Lecture 04 Chem 3
... molecule that binds to a metal through either coordinate covalent or ionic bonds. Water is a neutral ligand, CN is a charged ligand. ...
... molecule that binds to a metal through either coordinate covalent or ionic bonds. Water is a neutral ligand, CN is a charged ligand. ...
Coordination Chemistry
... CO groups donating to only one metal atom are called terminal carbonyl groups. They donate a pair of electrons to that metal atom. CO groups which bond to two metal atoms at the same time are called bridging carbonyl groups. They contribute one electron to each of the two metal atoms to form covalen ...
... CO groups donating to only one metal atom are called terminal carbonyl groups. They donate a pair of electrons to that metal atom. CO groups which bond to two metal atoms at the same time are called bridging carbonyl groups. They contribute one electron to each of the two metal atoms to form covalen ...
Organometallic Organometallic Chemistry
... non-reactivity in either a stoichiometric or catalytic sense. iii. It is especially useful for organometallic complexes of the Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co triads, and applies to compounds such as ferrocene, iron pentacarbonyl, chromium carbonyl and nickel carbonyl. ...
... non-reactivity in either a stoichiometric or catalytic sense. iii. It is especially useful for organometallic complexes of the Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co triads, and applies to compounds such as ferrocene, iron pentacarbonyl, chromium carbonyl and nickel carbonyl. ...
Counting atoms
... million times its original size and that this observation can be used to arrive at a primitive estimate of an atom’s size1. From the ratio of the volumes of the interior of the church and the minimal amount of evenly dispersed incense that one can sense, which he estimated to be to one-thousandth of ...
... million times its original size and that this observation can be used to arrive at a primitive estimate of an atom’s size1. From the ratio of the volumes of the interior of the church and the minimal amount of evenly dispersed incense that one can sense, which he estimated to be to one-thousandth of ...
File
... indicate the number. If the ligand contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis, tris, and tetrakis to indicate the number. ...
... indicate the number. If the ligand contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis, tris, and tetrakis to indicate the number. ...
Metal Complexes
... Metal Complexes • metal cation is attached to a group of surrounding molecules or ions (ligands) by coordinate covalent bonds – coordinate => ligand donates both electrons ...
... Metal Complexes • metal cation is attached to a group of surrounding molecules or ions (ligands) by coordinate covalent bonds – coordinate => ligand donates both electrons ...
Syntheses, Structures and Photophysical Properties of Metal
... emission wavelengths to the uncomplexed ligands (I and II). -However, an important finding was that the fluorescence quantum yields of the metal complexes were less than I and II by one to two orders of magnitude. - Quantum yield: # of species removed/number of photons absorbed. -this decrease in lu ...
... emission wavelengths to the uncomplexed ligands (I and II). -However, an important finding was that the fluorescence quantum yields of the metal complexes were less than I and II by one to two orders of magnitude. - Quantum yield: # of species removed/number of photons absorbed. -this decrease in lu ...
Electronic spectrum of a 0.1 M aqueous solution of [Ti(H2O)6]3+
... [Cr(H2O)6]3+ (∆O = 17,400 cm-1); [Mo(H2O)6]3+ (∆O = 26,000 cm-1) [Rh(NH3)6]3+ (∆O = 34,100 cm-1); [Ir(NH3)6]3+ (∆O = 41,200 cm-1) Note: An important result of this trend is that complexes of 4d and 5d transition metals have a much greater tendency to be low spin than those of 3d metals! 3. Number an ...
... [Cr(H2O)6]3+ (∆O = 17,400 cm-1); [Mo(H2O)6]3+ (∆O = 26,000 cm-1) [Rh(NH3)6]3+ (∆O = 34,100 cm-1); [Ir(NH3)6]3+ (∆O = 41,200 cm-1) Note: An important result of this trend is that complexes of 4d and 5d transition metals have a much greater tendency to be low spin than those of 3d metals! 3. Number an ...
Heme and Copper Oxygenases and Oxidases
... The two hydrogens on the agostic methylene are rapidly switching between terminal and agostic on the NMR time scale. ...
... The two hydrogens on the agostic methylene are rapidly switching between terminal and agostic on the NMR time scale. ...
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
... For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. ...
... For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. ...
Chapter 23 – Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
... Complex of porphine and metal is known as porphyrin. Variations possess diff. metals, diff. groups attached to porphine. This type of complex is a component of myoglobin (stores oxygen), hemoglobin (transports oxygen in blood) and chlorophyl (needed for photosynthesis in plants). The iron in hemoglo ...
... Complex of porphine and metal is known as porphyrin. Variations possess diff. metals, diff. groups attached to porphine. This type of complex is a component of myoglobin (stores oxygen), hemoglobin (transports oxygen in blood) and chlorophyl (needed for photosynthesis in plants). The iron in hemoglo ...
A1982NU66300001
... coordinated in a bidentate manner. The structure of the complex could only be revealed by X-ray diffraction studies, these showing it to be TiCl 2 diars, the first eight4known for a first-row coordinate complex ...
... coordinated in a bidentate manner. The structure of the complex could only be revealed by X-ray diffraction studies, these showing it to be TiCl 2 diars, the first eight4known for a first-row coordinate complex ...
Chem 174_Lecture 10a..
... • Aside of the p-acidity, the steric impact of the phosphine ligand has to be considered as well • C.A. Tolman (Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 313) summarizes the electronic parameters and cone angles of phosphine ligands: • The electronic parameter can be adjusted by changing the R-group (see above). Stronge ...
