coordination chemistry relevant to biological systems and material
... efficiently can fix the atmospheric CO 2 from the air and convert it into carbonate that bridges several metal ions. Hopefully, that these compounds can serve as green chlorophyll and reduce global warming by eliminating CO 2 from the air. Some examples of dinuclear and trinuclear Cu(II) bridged-car ...
... efficiently can fix the atmospheric CO 2 from the air and convert it into carbonate that bridges several metal ions. Hopefully, that these compounds can serve as green chlorophyll and reduce global warming by eliminating CO 2 from the air. Some examples of dinuclear and trinuclear Cu(II) bridged-car ...
Chem+174–Lecture12a
... to ligands like CO, CN, etc. Tolman observed for Ni(CO)3L that the carbonyl stretching frequency decreases as the donor ability of the R-group increases (i.e., PCy3 (2056 cm-1) vs. P(OMe)3 (2070 cm-1) vs. ...
... to ligands like CO, CN, etc. Tolman observed for Ni(CO)3L that the carbonyl stretching frequency decreases as the donor ability of the R-group increases (i.e., PCy3 (2056 cm-1) vs. P(OMe)3 (2070 cm-1) vs. ...
π bonded ligands
... In the ionic model, the L configuration does not change the oxidation state of the metal and is still considered a 2e donor. ...
... In the ionic model, the L configuration does not change the oxidation state of the metal and is still considered a 2e donor. ...
Section 3.2 Atoms and Compounds
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
Metal Sequestration (English version)
... The term “sequestration” was first used in relation to Chemistry by R.E. Hall [1] in a patent concerning the properties of certain phosphates. With the introduction of the amino carboxylic acids and particularly ethylene diamino tetracarboxylic acid (EDTA) the term has become increasingly associated ...
... The term “sequestration” was first used in relation to Chemistry by R.E. Hall [1] in a patent concerning the properties of certain phosphates. With the introduction of the amino carboxylic acids and particularly ethylene diamino tetracarboxylic acid (EDTA) the term has become increasingly associated ...
Are diglycolamide ligands hard or soft Lewis bases?
... The conclusion on the greater covalency of M–Oamid than M–Oether bonds results as well from quantum-mechanical bond analysis in the [M(TEDGA)3]3+ complexes: e.g. from Wiberg bond indices; from QTAIM parameters of the M–O bonds (e.g. electron densities, ρb, in the Bond Central Point) etc.; cf. the o ...
... The conclusion on the greater covalency of M–Oamid than M–Oether bonds results as well from quantum-mechanical bond analysis in the [M(TEDGA)3]3+ complexes: e.g. from Wiberg bond indices; from QTAIM parameters of the M–O bonds (e.g. electron densities, ρb, in the Bond Central Point) etc.; cf. the o ...
Transition Metal Chemistry - WordPress.com
... • Transition metals are defined as metallic elements with an incomplete d sub-shell in at least one of their ions. • Form positive (+) ions by losing electrons. • These electrons come from the 4s sub-shell first, then from the 3d sub-shell: Fe atom: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d6 Fe2+ ion: ...
... • Transition metals are defined as metallic elements with an incomplete d sub-shell in at least one of their ions. • Form positive (+) ions by losing electrons. • These electrons come from the 4s sub-shell first, then from the 3d sub-shell: Fe atom: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d6 Fe2+ ion: ...
Staff demonstrating hours for level-3 Inorganic Lab
... 2.15 Å W(=CH2) 1.94 Å Difficult to separate effects of 3 components in metal complexes. Evidence for -donor orbital (cases where no -bonding is possible) Lewis adduct H3BCO. Complex has (CO) at 2164cm-1 , free CO at 2143cm-1 therefore C-O bond order is increased with donation, as predicted. ...
... 2.15 Å W(=CH2) 1.94 Å Difficult to separate effects of 3 components in metal complexes. Evidence for -donor orbital (cases where no -bonding is possible) Lewis adduct H3BCO. Complex has (CO) at 2164cm-1 , free CO at 2143cm-1 therefore C-O bond order is increased with donation, as predicted. ...
(over) Candidate: Agozie Nnaemeka Oyeamalu For the degree of
... X-ray crystallography. This resulted in specifically two crystallographically independent molecules in the unit cell complex of the metallacarborane cluster framework [3,3-(CO)2-3-NO-closo-Re(8-O(CH2)2O(CH2)2I-3,1,2-C2B9H10)]. The ReC2B9 moiety is comprised of the usual closo-icosahedral framework w ...
