9 - Mr. Neason`s Earth Science
... The magnetic properties of the rock that makes up the ocean floor provided evident for sea-floor spreading. Recall that Earth’s magnetic field is much like that of a bar magnet. Geophysicists learned that Earth’s magnetic field occasionally reverse polarity. That is, the north magnetic pole becomes ...
... The magnetic properties of the rock that makes up the ocean floor provided evident for sea-floor spreading. Recall that Earth’s magnetic field is much like that of a bar magnet. Geophysicists learned that Earth’s magnetic field occasionally reverse polarity. That is, the north magnetic pole becomes ...
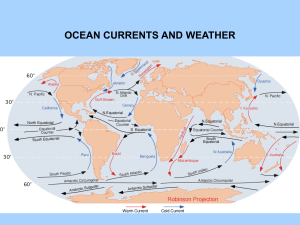
ocean currents and weather
... 1. SOLAR HEATING - THE SUN HEATS THE WATER ALONG THE EQUATOR. THIS CAUSES THE WATER TO EXPAND. THE WATER ALONG THE EQUATOR IS ABOUT 8 CM HIGHER THAN IN THE MIDDLE LATITUDES. THIS CAUSES A SLIGHT RISE, AND WATER WANTS TO FLOW DOWN THAT RISE. 2. WIND - THE FRICTION OF THE WIND BLOWING ON THE WATER WIL ...
... 1. SOLAR HEATING - THE SUN HEATS THE WATER ALONG THE EQUATOR. THIS CAUSES THE WATER TO EXPAND. THE WATER ALONG THE EQUATOR IS ABOUT 8 CM HIGHER THAN IN THE MIDDLE LATITUDES. THIS CAUSES A SLIGHT RISE, AND WATER WANTS TO FLOW DOWN THAT RISE. 2. WIND - THE FRICTION OF THE WIND BLOWING ON THE WATER WIL ...
Ocean noise pollution
... Other measures for quieting include adding layers of sound-absorbing tiles to the walls of noisy rooms as well as mounting engines, pumps, air compressors, and other types of reciprocating machinery on vibration isolators. Mr. Bahtiarian of Noise Control Engineering, who has written extensively on t ...
... Other measures for quieting include adding layers of sound-absorbing tiles to the walls of noisy rooms as well as mounting engines, pumps, air compressors, and other types of reciprocating machinery on vibration isolators. Mr. Bahtiarian of Noise Control Engineering, who has written extensively on t ...
Unit 9 Day 1 Notes
... 1. Discuss the origin of the oceans and describe the distribution of oceans and seas 2. Describe the composition of sea water and variations in salinity concentrations 3. Explain ocean layering and effects of 4. Describe variations in ...
... 1. Discuss the origin of the oceans and describe the distribution of oceans and seas 2. Describe the composition of sea water and variations in salinity concentrations 3. Explain ocean layering and effects of 4. Describe variations in ...
The Great Conveyor Belt and Abrupt Climate Change
... changing temperatures, moving their habitats to cooler climates so swiftly that they’ve surprised scientists.” (Newitz, 2011) Animals are already changing as the global temperatures increase. Newitz goes on to say that, “This study also reveals that the ...
... changing temperatures, moving their habitats to cooler climates so swiftly that they’ve surprised scientists.” (Newitz, 2011) Animals are already changing as the global temperatures increase. Newitz goes on to say that, “This study also reveals that the ...
Oceans in motion vocab - Raleigh Charter High School
... river delta a type of primary coast formed where a river deposits soil and other material as it enters the sea. river-dominated delta a type of delta formed when there are large amounts of material in the water, and tidal action is relatively low. seamount began life as volcanoes formed over hot spo ...
... river delta a type of primary coast formed where a river deposits soil and other material as it enters the sea. river-dominated delta a type of delta formed when there are large amounts of material in the water, and tidal action is relatively low. seamount began life as volcanoes formed over hot spo ...
Centre for Interdisciplinary Marine Science Kiel University Kiel
... Which strategies are best suited for predicting the effects of sea level rise, tsunamis and extrme storms on coastal hydrodynamics and morphodynamics? Which are the best strategies for predicting human ...
... Which strategies are best suited for predicting the effects of sea level rise, tsunamis and extrme storms on coastal hydrodynamics and morphodynamics? Which are the best strategies for predicting human ...
Lesson 5 - Plate Boundaries
... The convection currents exert shear forces on both plates forcing them to slide past one another. ...
... The convection currents exert shear forces on both plates forcing them to slide past one another. ...
At the Frontlines of Climate Change—Oceans, Coasts, and Small
... The world’s oceans play a vital role in sustaining life on Earth by generating oxygen, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, regulating climate and temperature, and providing resources and services to billions of people across the globe. The oceans serve as the world’s largest carbon pool, r ...
... The world’s oceans play a vital role in sustaining life on Earth by generating oxygen, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, regulating climate and temperature, and providing resources and services to billions of people across the globe. The oceans serve as the world’s largest carbon pool, r ...
