The beginning…Early Middle Ages
... • (former city of Byzantium) became new capital and control centre for Roman Empire • Was largest city by population in the world west of China • Strategic location on trade routes • One of largest natural harbours in the world linked the east and west • Byzantine gold coin (bezant) was the main cur ...
... • (former city of Byzantium) became new capital and control centre for Roman Empire • Was largest city by population in the world west of China • Strategic location on trade routes • One of largest natural harbours in the world linked the east and west • Byzantine gold coin (bezant) was the main cur ...
Emerging Europe and the Byzantine Empire
... Holy Roman Empire • Saxon dukes became kings of the eastern Frankish kingdom which came to be known as Germany. • In 962, Otto I became the emperor of the Romans by offering protection to the pope. • Kings Frederick I and Frederick II tried to take over Germany and Italy with Italy becoming the sta ...
... Holy Roman Empire • Saxon dukes became kings of the eastern Frankish kingdom which came to be known as Germany. • In 962, Otto I became the emperor of the Romans by offering protection to the pope. • Kings Frederick I and Frederick II tried to take over Germany and Italy with Italy becoming the sta ...
The Eastern Empire Survives
... Eastern Portion with the capital at Constantinople, became the center for Christianity ...
... Eastern Portion with the capital at Constantinople, became the center for Christianity ...
Chapter 10 Outline
... 1. Independent, self-governing cities emerged first in Italy and Flanders. They relied on manufacturing and trade for their income, and they had legal independence so that their laws could favor manufacturing and trade. 2. In Italy, Venice emerged as a dominant sea power, trading in Muslim ports for ...
... 1. Independent, self-governing cities emerged first in Italy and Flanders. They relied on manufacturing and trade for their income, and they had legal independence so that their laws could favor manufacturing and trade. 2. In Italy, Venice emerged as a dominant sea power, trading in Muslim ports for ...
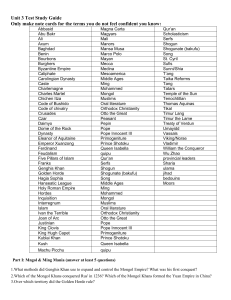
Unit 3 Test Study Guide Only make note cards for the terms you do
... 4. What was the cause of division between the Mongol khans in 1265? 6.What factors contributed to Mongol military supremacy? 7.Which explorer’s narratives of the Mongol Empire piqued European interest Asia? 8.What was the worst thing to spread via Mongol trade routes? 9.To which religion did the Il ...
... 4. What was the cause of division between the Mongol khans in 1265? 6.What factors contributed to Mongol military supremacy? 7.Which explorer’s narratives of the Mongol Empire piqued European interest Asia? 8.What was the worst thing to spread via Mongol trade routes? 9.To which religion did the Il ...
Intro to the Dark and Middle Ages
... Germanic tribes took over Roman lands. Hundreds of little kingdoms took the place of the Western Roman Empire in Europe. Initially, there was no system for collecting taxes. Kingdoms were always at war with one another. People lost interest in learning. ...
... Germanic tribes took over Roman lands. Hundreds of little kingdoms took the place of the Western Roman Empire in Europe. Initially, there was no system for collecting taxes. Kingdoms were always at war with one another. People lost interest in learning. ...
6 The Middle Ages
... Strong ruler of England; strengthened the royal courts of justice – introduced use of the jury Founder of Capetian dynasty Strongest ruler of medieval Germany, created the German-Italian empire later known as the Holy Roman Empire First ruler to call his lands the Holy Roman Empire Christian scholar ...
... Strong ruler of England; strengthened the royal courts of justice – introduced use of the jury Founder of Capetian dynasty Strongest ruler of medieval Germany, created the German-Italian empire later known as the Holy Roman Empire First ruler to call his lands the Holy Roman Empire Christian scholar ...
Middle Ages - Tioga Central School District
... ->3rd was a fight between Richard I of England and Saladin ->4th resulted in Constantinople being destroyed ...
... ->3rd was a fight between Richard I of England and Saladin ->4th resulted in Constantinople being destroyed ...
Middle Ages
... • Germanic people located in Gaul • Leader was Clovis • His wife urged him to convert to Christianity ...