... X-ray crystallography. This resulted in specifically two crystallographically independent molecules in the unit cell complex of the metallacarborane cluster framework [3,3-(CO)2-3-NO-closo-Re(8-O(CH2)2O(CH2)2I-3,1,2-C2B9H10)]. The ReC2B9 moiety is comprised of the usual closo-icosahedral framework w ...
Trace Metal Biogeochemistry 12.755
... Preview: Software for Metal Speciation • Mineql – Westall et al. a program made for calculating aqueous speciation and solubility at low temperature geochemical conditions • Critical.exe – Smith and Martell volumes built into a DOS baseddatabase. • But need to know how to do it by hand well in orde ...
... Preview: Software for Metal Speciation • Mineql – Westall et al. a program made for calculating aqueous speciation and solubility at low temperature geochemical conditions • Critical.exe – Smith and Martell volumes built into a DOS baseddatabase. • But need to know how to do it by hand well in orde ...
SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
... for the name of ligands and not their prefixes ) If the ligand itself contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis (2), tris (3), and tetrakis (4) to indicate the number of ligands present. The ligand ethylenediamine already contains the term di; therefore bis(ethylenediamine) is used to indicate t ...
... for the name of ligands and not their prefixes ) If the ligand itself contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis (2), tris (3), and tetrakis (4) to indicate the number of ligands present. The ligand ethylenediamine already contains the term di; therefore bis(ethylenediamine) is used to indicate t ...
Dinitrogen Cleavage by a Molybdenum(III) Complex
... synthesized the compound (Me2N)3Mo≡Mo(NMe2)3;14 please comment on this compound as compared to Mo(N[R]Ar)3. Electronic Structure • Mo is in group 6 o Mo, W stabilize high oxidation states more easily than does Cr o d orbitals: What does not favor multiple bonding to ligands? “The very early transiti ...
... synthesized the compound (Me2N)3Mo≡Mo(NMe2)3;14 please comment on this compound as compared to Mo(N[R]Ar)3. Electronic Structure • Mo is in group 6 o Mo, W stabilize high oxidation states more easily than does Cr o d orbitals: What does not favor multiple bonding to ligands? “The very early transiti ...
Show all work – Homework 5 –
... totally of such clusters. c) Determine the numbers of Fe2+ and Fe3+ in octahedral sites. 3. Zeolite structures contains pores with different sizes. Download and open the *.diamdoc files in the demo version 4.0.2 of Diamond by Crystal Impact (http://www.crystalimpact.com/diamond/ ). Rotate the struct ...
... totally of such clusters. c) Determine the numbers of Fe2+ and Fe3+ in octahedral sites. 3. Zeolite structures contains pores with different sizes. Download and open the *.diamdoc files in the demo version 4.0.2 of Diamond by Crystal Impact (http://www.crystalimpact.com/diamond/ ). Rotate the struct ...
Powerpoint - mvhs
... Electrophile: species that is “e- poor” and seeks e- (gets attacked by nucleophile) ◦ Ligand or complexing agent: molecule or ion with a lone pair of e- that bonds to a metal ion Acts as a Lewis base (e- pair donor) Coordinate covalent bond: metal-ligand bond Nucleophile: species that is “e- ...
... Electrophile: species that is “e- poor” and seeks e- (gets attacked by nucleophile) ◦ Ligand or complexing agent: molecule or ion with a lone pair of e- that bonds to a metal ion Acts as a Lewis base (e- pair donor) Coordinate covalent bond: metal-ligand bond Nucleophile: species that is “e- ...
Transition Elements and Complexes
... Structure of complex compounds Central metal cation surrounded by ligands (anions or molecules) Ligand is bonded to metal through an electron pair Ligands act like Lewis bases by donating an electron pair Ligands bond in first coordination sphere [does not dissociate in water] Coordination number- t ...
... Structure of complex compounds Central metal cation surrounded by ligands (anions or molecules) Ligand is bonded to metal through an electron pair Ligands act like Lewis bases by donating an electron pair Ligands bond in first coordination sphere [does not dissociate in water] Coordination number- t ...
Staff demonstrating hours for level-3 Inorganic Lab
... KReO4 + K/EtOH "K2Re" white crystalline solid Modern techniques X-ray, NMR not available. Compound actually contains the anion [ReH9]2- - an 18 electron complex !! ...
... KReO4 + K/EtOH "K2Re" white crystalline solid Modern techniques X-ray, NMR not available. Compound actually contains the anion [ReH9]2- - an 18 electron complex !! ...
Chapter 2 cont’
... do not turn into other elements ◦ Dalton’s Atomic Theory since the number of protons determines the kind of element, the number of protons in the atom does not change in a chemical reaction however, many reactions involve transferring electrons from one atom to another ...
