REPSA-Directed Identification of DNA
... Unexpected Consensus Sequences Round 7: 553/1000 sequences ...
... Unexpected Consensus Sequences Round 7: 553/1000 sequences ...
Freshman Seminar
... Sequence databases • What is a database? – An indexed set of records – Records retrieved using a query language – Database technology is well established ...
... Sequence databases • What is a database? – An indexed set of records – Records retrieved using a query language – Database technology is well established ...
Doc
... interesting new gene family members. This opens many new opportunities for structural structure based functional annotation and molecular design. First, we have developed two new techniques to assist rational drug design using crystallographic structures or models by homology. The binding pockets ca ...
... interesting new gene family members. This opens many new opportunities for structural structure based functional annotation and molecular design. First, we have developed two new techniques to assist rational drug design using crystallographic structures or models by homology. The binding pockets ca ...
tutorial10_3D_structure
... identity, but they are structurally similar. • We will download their pdb files from the PDB, and structurally align them using Dalilite. ...
... identity, but they are structurally similar. • We will download their pdb files from the PDB, and structurally align them using Dalilite. ...
A dead-end street of protein folding
... Amino acid sequences of globular proteins encode their 3D-structures linked to their biological function. More evidence supports that for many proteins a second, well organized, but quite different 3Dstructure also exists. The latter types of conformers have an architecture similar to the aggregated ...
... Amino acid sequences of globular proteins encode their 3D-structures linked to their biological function. More evidence supports that for many proteins a second, well organized, but quite different 3Dstructure also exists. The latter types of conformers have an architecture similar to the aggregated ...
LectureIV
... • A centralized database (PDB) contains all solved protein structures – XYZ coordinate of atoms within specified precision – ~19,000 solved structures ...
... • A centralized database (PDB) contains all solved protein structures – XYZ coordinate of atoms within specified precision – ~19,000 solved structures ...
HOW GOOD DO WE HAVE TO BE TO SOLVE THE PROTEIN FOLDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND SCORING PROBLEMS?
... challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of ...
... challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of ...
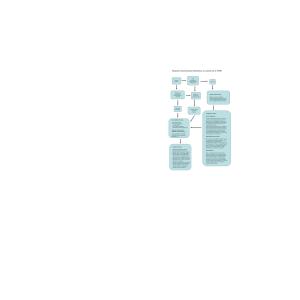
A One- or Two-Day Course for Your Campus on
... Visual exploration of the 3D structures of macromolecules, such as proteins bound to ligands or nucleic acids. Where to find protein structures related to your research, how they are determined, how much of the genome is (and is not) known, and why. Teaching protein 3D structure, ligand interactions ...
... Visual exploration of the 3D structures of macromolecules, such as proteins bound to ligands or nucleic acids. Where to find protein structures related to your research, how they are determined, how much of the genome is (and is not) known, and why. Teaching protein 3D structure, ligand interactions ...
View video content as a PDF
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
PROTEINS
... question how can a protein fold so fasts • The folding code: The ”thermodynamic” question of how a native structure results from interatomic forces acting on an amino acid sequence ...
... question how can a protein fold so fasts • The folding code: The ”thermodynamic” question of how a native structure results from interatomic forces acting on an amino acid sequence ...
Knuffke Prezi- Macromolecules
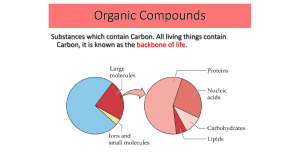
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
Introduction to 3D-Structure Visualization and Homology Modeling
... Template identification: Blast, PSI-Blast PDB: database of protein structures ...
... Template identification: Blast, PSI-Blast PDB: database of protein structures ...
slides
... A significant increase in accuracy (to nearly ~80%) was made by exploiting multiple sequence alignment; knowing the full distribution of amino acids that occur at a position (and in its vicinity, typically ~7 residues on either side) throughout evolution provides a much better picture of the struct ...
... A significant increase in accuracy (to nearly ~80%) was made by exploiting multiple sequence alignment; knowing the full distribution of amino acids that occur at a position (and in its vicinity, typically ~7 residues on either side) throughout evolution provides a much better picture of the struct ...
AASK Additional Activities
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of side chains that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected ...
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of side chains that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected ...
Protein Structure Determination and Design
... Part II: Model Design Practice. 1. Open one of your selected PDB file structures in Jmol. 2. Change the background color to white. 3. Display and color the alpha carbon backbone of your protein model. 4. Highlight the secondary structures in your protein model. 5. Practice saving your model as a JP ...
... Part II: Model Design Practice. 1. Open one of your selected PDB file structures in Jmol. 2. Change the background color to white. 3. Display and color the alpha carbon backbone of your protein model. 4. Highlight the secondary structures in your protein model. 5. Practice saving your model as a JP ...
Answers
... CLUSTALW 1.8 was used for multiple alignment of the three sequences. Areas where there were difference between the sequences were identified using Boxshade version 3.21 – these are shown in the file “Boxshade results”. It can be see that the VEGA sequence has an extra 22 amino acids at the N terminu ...
... CLUSTALW 1.8 was used for multiple alignment of the three sequences. Areas where there were difference between the sequences were identified using Boxshade version 3.21 – these are shown in the file “Boxshade results”. It can be see that the VEGA sequence has an extra 22 amino acids at the N terminu ...
Proteins - Wesleyan College Faculty
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
Fast Categorization of Bacteriophage Protein Families using
... Psi-pred is one of the most reliable available Secondary Structure Prediction Programs ...
... Psi-pred is one of the most reliable available Secondary Structure Prediction Programs ...
1. Overview
... • Protein is crystallized (sometimes low-gravity atmosphere is helpful e.g. NASA) • X-Rays are scattered by electrons in molecule • Diffraction produces a pattern of spots on a film that ...
... • Protein is crystallized (sometimes low-gravity atmosphere is helpful e.g. NASA) • X-Rays are scattered by electrons in molecule • Diffraction produces a pattern of spots on a film that ...
The World of Chemistry
... 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
... 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.