factors affecting strength of acids
... - Bases are proton acceptors - Not restricted to aqueous solutions NH3, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) - Proton donation cannot occur unless an acceptor is present ...
... - Bases are proton acceptors - Not restricted to aqueous solutions NH3, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) - Proton donation cannot occur unless an acceptor is present ...
! !! ! n nn N P =
... 2. Normal rain is usually a bit acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide dissolving in water makes the solution slightly acidic: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ...
... 2. Normal rain is usually a bit acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide dissolving in water makes the solution slightly acidic: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ...
(null): 110.ReactionsIntro
... A. Reactions Rule / Reaction Rules 1. Rules: Reactions always Re-arrange (= move around but never gain or lose!) a. Re-arrange electrons 1) Electrons cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex ...
... A. Reactions Rule / Reaction Rules 1. Rules: Reactions always Re-arrange (= move around but never gain or lose!) a. Re-arrange electrons 1) Electrons cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... 4NH3+ 5O24NO + 6H2O. When one mole of ammonia and one mole of oxygen are made to react to completion, then (a) 1.0 mole of H2O is produced (b)all the oxygen is consumed (c) 1.0 mole of NO is formed (d)all the ammonia is consumed One mole of calcium phosphide on reaction with excess of water gives (a ...
... 4NH3+ 5O24NO + 6H2O. When one mole of ammonia and one mole of oxygen are made to react to completion, then (a) 1.0 mole of H2O is produced (b)all the oxygen is consumed (c) 1.0 mole of NO is formed (d)all the ammonia is consumed One mole of calcium phosphide on reaction with excess of water gives (a ...
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND SOLUTION CHEMISTRY
... Liquid water consists of a collection of H2O molecules. The H2O molecule is __________ or Vshaped with an H-O-H bond angle of about 1050. ...
... Liquid water consists of a collection of H2O molecules. The H2O molecule is __________ or Vshaped with an H-O-H bond angle of about 1050. ...
American-Journal-of-Oil-and-Chemical-Technologies
... A solution of H2pydco (0.037 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (10 ml) was added dropwise to a solution of 1,10phenanthroline (0.039 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (5 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2h. Then, a solution of CdCl2·2H2O (0.043 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (5 ml) is added to the reaction mi ...
... A solution of H2pydco (0.037 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (10 ml) was added dropwise to a solution of 1,10phenanthroline (0.039 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (5 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2h. Then, a solution of CdCl2·2H2O (0.043 g, 0.2 mmol) in water (5 ml) is added to the reaction mi ...
Tests for functional groups
... Add a spatula measure of PCl5 solid to 1 cm of the liquid to be tested. An exothermic reaction which evolves steamy fumes (HCl) which turn damp litmus red and form a white ‘smoke’ with ammonia gas confirms the presence of an –OH group in the molecule. As this also gives a positive result with water ...
... Add a spatula measure of PCl5 solid to 1 cm of the liquid to be tested. An exothermic reaction which evolves steamy fumes (HCl) which turn damp litmus red and form a white ‘smoke’ with ammonia gas confirms the presence of an –OH group in the molecule. As this also gives a positive result with water ...
Chem 30A Final Exam
... 1. Draw valid Lewis structures for the simplest compounds of the second row elements (except for Li) with flourine including lone pair electrons. Indicate the valence (i.e. # of bonds), the central atom geometry, and the approximate bond angles in each case. Also indicate when there is an exception ...
... 1. Draw valid Lewis structures for the simplest compounds of the second row elements (except for Li) with flourine including lone pair electrons. Indicate the valence (i.e. # of bonds), the central atom geometry, and the approximate bond angles in each case. Also indicate when there is an exception ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... (b).Oligonucleotide Single strand DNA Double strand DNA: which interactions? ...
... (b).Oligonucleotide Single strand DNA Double strand DNA: which interactions? ...
Writing Net Ionic Equations
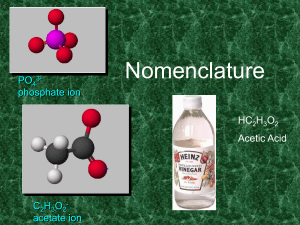
... 1. The six common strong acids, and thus strong electrolytes, are HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3 and H2SO4. (Memorize these!) All other common acids are weak acids and thus weak electrolytes. (HC2H3O2 or CH3COOH, H3PO4, HF and HNO2 are examples of weak acids. Note: All organic acids (R-COOH) are weak ele ...
... 1. The six common strong acids, and thus strong electrolytes, are HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3 and H2SO4. (Memorize these!) All other common acids are weak acids and thus weak electrolytes. (HC2H3O2 or CH3COOH, H3PO4, HF and HNO2 are examples of weak acids. Note: All organic acids (R-COOH) are weak ele ...
Chapter 4
... intermolecular attractions between the ions and water, as well as the intramolecular attractions of the cations and anions of the ...
... intermolecular attractions between the ions and water, as well as the intramolecular attractions of the cations and anions of the ...
Chapter 4
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
Summary of 5.4
... Phenol dissolves in aqueous sodium hydroxide because phenol behaves as an acid and gives up its proton to the hydroxide ion which is a base. A soluble ionic product is formed. C6H5OH(aq) + NaOH(aq) ----> C6H5O-Na+(aq) + H2O(l) phenol sodium phenoxide Phenol is too weak an acid to react with sodium c ...
... Phenol dissolves in aqueous sodium hydroxide because phenol behaves as an acid and gives up its proton to the hydroxide ion which is a base. A soluble ionic product is formed. C6H5OH(aq) + NaOH(aq) ----> C6H5O-Na+(aq) + H2O(l) phenol sodium phenoxide Phenol is too weak an acid to react with sodium c ...
Summary notes - Kelso High School
... You can find out if a substance is an acid or and alkali by dissolving it in water and adding an indicator. An indicator is a chemical which changes colour in different pH environments so by matching the colour of the solution to the colour chart, the pH of the substance can be found. The two most c ...
... You can find out if a substance is an acid or and alkali by dissolving it in water and adding an indicator. An indicator is a chemical which changes colour in different pH environments so by matching the colour of the solution to the colour chart, the pH of the substance can be found. The two most c ...
Lotioncrafter - Stearic Acid
... laws and regulations and in conformance with Good Engineering Practices. Avoid landfilling of liquids. Reclaim where possible. ...
... laws and regulations and in conformance with Good Engineering Practices. Avoid landfilling of liquids. Reclaim where possible. ...
Percent Ionization
... Base-Ionization Constant, Kb (base-dissociation constant - equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak acid B (aq) + H2O (l) HB+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Kb = [BH+][OH-] [B] ...
... Base-Ionization Constant, Kb (base-dissociation constant - equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak acid B (aq) + H2O (l) HB+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Kb = [BH+][OH-] [B] ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.