D O E I
... oxidizing and reducing power, and of nutrients are interwoven so intricately that the system can only be described as a web. And most of it takes place in the dark. How, exactly, does all of this fit together? Based on research in the last dozen years, there is both direct and indirect evidence for ...
... oxidizing and reducing power, and of nutrients are interwoven so intricately that the system can only be described as a web. And most of it takes place in the dark. How, exactly, does all of this fit together? Based on research in the last dozen years, there is both direct and indirect evidence for ...
Geologic History
... Climate Regulation The CO2 Cycle as a Thermostat If the global average temperature increases, ocean H2O evaporation increases Increases cloud formation & rainfall Increases weathering of silicates & more CO2 dissolved out of atmosphere CO2 in oceans forms carbonate rocks faster More CO2 able to be ...
... Climate Regulation The CO2 Cycle as a Thermostat If the global average temperature increases, ocean H2O evaporation increases Increases cloud formation & rainfall Increases weathering of silicates & more CO2 dissolved out of atmosphere CO2 in oceans forms carbonate rocks faster More CO2 able to be ...
Developing a Vision for Climate Variability Research in the
... Southern Ocean Atmosphere The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) is the prominent pattern of large-scale climate variability in Southern Hemisphere mid-high latitude circulation. Variations in the SAM influence weather across broad regions of the Southern Hemisphere ocean and land areas (see Thompson et al ...
... Southern Ocean Atmosphere The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) is the prominent pattern of large-scale climate variability in Southern Hemisphere mid-high latitude circulation. Variations in the SAM influence weather across broad regions of the Southern Hemisphere ocean and land areas (see Thompson et al ...
ocean exploration: timeline
... The first ever Census of Marine Life catalogs the diversity, abundance, and distribution of marine species collected in an online database. First Successful Solo Dive to the Mariana Trench National Geographic Explorer-in-Residence James Cameron successfully travels to the bottom of the deepest known ...
... The first ever Census of Marine Life catalogs the diversity, abundance, and distribution of marine species collected in an online database. First Successful Solo Dive to the Mariana Trench National Geographic Explorer-in-Residence James Cameron successfully travels to the bottom of the deepest known ...
A>E - Butler at UTB
... down, Northern Europe’s climate would become much colder because the heat from the south would not make it up there. (Lindstrom) According to Lindstrom, the conveyor belt regulates temperatures at high altitudes because “warm water from the tropical Atlantic moves pole ward near the surface where it ...
... down, Northern Europe’s climate would become much colder because the heat from the south would not make it up there. (Lindstrom) According to Lindstrom, the conveyor belt regulates temperatures at high altitudes because “warm water from the tropical Atlantic moves pole ward near the surface where it ...
Answer - Scioly.org
... 30. The layer of Earth that is rigid, mobile, and includes the continents is called the a. Asthenosphere b. Mesosphere c. Lithosphere d. Mantle 31. Name the three types of breaking waves. Mention the shape of the wave and ocean slope associated with each type. Spilling breakers = ocean floor has a g ...
... 30. The layer of Earth that is rigid, mobile, and includes the continents is called the a. Asthenosphere b. Mesosphere c. Lithosphere d. Mantle 31. Name the three types of breaking waves. Mention the shape of the wave and ocean slope associated with each type. Spilling breakers = ocean floor has a g ...
Methods and Equipment Used by Marine Geologists
... of miles across the ocean to expend their destructive energies on distant shores. These tsunamis now can be forecasted in time for public warning, but local waves generated by submarine landslides are a more insidious hazard. When submarne landslides are set in motion by seismic vibrations, the wate ...
... of miles across the ocean to expend their destructive energies on distant shores. These tsunamis now can be forecasted in time for public warning, but local waves generated by submarine landslides are a more insidious hazard. When submarne landslides are set in motion by seismic vibrations, the wate ...
Ocean Salt and Circulation
... the thermohaline circulation on the climate of the United Kingdom and Ireland. As warm, less-‐dense water cruises past these islands to return to the North Atlantic, it creates a temperate climate in th ...
... the thermohaline circulation on the climate of the United Kingdom and Ireland. As warm, less-‐dense water cruises past these islands to return to the North Atlantic, it creates a temperate climate in th ...
Going deep for drug discovery: an ocean to Bedside Approach to
... producers have been cultured in multi-liter scale, and chemical investigations of their bioactive compounds are underway. Once the antibiotic agents have been purified and the structures have been determined, novel agents will be tested for their growth inhibitory activities against an array of clin ...
... producers have been cultured in multi-liter scale, and chemical investigations of their bioactive compounds are underway. Once the antibiotic agents have been purified and the structures have been determined, novel agents will be tested for their growth inhibitory activities against an array of clin ...
Open File - Earth Science > Home
... temperatures, and low water pressure. These are ideal conditions for marine life. Nekton are common in the neritic zone. These nekton include many fish and other types of seafood that humans eat. The oceanic zone stretches into the deep waters past the continental shelf. The oceanic zone is divided ...
