have low compositional complexity This leaves the biologically interesting regions of the query sequence available for matching against database sequences ...
... query sequence that have low compositional complexity This leaves the biologically interesting regions of the query sequence available for matching against database sequences ...
proteinskubalova
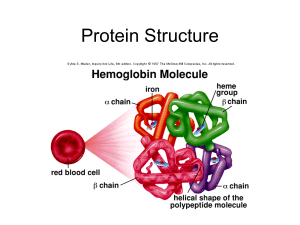
... of different protein chains (heteroliogomers). The different chains within the oligomer may be held together by noncovalent intermolecular forces or may also contain covalent interchain disulfides. held(hold) = držet ...
... of different protein chains (heteroliogomers). The different chains within the oligomer may be held together by noncovalent intermolecular forces or may also contain covalent interchain disulfides. held(hold) = držet ...
Estimation of the protein secondary structure in aqueous solutions
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
ECS 189K - UC Davis
... http://www.rcsb.org, you can locate proteins by keyword searching or by entering the PDB accession number for the structure file, like 5PTI. Details on the molecule (how the structure was determined, pertinent research articles, position of secondary structures, unusual amino acids, etc) can be fou ...
... http://www.rcsb.org, you can locate proteins by keyword searching or by entering the PDB accession number for the structure file, like 5PTI. Details on the molecule (how the structure was determined, pertinent research articles, position of secondary structures, unusual amino acids, etc) can be fou ...
Hidden Markov models for detecting remote protein homologies
... Homologs are chromosomes carrying the same genetic loci; a diploid cell has 2 copies of each homolog, one derived from each parent. A profile of a protein family is a labeling of the positions of the amino acids in the secondary structure and a probability distribution for each position. The stru ...
... Homologs are chromosomes carrying the same genetic loci; a diploid cell has 2 copies of each homolog, one derived from each parent. A profile of a protein family is a labeling of the positions of the amino acids in the secondary structure and a probability distribution for each position. The stru ...
To determine whether related genes appear in other species
... proteins which often contain many copies of closely related domain. Fibronectin: a large extracellular protein involved in cell adhesion and migration contains 29 domains including multiple tandem repeats of three typesof domains called F1, F2 and F3 ...
... proteins which often contain many copies of closely related domain. Fibronectin: a large extracellular protein involved in cell adhesion and migration contains 29 domains including multiple tandem repeats of three typesof domains called F1, F2 and F3 ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
Quiz-2
... 11. MALDI Mass spectrometric analysis of proteins following trypsin digestion is very useful in the identification of proteins. Can you identify a novel protein by this method? Explain your answer. 12. How many amino acids are found in b turn? 13. What weak interactions contribute to the close pack ...
... 11. MALDI Mass spectrometric analysis of proteins following trypsin digestion is very useful in the identification of proteins. Can you identify a novel protein by this method? Explain your answer. 12. How many amino acids are found in b turn? 13. What weak interactions contribute to the close pack ...
Finding an upper bound for the number of contacts in hydrophobic
... It is believed that the functional properties of the protein are dependent on its structure. Therefore, it is critical to predict the protein's structure to understand the functional properties. One of the most widely studied protein structure prediction models is the hydrophobic-hydrophilic (HP) mo ...
... It is believed that the functional properties of the protein are dependent on its structure. Therefore, it is critical to predict the protein's structure to understand the functional properties. One of the most widely studied protein structure prediction models is the hydrophobic-hydrophilic (HP) mo ...
Align sequence to structure - Computational Bioscience Program
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
ppt - Avraham Samson`s Lab
... conformations. For example, a polypeptide of 100 residues will have 99 peptide bonds, and therefore 198 different phi and psi bond angles. If each of these bond angles can be in one of three stable conformations, the protein may misfold into a maximum of 3198 (~10100) different conformations. Theref ...
... conformations. For example, a polypeptide of 100 residues will have 99 peptide bonds, and therefore 198 different phi and psi bond angles. If each of these bond angles can be in one of three stable conformations, the protein may misfold into a maximum of 3198 (~10100) different conformations. Theref ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE CLASSIFICATION
... “Nearly all proteins have structural similarities with other proteins and, in some of these cases, share a common evolutionary origin. The SCOP database, created by manual inspection and abetted by a battery of automated methods, aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive description of the struct ...
... “Nearly all proteins have structural similarities with other proteins and, in some of these cases, share a common evolutionary origin. The SCOP database, created by manual inspection and abetted by a battery of automated methods, aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive description of the struct ...
Document
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
... • Threading: Align sequence to structure (templates) For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino aci ...
structbio_lecture_BCH339N_2016
... Sequence Profiles Profiles can be built from multiple sequence alignments and contain frequencies of all amino acids in each column. This has more information than a single sequence. ...
... Sequence Profiles Profiles can be built from multiple sequence alignments and contain frequencies of all amino acids in each column. This has more information than a single sequence. ...
Hands-on Exercise: Locating Protein Information
... A variant of this protein with mutations in its amino acid sequence has been isolated (see link http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics/tutorials). ...
... A variant of this protein with mutations in its amino acid sequence has been isolated (see link http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics/tutorials). ...
structbio_lecture_BCH391L_20150212.ppt
... = 3^(246) = 10^118 possible states Assume each state takes a picosecond to sample. = 10^20 years to test all states > 13.8 x 10^9 age of universe Proteins take millisecs to microsecs to fold < the age of the universe) Thus a paradox, how do proteins do it? ...
... = 3^(246) = 10^118 possible states Assume each state takes a picosecond to sample. = 10^20 years to test all states > 13.8 x 10^9 age of universe Proteins take millisecs to microsecs to fold < the age of the universe) Thus a paradox, how do proteins do it? ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.