... • Germanic people located in Gaul • Leader was Clovis • His wife urged him to convert to Christianity ...
Study Guide For the Final Exam
... primary source you consult, either taken on your own or drawn from the Key Terms posted online (one tip is to print out blank copies of the Key Terms and see if you can fill them in from memory). Your textbook is helpful in providing information when you might be uncertain about the features of part ...
... primary source you consult, either taken on your own or drawn from the Key Terms posted online (one tip is to print out blank copies of the Key Terms and see if you can fill them in from memory). Your textbook is helpful in providing information when you might be uncertain about the features of part ...
Unit 9: Medieval Europe Part 1 Early Medieval
... Western Rome was transformed between 300 and 700 A.D. ...
... Western Rome was transformed between 300 and 700 A.D. ...
Song of Roland - St. Olaf Pages
... • What are the unifying features? How do we decide what features are worth emphasizing over others? • Specific questions: – The “end” of Rome: fall or transition? – The “Renaissance”: new period? ...
... • What are the unifying features? How do we decide what features are worth emphasizing over others? • Specific questions: – The “end” of Rome: fall or transition? – The “Renaissance”: new period? ...
Happy Constitution Day
... • Created a united Christian Europe – Worked with church to spread Christianity ...
... • Created a united Christian Europe – Worked with church to spread Christianity ...
hhhss - SFP Online!
... Germanic tribes migrated across Europe and made small kingdoms in Europe, the most successful of those tribes were the Franks. The Franks were ruled by Clovis who conquered the Roman province Gaul and he also converted to Christianity because that was the religion in Gaul which made him gain the res ...
... Germanic tribes migrated across Europe and made small kingdoms in Europe, the most successful of those tribes were the Franks. The Franks were ruled by Clovis who conquered the Roman province Gaul and he also converted to Christianity because that was the religion in Gaul which made him gain the res ...
Chapter 9 Byzantine Empire
... • In 980, he became Grand Prince of Kiev. • Chose Orthodox Christianity as the religion of his state. • Imitated the culture of the Byzantine ...
... • In 980, he became Grand Prince of Kiev. • Chose Orthodox Christianity as the religion of his state. • Imitated the culture of the Byzantine ...
The Middle Ages
... The empire was largely held together not by Christianity which was the common religion, but by loyalty to a single ruler who was strong enough to ensure loyalty ...
... The empire was largely held together not by Christianity which was the common religion, but by loyalty to a single ruler who was strong enough to ensure loyalty ...
Overview and Foundation: SS 8-T300-16-17
... neighboring kingdoms. These challenges gave rise to the economic and political system historians call feudalism (FEWD-ahl-ism). In the feudal system, people pledged loyalty to a lord—a ruler or powerful landholder. In return, they received protection from that lord. Warriors fought on behalf of thei ...
... neighboring kingdoms. These challenges gave rise to the economic and political system historians call feudalism (FEWD-ahl-ism). In the feudal system, people pledged loyalty to a lord—a ruler or powerful landholder. In return, they received protection from that lord. Warriors fought on behalf of thei ...
Highlights of European History
... The signing of the Magna Carta -- 1215 •Limited the power of the king – the king must follow the law! •Granted certain rights to individuals including the right to not be arrested without showing proof that a crime was committed •The Magna Carta provided a basis for constitutional democracy – the i ...
... The signing of the Magna Carta -- 1215 •Limited the power of the king – the king must follow the law! •Granted certain rights to individuals including the right to not be arrested without showing proof that a crime was committed •The Magna Carta provided a basis for constitutional democracy – the i ...
Fall of Rome, Dark Ages
... was a bad king so his nobles forced him to sign it. Limited powers of king. ...
... was a bad king so his nobles forced him to sign it. Limited powers of king. ...
The Middle Ages - Coach Kitchens` Weebly Page
... • In the Roman province of Gaul (modern day France & Switzerland), Germanic people called the Franks were in power • Leader = Clovis; he brought Christianity to the region ...
... • In the Roman province of Gaul (modern day France & Switzerland), Germanic people called the Franks were in power • Leader = Clovis; he brought Christianity to the region ...