... do not turn into other elements ◦ Dalton’s Atomic Theory since the number of protons determines the kind of element, the number of protons in the atom does not change in a chemical reaction however, many reactions involve transferring electrons from one atom to another ...
Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
... Some History In the 19th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia, chloride, water and cyanide They were very interesting because their formulae gave little clue as to how they were bonded together Example: Co(NH3)6Cl3 ...
... Some History In the 19th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia, chloride, water and cyanide They were very interesting because their formulae gave little clue as to how they were bonded together Example: Co(NH3)6Cl3 ...
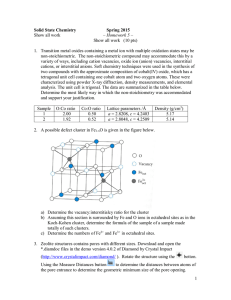
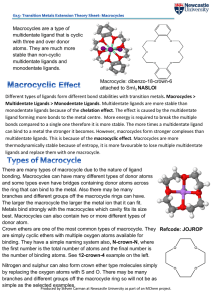
Different types of ligands form different bond stabilities with transition
... ligand forming more bonds to the metal centre. More energy is required to break the multiple bonds compared to a single one therefore it is more stable. The more times a multidentate ligand can bind to a metal the stronger it becomes. However, macrocycles form stronger complexes than multidentate li ...
... ligand forming more bonds to the metal centre. More energy is required to break the multiple bonds compared to a single one therefore it is more stable. The more times a multidentate ligand can bind to a metal the stronger it becomes. However, macrocycles form stronger complexes than multidentate li ...
Ultra rigid cross-bridged tetraazamacrocycles as ligands—the
... ion and the Nax–M–Nax bond angle, which increases smoothly from MnII through CuII as the smaller metal ions can more easily be engulfed by the macrobicycle. MnII(5)Cl2 (Fig. 1) exemplifies these structures,§ and in this example the N(3)–Mn(1)–N(4) angle is 158.0°. Because of their great importance i ...
... ion and the Nax–M–Nax bond angle, which increases smoothly from MnII through CuII as the smaller metal ions can more easily be engulfed by the macrobicycle. MnII(5)Cl2 (Fig. 1) exemplifies these structures,§ and in this example the N(3)–Mn(1)–N(4) angle is 158.0°. Because of their great importance i ...
Lecture 1 Handout - Imperial College London
... 1. Use simple MO theory to explain how a carbon-carbon p-cloud bonds to a metal. 2. To list methods used to synthesise metal complexes of alkenes and polyenes, and metal-carbon multiple bonds. 3. To describe typical reactions of these complexes. 4. To appreciate how polyene ligands may respond to th ...
... 1. Use simple MO theory to explain how a carbon-carbon p-cloud bonds to a metal. 2. To list methods used to synthesise metal complexes of alkenes and polyenes, and metal-carbon multiple bonds. 3. To describe typical reactions of these complexes. 4. To appreciate how polyene ligands may respond to th ...
1 5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. Nocera Lecture 9 May 11
... Lecture 9 May 11: Bimetallic and Cluster Complexes Metal-metal bonding is common for metals in low oxidation states, and generally increases in strength along the series 3d << 4d < 5d. There are limiting forms of metal-metal bonding depending on d-orbital occupation. Usually d1 and d2 metals do not ...
... Lecture 9 May 11: Bimetallic and Cluster Complexes Metal-metal bonding is common for metals in low oxidation states, and generally increases in strength along the series 3d << 4d < 5d. There are limiting forms of metal-metal bonding depending on d-orbital occupation. Usually d1 and d2 metals do not ...
Gas-phase study of the reactivity of optical coating desktop-size extreme-ultraviolet laser
... improvement of industrial processes. The experiments were based on the use of a compact capillary discharge EUV laser in the study of clusters and cluster reactions. The EUV laser was used to provide single-photon ionization of the neutral clusters for mass spectroscopy studies, with the significant ...
... improvement of industrial processes. The experiments were based on the use of a compact capillary discharge EUV laser in the study of clusters and cluster reactions. The EUV laser was used to provide single-photon ionization of the neutral clusters for mass spectroscopy studies, with the significant ...
Photoelectron spectroscopy of chromium
... If specific sizes are stable enough to form cluster assembled materials, silicon-encapsulated metal atom nanoclusters could be used to tailor band gaps with heretofore unattainable specificity. This could lead to applications in both the microelectronics and optoelectronic industries. One can also i ...
... If specific sizes are stable enough to form cluster assembled materials, silicon-encapsulated metal atom nanoclusters could be used to tailor band gaps with heretofore unattainable specificity. This could lead to applications in both the microelectronics and optoelectronic industries. One can also i ...