Plate Boundaries Power Point
... Divergent boundaries build chains of volcanoes and rift valleys called a mid-ocean ridge. Mid-ocean ridges are found in the oceans-they are like mountain ranges on the ocean floor created by the new lava that is bubbling up! Little by little, as each batch of molten rock erupts at the mid-ocean rid ...
... Divergent boundaries build chains of volcanoes and rift valleys called a mid-ocean ridge. Mid-ocean ridges are found in the oceans-they are like mountain ranges on the ocean floor created by the new lava that is bubbling up! Little by little, as each batch of molten rock erupts at the mid-ocean rid ...
Executive summary of the updated synthesis of the impacts of
... ACIDIFICATION ON MARINE BIODIVERSITY ...
... ACIDIFICATION ON MARINE BIODIVERSITY ...
Place Matters: Geospatial Tools for Marine Science, Conservation, and Management in the Pacific
... Management in the Pacific Northwest Edited by Dawn J. Wright and Astrid J. Scholz Foreword by Sylvia A. Earle ...
... Management in the Pacific Northwest Edited by Dawn J. Wright and Astrid J. Scholz Foreword by Sylvia A. Earle ...
The role of the Southern Ocean in Earth System modelling
... § uptake of CO2 and heat The Southern Ocean (south of 30S) accounts for § 43% ± 3% (42 ± 5 PgC) of anthropogenic CO2 uptake § 75% ± 22% (23 ± 9 × 1022 J) of heat uptake over the historical period (1850-2005), though only occupying 30% of the ocean surface area. (results from an Earth System Modelli ...
... § uptake of CO2 and heat The Southern Ocean (south of 30S) accounts for § 43% ± 3% (42 ± 5 PgC) of anthropogenic CO2 uptake § 75% ± 22% (23 ± 9 × 1022 J) of heat uptake over the historical period (1850-2005), though only occupying 30% of the ocean surface area. (results from an Earth System Modelli ...
Ocean Depth through Deep Time
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
Read the Abstract
... SUMMARY: The Appalachian-Caledonide orogen was the first to be interpreted as a zone of plate-tectonic collision. Wilson's original question "Did the Atlantic close and then reopen?" addresses only part of what was subsequently termed the "Wilson Cycle". The transition from an expanding to a closin ...
... SUMMARY: The Appalachian-Caledonide orogen was the first to be interpreted as a zone of plate-tectonic collision. Wilson's original question "Did the Atlantic close and then reopen?" addresses only part of what was subsequently termed the "Wilson Cycle". The transition from an expanding to a closin ...
the earth´s relief - Junta de Andalucía
... THE EARTH´S RELIEF Summary 1. Inside Earth The Earth is made of many different and distinct layers. The deeper layers are composed of heavier materials, they are hotter, denser and under much greater pressure than the outer layers. ...
... THE EARTH´S RELIEF Summary 1. Inside Earth The Earth is made of many different and distinct layers. The deeper layers are composed of heavier materials, they are hotter, denser and under much greater pressure than the outer layers. ...
Plate Tectonics Inside Earth Chapter 1 Study
... Earth’s Interior 1) Compare constructive forces to destructive forces. Give an example of each. Constructive forces shape the surface by building up mountains and landmasses. Destructive forces are those that slowly wear away the mountains and, eventually, every other feature on the surface. 2) ...
... Earth’s Interior 1) Compare constructive forces to destructive forces. Give an example of each. Constructive forces shape the surface by building up mountains and landmasses. Destructive forces are those that slowly wear away the mountains and, eventually, every other feature on the surface. 2) ...
Deep Ocean Basins
... (62 mi) of the continental coastline. This is observed, for example, along the west coasts of Central and South America (the Middle America Trench and the Peru-Chile Trench). Where two oceanic plates converge with each other, a more complex situation exists because the densities and thicknesses of ...
... (62 mi) of the continental coastline. This is observed, for example, along the west coasts of Central and South America (the Middle America Trench and the Peru-Chile Trench). Where two oceanic plates converge with each other, a more complex situation exists because the densities and thicknesses of ...
Chapter 10-2 - Seafloor Spreading
... During World War I German scientists introduced the ideas of using sound waves to detect (to find) submarines. In the 1940’s during World War II, scientists began to use sound waves to map the ocean floor. This is sometimes called echo sounding. Sound waves echo off the bottom of the ocean, ...
... During World War I German scientists introduced the ideas of using sound waves to detect (to find) submarines. In the 1940’s during World War II, scientists began to use sound waves to map the ocean floor. This is sometimes called echo sounding. Sound waves echo off the bottom of the ocean, ...
practice exam #1
... b. An asteroid impact destroyed most of the Precambrian rock record c. Nothing lived during the Precambrian, so there is no fossil record d. Organisms that lived during that time had no hard parts e. More of the geologic record of the Precambrian has been destroyed compared to more recent time perio ...
... b. An asteroid impact destroyed most of the Precambrian rock record c. Nothing lived during the Precambrian, so there is no fossil record d. Organisms that lived during that time had no hard parts e. More of the geologic record of the Precambrian has been destroyed compared to more recent time perio ...
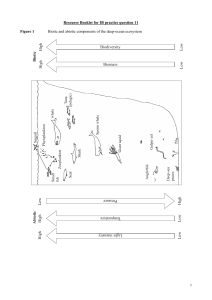
Resource Booklet for IB practice question 11
... The habitat is a predominately dark and cold environment with much lower productivity than shallower waters. No light penetrates beyond 1000 m and even at depths of 150 m light levels are reduced to 1 % of those at the surface and are insufficient to support photosynthesis. Therefore, organic materi ...