... • Aside of the p-acidity, the steric impact of the phosphine ligand has to be considered as well • C.A. Tolman (Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 313) summarizes the electronic parameters and cone angles of phosphine ligands: • The electronic parameter can be adjusted by changing the R-group (see above). Stronge ...
Lecture1
... Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistry", metals display new and unusual reaction types. ...
... Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistry", metals display new and unusual reaction types. ...
lecture1 - Unaab.edu.ng
... (iii) Electron transfer – metal-containing electron transfer agents such as ferrodoxins (Fe) and many copper-containing “blue proteins” are involved in electron transfer chemistry that goes on in the biological systems. (iv) Metalloenzymes and metallocoenzymes have metal ions at their active sites. ...
... (iii) Electron transfer – metal-containing electron transfer agents such as ferrodoxins (Fe) and many copper-containing “blue proteins” are involved in electron transfer chemistry that goes on in the biological systems. (iv) Metalloenzymes and metallocoenzymes have metal ions at their active sites. ...
Chem Ch 4 test review
... 8. Identify the 9 major areas of periodic table and select elements in each area. What is a group? What is a period? Identify elements on the periodic table by their periods or groups. What do elements in groups have in common? Why? 9. Describe the natural states of the elements, i.e., which are sol ...
... 8. Identify the 9 major areas of periodic table and select elements in each area. What is a group? What is a period? Identify elements on the periodic table by their periods or groups. What do elements in groups have in common? Why? 9. Describe the natural states of the elements, i.e., which are sol ...
Unit 4 - Dorman High School
... When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can be formed with monatomic ions as well as polyatomic ...
... When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can be formed with monatomic ions as well as polyatomic ...
Lecture notes for chapter 7
... orbital energy matching). See the next section on cyclobutadiene for a particularly remarkable example. ...
... orbital energy matching). See the next section on cyclobutadiene for a particularly remarkable example. ...
Chapter_23_Transition_Metal_Chemistry
... (a) The CO ligands are neutral species and therefore the Ni atom bears no net charge. The compound is called tetracarbonylnickel(0) , or more commonly, nickel ...
... (a) The CO ligands are neutral species and therefore the Ni atom bears no net charge. The compound is called tetracarbonylnickel(0) , or more commonly, nickel ...
Introducing Transition Metals
... The d block elements are found in the centre of the periodic table. As you move across the d block, five d orbitals are filled, up to a total of ten electrons. Transition metals are d block elements that can form at least one stable ion with an incomplete d sub-level. Transition metals have typical ...
... The d block elements are found in the centre of the periodic table. As you move across the d block, five d orbitals are filled, up to a total of ten electrons. Transition metals are d block elements that can form at least one stable ion with an incomplete d sub-level. Transition metals have typical ...
e-nomenclature-of-coordination-compounds-take-home-2
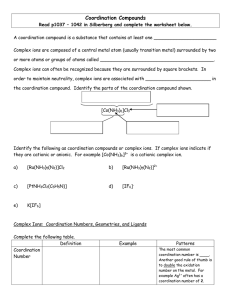
... A coordination compound is a substance that contains at least one ______________________ Complex ions are composed of a central metal atom (usually transition metal) surrounded by two or more atoms or groups of atoms called ________________________________________. Complex ions can often be recogniz ...
... A coordination compound is a substance that contains at least one ______________________ Complex ions are composed of a central metal atom (usually transition metal) surrounded by two or more atoms or groups of atoms called ________________________________________. Complex ions can often be recogniz ...
Coordination Compounds Coordination
... These are the complex compounds in which transition metal atoms are bound to a number of anions or neutral molecules. Postulates of Werner’s theory of coordination compounds: In coordination compounds, there are two types of linkages (valences) – primary and secondary. The primary valences are ionis ...
... These are the complex compounds in which transition metal atoms are bound to a number of anions or neutral molecules. Postulates of Werner’s theory of coordination compounds: In coordination compounds, there are two types of linkages (valences) – primary and secondary. The primary valences are ionis ...
Document
... • Structures which have this preferred count are called electron-precise • Every orbital wants to be “used", i.e. contribute to binding an electron pair The strength of the preference for electron-precise structures depends on the position of the element in the periodic table • For early transition ...
... • Structures which have this preferred count are called electron-precise • Every orbital wants to be “used", i.e. contribute to binding an electron pair The strength of the preference for electron-precise structures depends on the position of the element in the periodic table • For early transition ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... • Structures which have this preferred count are called electron-precise • Every orbital wants to be “used", i.e. contribute to binding an electron pair The strength of the preference for electron-precise structures depends on the position of the element in the periodic table • For early transition ...
... • Structures which have this preferred count are called electron-precise • Every orbital wants to be “used", i.e. contribute to binding an electron pair The strength of the preference for electron-precise structures depends on the position of the element in the periodic table • For early transition ...
Organometallic Compounds
... – This includes interactions between the d-orbitals and the donor/-acceptor orbitals of the six ligands. – Understand this diagram in terms and strengths of the different types of interactions. – 18-electron is the most stable for this type of complex. Assuming the d-orbitals to be at similar ener ...
... – This includes interactions between the d-orbitals and the donor/-acceptor orbitals of the six ligands. – Understand this diagram in terms and strengths of the different types of interactions. – 18-electron is the most stable for this type of complex. Assuming the d-orbitals to be at similar ener ...






![Electronic spectrum of a 0.1 M aqueous solution of [Ti(H2O)6]3+](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005719667_1-a6d66a78471c6778162e27e0ef555131-300x300.png)