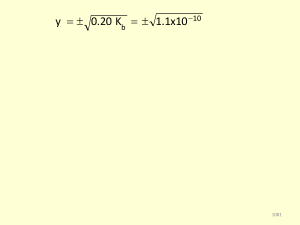LECTURE_Solutions2013(1)
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
Various Types of RXNS
... 3 Metathesis Reactions - reactions w/ two reactants, and ending with two products. 3A. Examples 1. dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of barium acetate --identify the spectator ions in this reaction; explain. 2. solutions of sodium phosphate and calcium chloride are mixed --what is the mos ...
... 3 Metathesis Reactions - reactions w/ two reactants, and ending with two products. 3A. Examples 1. dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of barium acetate --identify the spectator ions in this reaction; explain. 2. solutions of sodium phosphate and calcium chloride are mixed --what is the mos ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
chemisty_ass_2
... 5a. NH4Cl → NH3 +HCl KC = [NH3] [HCl]/[NH4Cl] Kp=p[MH3] p[HCl]/P[NH4Cl] B. CO2 +2NH3 → CO(NH2)2 +H2O KC = [CO(NH2)2] [H2O]/ [CO2] [NH3]^2. ...
... 5a. NH4Cl → NH3 +HCl KC = [NH3] [HCl]/[NH4Cl] Kp=p[MH3] p[HCl]/P[NH4Cl] B. CO2 +2NH3 → CO(NH2)2 +H2O KC = [CO(NH2)2] [H2O]/ [CO2] [NH3]^2. ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... - have higher melting & boiling points Charges must balance because one element gives up electrons and the other one accepts these same electrons. The formula is the ratio of one ion to another. Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain el ...
... - have higher melting & boiling points Charges must balance because one element gives up electrons and the other one accepts these same electrons. The formula is the ratio of one ion to another. Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain el ...
Copy of Acids, bases, salts answer key
... Limitations of Arrhenius theory : Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a ...
... Limitations of Arrhenius theory : Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a ...
activity series
... occurs between ions in aqueous solution. A reaction will occur when a pair of ions come together to produce at least one of the following: 1. a precipitate 2. a gas 3. water or some other non-ionized substance. ...
... occurs between ions in aqueous solution. A reaction will occur when a pair of ions come together to produce at least one of the following: 1. a precipitate 2. a gas 3. water or some other non-ionized substance. ...
7.9 Other polyamide polymers. Man
... 7.9 Other polyamide polymers. Man-made polyamide polymers can be made by reacting the carboxylic acid and amine functional groups of multiple monomers and linking them together by means of amide linkages. Some well known examples are shown below: Nylon 6 ...
... 7.9 Other polyamide polymers. Man-made polyamide polymers can be made by reacting the carboxylic acid and amine functional groups of multiple monomers and linking them together by means of amide linkages. Some well known examples are shown below: Nylon 6 ...
Microsoft Word
... The indicator methyl red turns from yellow to red when the solution in which it is dissolved changes from basic to acidic. A 25.00-mL volume of a sodium hydroxide solution is titrated with 0.8367 M HCl. It takes 22.48 mL of this acid to reach a methyl-red end-point. Find the molarity of the sodium h ...
... The indicator methyl red turns from yellow to red when the solution in which it is dissolved changes from basic to acidic. A 25.00-mL volume of a sodium hydroxide solution is titrated with 0.8367 M HCl. It takes 22.48 mL of this acid to reach a methyl-red end-point. Find the molarity of the sodium h ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
Reaction Predictions
... Hydrolysis: The reaction of a salt with water to form molecular species. Salts of a strong acid + a weak base will always hydrolyze to give an acidic solution. Neutralization: Acid and base react to form a salt and water. Catalyst: A molecule that speeds that speeds a reaction but that does not appe ...
... Hydrolysis: The reaction of a salt with water to form molecular species. Salts of a strong acid + a weak base will always hydrolyze to give an acidic solution. Neutralization: Acid and base react to form a salt and water. Catalyst: A molecule that speeds that speeds a reaction but that does not appe ...
weak conjugate base
... Ex: HCl(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+ + ClBase-conjugate acid pair H3O+ --> hydronium ion ...
... Ex: HCl(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+ + ClBase-conjugate acid pair H3O+ --> hydronium ion ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound Coefficients are inserted to balance the equation ...
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound Coefficients are inserted to balance the equation ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound Coefficients are inserted to balance the equation ...
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound Coefficients are inserted to balance the equation ...
Semester II Review
... SM II Review • If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the pressure within the container? Increase • What happens to the temperature of a gas when it is compressed? Increases • What happens to the pressure of a gas inside a container, if the temperature of the gas ...
... SM II Review • If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the pressure within the container? Increase • What happens to the temperature of a gas when it is compressed? Increases • What happens to the pressure of a gas inside a container, if the temperature of the gas ...
Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
... • The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of a solid salt into its aqueous ions is called the solubility product, K sp • For an ionic solid MnXm, the dissociation reaction is: MnXm(s) ⇔ nMm+(aq) + mXn−(aq) • The solubility product would be K sp = [Mm+] n[Xn−] m • For example, the dissociation ...
... • The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of a solid salt into its aqueous ions is called the solubility product, K sp • For an ionic solid MnXm, the dissociation reaction is: MnXm(s) ⇔ nMm+(aq) + mXn−(aq) • The solubility product would be K sp = [Mm+] n[Xn−] m • For example, the dissociation ...
Review Material
... The equilibrium constant for an equilibrium of this sort is referred to as the solubility product, and it is given the symbol KSP. In this example: ...
... The equilibrium constant for an equilibrium of this sort is referred to as the solubility product, and it is given the symbol KSP. In this example: ...
chemical reaction
... HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) A base is a substance that contains the hydroxyl group and dissociates to produce Hydroxide ion : OH – ...
... HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) A base is a substance that contains the hydroxyl group and dissociates to produce Hydroxide ion : OH – ...
makeup2
... 5. If the hydrocarbon C2H4 is burned in oxygen gas, carbon dioxide and water are formed as described by the unbalanced chemical equation C2H4 + O2 ----> CO2 + H2O When this equation is balanced properly, we predict that one mole of C2H4 will (A) react with one mole of O2 (B) form two moles of CO2. ( ...
... 5. If the hydrocarbon C2H4 is burned in oxygen gas, carbon dioxide and water are formed as described by the unbalanced chemical equation C2H4 + O2 ----> CO2 + H2O When this equation is balanced properly, we predict that one mole of C2H4 will (A) react with one mole of O2 (B) form two moles of CO2. ( ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.