... The habitat is a predominately dark and cold environment with much lower productivity than shallower waters. No light penetrates beyond 1000 m and even at depths of 150 m light levels are reduced to 1 % of those at the surface and are insufficient to support photosynthesis. Therefore, organic materi ...
ocean basin floor - Plain Local Schools
... The ocean basin floor is the area of the deep-ocean floor between the continental margin and the oceanic ridge. Deep-Ocean Trenches • Trenches form at the sites of plate convergence where one moving plate descends beneath another and plunges back into the mantle. ...
... The ocean basin floor is the area of the deep-ocean floor between the continental margin and the oceanic ridge. Deep-Ocean Trenches • Trenches form at the sites of plate convergence where one moving plate descends beneath another and plunges back into the mantle. ...
Visualization of Ocean Currents and Eddies in a High
... meshes based on Voronoi tessellations [4]. MPAS-Ocean has several next-generation features as a climate model. In addition to the multi-resolution capabilities, it includes conservation properties required for century-long climate simulations: conservation of volume and volume-weighted tracers; ener ...
... meshes based on Voronoi tessellations [4]. MPAS-Ocean has several next-generation features as a climate model. In addition to the multi-resolution capabilities, it includes conservation properties required for century-long climate simulations: conservation of volume and volume-weighted tracers; ener ...
AYC Ecology North - Associated Yacht Clubs
... A 35-mile rift in the desert of Ethiopia will likely become a new ocean eventually, researchers now confirm. The crack, 20 feet wide in spots, opened in 2005 and some geologists believed then that it would spawn a new ocean. But that view was controversial, and the rift had not been well studied. A ...
... A 35-mile rift in the desert of Ethiopia will likely become a new ocean eventually, researchers now confirm. The crack, 20 feet wide in spots, opened in 2005 and some geologists believed then that it would spawn a new ocean. But that view was controversial, and the rift had not been well studied. A ...
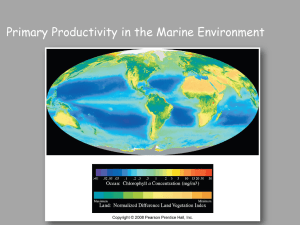
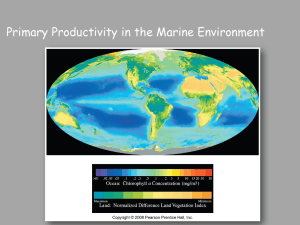
Chapter 13: Biological productivity and energy
... On average, about 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level ...
... On average, about 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level ...
Ocean Basin Physiography
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulte ...
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulte ...
Chapter 13: Biological productivity and energy transfer
... On average, about 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level ...
... On average, about 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level ...
Plate Tectonics: Ch. 22.4 Self Quiz
... in the diagram above. 16. Describe what is happening. 17. When two plates collide, what determines which one will sink back into the mantle? ...
... in the diagram above. 16. Describe what is happening. 17. When two plates collide, what determines which one will sink back into the mantle? ...
Plate Tectonics: Ch. 22.4 Self Quiz
... in the diagram above. 16. Describe what is happening. 17. When two plates collide, what determines which one will sink back into the mantle? ...
... in the diagram above. 16. Describe what is happening. 17. When two plates collide, what determines which one will sink back into the mantle? ...
and Millennial Timescales to Improve Our Understanding of Climate
... In another example, between roughly 3 and 1 million years ago, paleoclimate data indicate a pattern of advances and retreats of continental ice sheets with a period of 41,000 years, the tempo of changes in Earth’s obliquity. It is widely believed that virtually all of this ice accumulated and melte ...
... In another example, between roughly 3 and 1 million years ago, paleoclimate data indicate a pattern of advances and retreats of continental ice sheets with a period of 41,000 years, the tempo of changes in Earth’s obliquity. It is widely believed that virtually all of this ice accumulated and melte ...
Ocean acidification

Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. An estimated 30–40% of the carbon dioxide from human activity released into the atmosphere dissolves into oceans, rivers and lakes. To achieve chemical equilibrium, some of it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. Some of these extra carbonic acid molecules react with a water molecule to give a bicarbonate ion and a hydronium ion, thus increasing ocean acidity (H+ ion concentration). Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14, representing an increase of almost 30% in H+ ion concentration in the world's oceans. Since current and projected ocean pH levels are above 7.0, the oceans are technically alkaline now and will remain so; referring to this effect as ""decreasing ocean alkalinity"" would be equally correct if less politically useful. Earth System Models project that within the last decade ocean acidity exceeded historical analogs and in combination with other ocean biogeochemical changes could undermine the functioning of marine ecosystems and disrupt the provision of many goods and services associated with the ocean.Increasing acidity is thought to have a range of possibly harmful consequences, such as depressing metabolic rates and immune responses in some organisms, and causing coral bleaching. This also causes decreasing oxygen levels as it kills off algae.Other chemical reactions are triggered which result in a net decrease in the amount of carbonate ions available. This makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form biogenic calcium carbonate, and such structures become vulnerable to dissolution. Ongoing acidification of the oceans threatens food chains connected with the oceans. As members of the InterAcademy Panel, 105 science academies have issued a statement on ocean acidification recommending that by 2050, global CO2 emissions be reduced by at least 50% compared to the 1990 level.Ocean acidification has been called the ""evil twin of global warming"" and ""the other CO2 problem"".Ocean acidification has occurred previously in Earth's history. The most notable example is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which occurred approximately 56 million years ago. For reasons that are currently uncertain, massive amounts of carbon entered the ocean and atmosphere, and led to the dissolution of carbonate sediments in all ocean basins.