AP Review Chp 1 and Chp 2 Wed 10/9/2013 1. Near room
... milliliters, of fresh gastric juice, corresponding in acidity to 0.17 M HCl, could be neutralized by 104 mg of magnesium oxide? II) Predict whether or not a solid is formed when we mix the following; identify any solid product by name and identify the reaction type: (a) copper (II) nitrate solution ...
... milliliters, of fresh gastric juice, corresponding in acidity to 0.17 M HCl, could be neutralized by 104 mg of magnesium oxide? II) Predict whether or not a solid is formed when we mix the following; identify any solid product by name and identify the reaction type: (a) copper (II) nitrate solution ...
x - A Level Tuition
... compared to 1.0 mol dm-3 nitric acid for the same number of moles of water formed. This is because some of the energy evolved from the neutralisation process is used to further dissociate the ethanoic acid completely. ...
... compared to 1.0 mol dm-3 nitric acid for the same number of moles of water formed. This is because some of the energy evolved from the neutralisation process is used to further dissociate the ethanoic acid completely. ...
Soluble salts
... to ‘hydracids’ (e.g. HCl) lacking oxygen. More strictly, the term oxoacid designates a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of one or more hydrogen ions. H2SO4 ...
... to ‘hydracids’ (e.g. HCl) lacking oxygen. More strictly, the term oxoacid designates a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of one or more hydrogen ions. H2SO4 ...
Specific Reactions Quiz.wpd
... a) various carbon products created due to lack of oxygen including solid carbon (black component) b) as air contacts the random carbon products (smaller hydrocarbons) created, they may further combust c) since energy is still tied up in carbon product bonds, energy is not released all at once d) the ...
... a) various carbon products created due to lack of oxygen including solid carbon (black component) b) as air contacts the random carbon products (smaller hydrocarbons) created, they may further combust c) since energy is still tied up in carbon product bonds, energy is not released all at once d) the ...
Structure of atoms
... Concentrated and dilute ‘Strong’ and weak’ when applied to acids and bases have a different meaning from ‘concentrated’ and ‘dilute’. In a given volume of water: • a concentrated acid or base solution has many molecules of acid or base present and/or dissolved • a dilute solution has fewer acid or ...
... Concentrated and dilute ‘Strong’ and weak’ when applied to acids and bases have a different meaning from ‘concentrated’ and ‘dilute’. In a given volume of water: • a concentrated acid or base solution has many molecules of acid or base present and/or dissolved • a dilute solution has fewer acid or ...
Technical Data Sheet (E
... 1. Take a 10 ml sample of the working solution, dilute with water to 25 ml and add 2 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid. 2. Titrate with 0.2N Potassium Permanganate until the solution turns purple. 3. The number of ml of 0.2N Potassium Permanganate equals the grams of iron per liter of EPhos 660 solut ...
... 1. Take a 10 ml sample of the working solution, dilute with water to 25 ml and add 2 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid. 2. Titrate with 0.2N Potassium Permanganate until the solution turns purple. 3. The number of ml of 0.2N Potassium Permanganate equals the grams of iron per liter of EPhos 660 solut ...
10th Carbon and Its Compounds Solved Paper-3
... of unsaturated carbon chains having double bonds between carbon atoms. When H2 gas is bubbled through vegetable oils in presence of Nickel as catalyst at 473K, some of these double bonds add H2 to form saturated carbon chains. As a result of this partial hydrogenation, vegetable ghee is formed. ...
... of unsaturated carbon chains having double bonds between carbon atoms. When H2 gas is bubbled through vegetable oils in presence of Nickel as catalyst at 473K, some of these double bonds add H2 to form saturated carbon chains. As a result of this partial hydrogenation, vegetable ghee is formed. ...
A Classification of AP Chemistry Reactions
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Monoprotic, diprotic, polyprotic, depending on how many hydrogens it donates. Ionization reactions- acid donates a proton to water to form a hydronium ion. You can only donate 1 proton at a time. HCl(aq) H+ + Cl- ...
... Monoprotic, diprotic, polyprotic, depending on how many hydrogens it donates. Ionization reactions- acid donates a proton to water to form a hydronium ion. You can only donate 1 proton at a time. HCl(aq) H+ + Cl- ...
Chemical Equilibrium Review Ch 13-14 2015
... 7. A gaseous mixture contains 0.30mol CO, 0.10mol H2, and 0.020mol H2O, plus an unknown amount of CH4, per liter. This mixture is at equilibrium at 1200.K. CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g) The equilibrium constant Kc = 3.92. What is the equilibrium concentration of CH4 in this mixture? 8. The reactio ...
... 7. A gaseous mixture contains 0.30mol CO, 0.10mol H2, and 0.020mol H2O, plus an unknown amount of CH4, per liter. This mixture is at equilibrium at 1200.K. CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g) The equilibrium constant Kc = 3.92. What is the equilibrium concentration of CH4 in this mixture? 8. The reactio ...
Instructions for AP/IB 2 Chem Summer Assignment Note
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
Ei otsikkoa
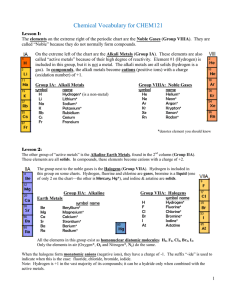
... Transition elements show characteristic properties: The acidity of aqueous solutions of chlorides increases across the period: NaCl : MgCl2 : AlCl3 : SiCl4 : PCl3 : PCl5 : Cl2 : ...
... Transition elements show characteristic properties: The acidity of aqueous solutions of chlorides increases across the period: NaCl : MgCl2 : AlCl3 : SiCl4 : PCl3 : PCl5 : Cl2 : ...
Chapter 8 Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
... What is the pH of a 1.0 x 10-4 mol/l HCl solution? – HCl is a strong acid and dissociates in water – If 1 mol HCl is placed in 1 L of aqueous solution it produces 1 mol [H3O+] – 1.0 x 10-4 mol/l HCl solution has [H3O+]=1.0x10-4 mol/l ...
... What is the pH of a 1.0 x 10-4 mol/l HCl solution? – HCl is a strong acid and dissociates in water – If 1 mol HCl is placed in 1 L of aqueous solution it produces 1 mol [H3O+] – 1.0 x 10-4 mol/l HCl solution has [H3O+]=1.0x10-4 mol/l ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... • increase across the periods in the Periodic Table for two reasons: • increasing nuclear charge • decreasing atomic radius F= most electronegative element. Halogens –decrease in reducing power down the group due to drop in electroneg. values. AG ...
... • increase across the periods in the Periodic Table for two reasons: • increasing nuclear charge • decreasing atomic radius F= most electronegative element. Halogens –decrease in reducing power down the group due to drop in electroneg. values. AG ...
2C - Edexcel
... (b) The equation for the reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is H2 + Cl2 o 2HCl Different names are used for the product, depending on its state symbol. (i) What are the names used for HCl(g) and HCl(aq)? ...
... (b) The equation for the reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is H2 + Cl2 o 2HCl Different names are used for the product, depending on its state symbol. (i) What are the names used for HCl(g) and HCl(aq)? ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.