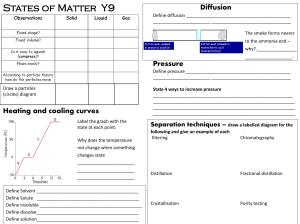
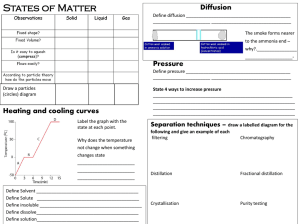
Chapter 6
... EX 4.14 (pg 162) A student carries out an experiment to standardize a sodium hydroxide solution. To do this, the student weighs out 1.3009 g sample of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H4O4 or KHP–molar mass 204.22 g/mol). The student dissolves the KHP in distilled water, adds phenolphthalein as an ...
... EX 4.14 (pg 162) A student carries out an experiment to standardize a sodium hydroxide solution. To do this, the student weighs out 1.3009 g sample of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H4O4 or KHP–molar mass 204.22 g/mol). The student dissolves the KHP in distilled water, adds phenolphthalein as an ...
Household Acids and Bases Lab
... A visual indicator is a chemical substance that reflects the nature of the chemical system in which it is placed by changing color. Most visual indicators are complex organic molecules that exist in multiple colored forms, one of which could be colorless, depending on the chemical environment. Many ...
... A visual indicator is a chemical substance that reflects the nature of the chemical system in which it is placed by changing color. Most visual indicators are complex organic molecules that exist in multiple colored forms, one of which could be colorless, depending on the chemical environment. Many ...
Homework Exercises
... Name substance X Write a balanced equation for the reaction What is meant by an excess of one chemical in a chemical reaction? When the reaction is finished, unreacted copper(II) carbonate would be left in the beaker. What else would be observed indicating that the reaction is over? (e) Draw a label ...
... Name substance X Write a balanced equation for the reaction What is meant by an excess of one chemical in a chemical reaction? When the reaction is finished, unreacted copper(II) carbonate would be left in the beaker. What else would be observed indicating that the reaction is over? (e) Draw a label ...
Chemistry Spell check on
... 5 If this information is correct, print your name and seat number in the boxes provided. 6 The answer to each question is either A, B, C or D. Decide what your answer is, then, using your pencil, put a horizontal line in the space provided (see sample question below). 7 There is only one co ...
... 5 If this information is correct, print your name and seat number in the boxes provided. 6 The answer to each question is either A, B, C or D. Decide what your answer is, then, using your pencil, put a horizontal line in the space provided (see sample question below). 7 There is only one co ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
Examples
... You will have a chart of activity series More active metals will replace less active metals from their compound in a solution A less active element will have no reaction when added to a more active element! Active metals replace hydrogen in water Active metals replace hydrogen in acids ...
... You will have a chart of activity series More active metals will replace less active metals from their compound in a solution A less active element will have no reaction when added to a more active element! Active metals replace hydrogen in water Active metals replace hydrogen in acids ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... aqueous solutions) occurs when product is insoluble • Produce insoluble ionic compounds • Double replacement (or metathesis reaction) • Solubility is the maximum amount of a solid that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature • Prediction based on solubility rules ...
... aqueous solutions) occurs when product is insoluble • Produce insoluble ionic compounds • Double replacement (or metathesis reaction) • Solubility is the maximum amount of a solid that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature • Prediction based on solubility rules ...
Lesson Plan
... running water (15 minutes) and followed up with immediate medical attention. In the case of highly concentrated acids, the acid should first be wiped off as much as possible, otherwise the reaction of the acid dissolving in the water could cause severe thermal burns. In addition to dangers from the ...
... running water (15 minutes) and followed up with immediate medical attention. In the case of highly concentrated acids, the acid should first be wiped off as much as possible, otherwise the reaction of the acid dissolving in the water could cause severe thermal burns. In addition to dangers from the ...