7-1-rise-of-europe
... How did the culture of the Germans differ from that of the Romans? How did Charlemagne enlarge his kingdom? P. 30 Why did Charlemagne use education? How did Charlemagne’s empire split? What invasion threatened the kingdom? How was the collapse of Charlemagne’s empire similar to the collapse of the R ...
... How did the culture of the Germans differ from that of the Romans? How did Charlemagne enlarge his kingdom? P. 30 Why did Charlemagne use education? How did Charlemagne’s empire split? What invasion threatened the kingdom? How was the collapse of Charlemagne’s empire similar to the collapse of the R ...
Unit 3
... o Under Ghengis Khan created the largest land empire in history o Introduced the use of gunpowder and cannons into Europe o After Ghengis Khan’s death – empire divided into four khanates Mongol Empire in China o Kublai Khan – conquered Chinese Song Dynasty o Established new dynasty Yuan Dynasty o ...
... o Under Ghengis Khan created the largest land empire in history o Introduced the use of gunpowder and cannons into Europe o After Ghengis Khan’s death – empire divided into four khanates Mongol Empire in China o Kublai Khan – conquered Chinese Song Dynasty o Established new dynasty Yuan Dynasty o ...
Was Medieval Europe really “Dark”?
... • The 'Dark Ages' were a difficult time in which to live: famine and disease were common. The 'Black Death' (bubonic plague) devastated Europe in the late 1340s, killing an estimated 100-‐200 million p ...
... • The 'Dark Ages' were a difficult time in which to live: famine and disease were common. The 'Black Death' (bubonic plague) devastated Europe in the late 1340s, killing an estimated 100-‐200 million p ...
European Kingdoms & The Crusades
... • Relations between the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church worsened during this period. • A division developed between the two main branches of Christianity. ...
... • Relations between the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church worsened during this period. • A division developed between the two main branches of Christianity. ...
Post-classical history

Post-classical history (also called the Postclassical Era) is the period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200-600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations the era follows are Han China (ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire (in 476), the Gupta Empire (in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire (in 651). The post-classical era itself was followed by the early modern era, and forms the middle period in a three-period division of world history: ancient, post-classical, and modern. The era is thought to be characterized by invasions from Central Asia, the development of the great world religions (Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism), and of networks of trade and military contact between civilizations.The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity (or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. In European history, ""post-classical"" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. In Europe, the fall of the Western Roman Empire saw the depopulation, deurbanization, and limited learning of the ""Dark Ages"" (except in Eastern Mediterranean Europe, where the Eastern Roman Empire flourished until 1204), but gradually revived somewhat under the institutions of feudalism and a powerful Catholic Church. Art and architecture were characterized by Christian themes. Several attempts by the Crusades to recapture the Holy Land for Christianity were unsuccessful.In Asia, the depredations of the Dark Ages were avoided, at least in the west, where the Spread of Islam created a new empire and civilization with trade between the Asian, African, and European continents, and advances in science. East Asia experienced the full establishment of power of Imperial China (after the interregnum chaos of the Six Dynasties), which established several prosperous dynasties influencing Korea, Vietnam, and Japan. Religions such as Buddhism and Neo-Confucianism spread. Gunpowder was originally developed in China during the post-classical era. The invention of gunpowder led to the invention of fireworks, then to its use in warfare. Also, the invention spread around the world. The Mongol Empire greatly affected much of Europe and Asia, the latter of which was conquered in many areas. The Mongols were able to create safe trade and stability between the two regions, but inadvertently encouraged the spread of the Black Plague.The timelines of the major civilizations of the Americas—Maya (AD 250 to 900), the Aztec (14th to 16th centuries), and the Inca (1438 to 1533)—do not correspond closely to the Classical Age of the Old World.Outstanding cultural achievement in the post-classical era include books like the Code of Justinian,The Story of the Western Wing, and The Tale of Genji; the mathematics of Fibonacci, Oresme, and Al-Khwārizmī; the philosophy of Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, Petrarch, Zhu Xi, and Kabir; the painting of Giotto, Behzād, and Dong Yuan; the astronomy of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Su Song; the poetry of Rumi, Dante, Chaucer, and the Li Bai; the travels of Marco Polo and Ibn Battuta; the historiography of Leonardo Bruni and Ibn Khaldun; and the architecture of places like Chartres, the Mezquita, Angkor Wat, and Machu Picchu.