... temperatures, and low water pressure. These are ideal conditions for marine life. Nekton are common in the neritic zone. These nekton include many fish and other types of seafood that humans eat. The oceanic zone stretches into the deep waters past the continental shelf. The oceanic zone is divided ...
Science Review Checklist5
... 109. Anything that has mass and takes up space is called: 110. _____ is the measure of the amount of matter in an object. 111. _____ is a measure of the gravitational pull on an object. 112. _____ are matter that’s made of only one type of atom like gold, hydrogen, and oxygen. 113. The smallest part ...
... 109. Anything that has mass and takes up space is called: 110. _____ is the measure of the amount of matter in an object. 111. _____ is a measure of the gravitational pull on an object. 112. _____ are matter that’s made of only one type of atom like gold, hydrogen, and oxygen. 113. The smallest part ...
sample paper
... m to 1 000 m and is very stable. Water density changes rapidly through the pycnocline with depth. This density change is a result of temperature and/or salinity. If the density change is a result of a rapid change in temperature it is referred to as a thermocline, whereas if the density change is a ...
... m to 1 000 m and is very stable. Water density changes rapidly through the pycnocline with depth. This density change is a result of temperature and/or salinity. If the density change is a result of a rapid change in temperature it is referred to as a thermocline, whereas if the density change is a ...
Adriana G - Butler at UTB
... down, Northern Europe’s climate would become much colder because the heat from the south would not make it up there. (Lindstrom) According to Lindstrom, the conveyor belt regulates temperatures at high altitudes because “warm water from the tropical Atlantic moves poleward near the surface where it ...
... down, Northern Europe’s climate would become much colder because the heat from the south would not make it up there. (Lindstrom) According to Lindstrom, the conveyor belt regulates temperatures at high altitudes because “warm water from the tropical Atlantic moves poleward near the surface where it ...
... One of the first photographs of a sediment trap sample shows cylindrical fecal pellets and other aggregates, planktonic tests (round white objects), transparent snail-like pteropod shells, radiolarians, and diatoms. The first deep-sea sediment trap was recovered on February 20, 1977, from 5,367 mete ...
CHAPTER 13 THE OCEAN FLOOR
... less than 3 m of relief over a distance that may exceed 1300 km. Scientists determined that abyssal plains low relief is due to the fact that thick accumulations of sediment, transported by turbidity currents, have buried rugged ocean floor. Abyssal plains are more extensive in the Atlantic Ocean th ...
... less than 3 m of relief over a distance that may exceed 1300 km. Scientists determined that abyssal plains low relief is due to the fact that thick accumulations of sediment, transported by turbidity currents, have buried rugged ocean floor. Abyssal plains are more extensive in the Atlantic Ocean th ...
requirements necessary to obtain an Oceanography Merit Badge
... important properties of water. Tell how the animals and plants of the ocean affect the chemical composition of seawater. Explain how differences in evaporation and precipitation affect the salt content of the oceans. 6. Describe some of the biologically important properties of seawater. Define benth ...
... important properties of water. Tell how the animals and plants of the ocean affect the chemical composition of seawater. Explain how differences in evaporation and precipitation affect the salt content of the oceans. 6. Describe some of the biologically important properties of seawater. Define benth ...
Ocean acidification

Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. An estimated 30–40% of the carbon dioxide from human activity released into the atmosphere dissolves into oceans, rivers and lakes. To achieve chemical equilibrium, some of it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. Some of these extra carbonic acid molecules react with a water molecule to give a bicarbonate ion and a hydronium ion, thus increasing ocean acidity (H+ ion concentration). Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14, representing an increase of almost 30% in H+ ion concentration in the world's oceans. Since current and projected ocean pH levels are above 7.0, the oceans are technically alkaline now and will remain so; referring to this effect as ""decreasing ocean alkalinity"" would be equally correct if less politically useful. Earth System Models project that within the last decade ocean acidity exceeded historical analogs and in combination with other ocean biogeochemical changes could undermine the functioning of marine ecosystems and disrupt the provision of many goods and services associated with the ocean.Increasing acidity is thought to have a range of possibly harmful consequences, such as depressing metabolic rates and immune responses in some organisms, and causing coral bleaching. This also causes decreasing oxygen levels as it kills off algae.Other chemical reactions are triggered which result in a net decrease in the amount of carbonate ions available. This makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form biogenic calcium carbonate, and such structures become vulnerable to dissolution. Ongoing acidification of the oceans threatens food chains connected with the oceans. As members of the InterAcademy Panel, 105 science academies have issued a statement on ocean acidification recommending that by 2050, global CO2 emissions be reduced by at least 50% compared to the 1990 level.Ocean acidification has been called the ""evil twin of global warming"" and ""the other CO2 problem"".Ocean acidification has occurred previously in Earth's history. The most notable example is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which occurred approximately 56 million years ago. For reasons that are currently uncertain, massive amounts of carbon entered the ocean and atmosphere, and led to the dissolution of carbonate sediments in all ocean basins.