Exam 2, Fall 2001
... Substitute Question for Page 4: Cobalt(III) ion forms many compounds with ammonia. To find the formula of one of these compounds, you titrate the NH3 in the compound with standardized acid. Co(NH3)xCl3(aq) + x HCl(aq) → x NH4+(aq) + Co3+(aq) + (x + 3) Cl-(aq) Assume that 23.63 mL of 1.500 M HCl is u ...
... Substitute Question for Page 4: Cobalt(III) ion forms many compounds with ammonia. To find the formula of one of these compounds, you titrate the NH3 in the compound with standardized acid. Co(NH3)xCl3(aq) + x HCl(aq) → x NH4+(aq) + Co3+(aq) + (x + 3) Cl-(aq) Assume that 23.63 mL of 1.500 M HCl is u ...
Snc2d Chapter 5 Practice Test
... b) In the diagram above, the Roman group number of P shows: c) The period number of P shows: d) Show a Bohr diagram above of P forming an ion, indicating beside your diagram the number of electrons gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to i ...
... b) In the diagram above, the Roman group number of P shows: c) The period number of P shows: d) Show a Bohr diagram above of P forming an ion, indicating beside your diagram the number of electrons gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to i ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
Chap. 4 AQUEOUS RXNS O
... NaOH(aq) + HCl(g) → NaCl(aq) + H2O MOLECULAR MOLECULAR EQUATION: EQUATION: Reactants Reactants and and products products shown shown as as intact, intact, undissociated undissociated compounds compounds ...
... NaOH(aq) + HCl(g) → NaCl(aq) + H2O MOLECULAR MOLECULAR EQUATION: EQUATION: Reactants Reactants and and products products shown shown as as intact, intact, undissociated undissociated compounds compounds ...
conductometric and potentiometric determination of the dissociation
... The goal of this exercise is to familiarise students with the practical approach to electrolytic dissociation and conductometric measurements. During the exercise, the students should apply the knowledge, gained during earlier physical chemistry courses, to determine the dissociation constant of a w ...
... The goal of this exercise is to familiarise students with the practical approach to electrolytic dissociation and conductometric measurements. During the exercise, the students should apply the knowledge, gained during earlier physical chemistry courses, to determine the dissociation constant of a w ...
Proton Resonance Frequencies in Several Organophosphorus Acids
... sociationt is operative in acetone and TMU, it appears the complex must dissociate at concentrations between 5 and 10 per cent. A possible formulation of the associated compiex is one involving H-bonds that resembles this complex formed by carboxylic acids, except for the presence of the second hydr ...
... sociationt is operative in acetone and TMU, it appears the complex must dissociate at concentrations between 5 and 10 per cent. A possible formulation of the associated compiex is one involving H-bonds that resembles this complex formed by carboxylic acids, except for the presence of the second hydr ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
IGCSE Revision document
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
Acid‒base reaction
... Since solvent-system definition depends on the solvent as well as on the compound itself, the same compound can change its role depending on the choice of the solvent. Thus, HClO4 is a strong acid in water, a weak acid in acetic acid, and a weak base in fluorosulfonic acid. This was seen as both a s ...
... Since solvent-system definition depends on the solvent as well as on the compound itself, the same compound can change its role depending on the choice of the solvent. Thus, HClO4 is a strong acid in water, a weak acid in acetic acid, and a weak base in fluorosulfonic acid. This was seen as both a s ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 4 - A
... A different mixture of hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide was left to reach equilibrium at the same temperature in a container of the same volume. This second equilibrium mixture contained 0.38 mol of hydrogen, 0.19 mol of iodine and 1.94 mol of hydrogen iodide. Calculate a value for Kc for this e ...
... A different mixture of hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide was left to reach equilibrium at the same temperature in a container of the same volume. This second equilibrium mixture contained 0.38 mol of hydrogen, 0.19 mol of iodine and 1.94 mol of hydrogen iodide. Calculate a value for Kc for this e ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.









![[edit]Occurrence in solution](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009755146_1-58e56f0cc08d3d020872dbc6c3acbb66-300x300.png)