effective oxidation states applied to endohedral - IQCC
... electronic or spin populations are only a pointer of the atom's OS. We have most recently shown that the so-called effective atomic orbitals (eff-AO's) can be utilized, treating alpha and beta electrons separately, to derive the most appropriate atomic electron configurations for the atoms or molecu ...
... electronic or spin populations are only a pointer of the atom's OS. We have most recently shown that the so-called effective atomic orbitals (eff-AO's) can be utilized, treating alpha and beta electrons separately, to derive the most appropriate atomic electron configurations for the atoms or molecu ...
Chemistry of free transition metal clusters
... • Most active particles are a few nm in diameter ...
... • Most active particles are a few nm in diameter ...
ORDANOCHROMIUM CHEMISTRY SUPPORTED BY -DIIMINE LIGANDS
... This molecule is a low-valent, coordinatively unsaturated chromium synthon accommodating variable oxidation states of the metal. It isomerizes and reacts with various small molecules (e. g. alkenes, alkynes and arenes) to produce novel organometallic molecules. It also catalyzes the selective trimer ...
... This molecule is a low-valent, coordinatively unsaturated chromium synthon accommodating variable oxidation states of the metal. It isomerizes and reacts with various small molecules (e. g. alkenes, alkynes and arenes) to produce novel organometallic molecules. It also catalyzes the selective trimer ...
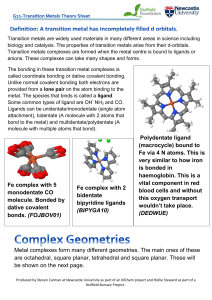
Polydentate ligand (macrocycle) bound to Fe via 4 N atoms. This is
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
Nugget
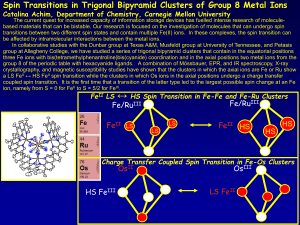
... three Fe ions with bis(tetramethylphenantroline)bis(cyanide) coordination and in the axial positions two metal ions from the group 8 of the periodic table with hexacyanide ligands. A combination of Mössbauer, EPR, and IR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, and magnetic susceptibility studies have s ...
... three Fe ions with bis(tetramethylphenantroline)bis(cyanide) coordination and in the axial positions two metal ions from the group 8 of the periodic table with hexacyanide ligands. A combination of Mössbauer, EPR, and IR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, and magnetic susceptibility studies have s ...
Review Quiz 7 - ltcconline.net
... Transition metal ions lose the s-orbital electrons before they lose the d orbital electrons. This happens because the energy of the (n-1)d orbital is significantly less than the ns electrons. Coordination compound: A complex ion and counterion with no net charge. Complex ion: Charged species consist ...
... Transition metal ions lose the s-orbital electrons before they lose the d orbital electrons. This happens because the energy of the (n-1)d orbital is significantly less than the ns electrons. Coordination compound: A complex ion and counterion with no net charge. Complex ion: Charged species consist ...
EXAMINING THE IMPACT OF LIGAND BASICITY ON THE REACTIVITY OF TRANSITION METAL SYSTEMS THROUGH COMPUTATIONAL METHODS
... the properties and observed reactivity of transition metal complexes. Indeed, gaining the ability to “tune” the properties of metal complexes is a primary goal in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. Unfortunately, a detailed understanding of the fundamental impact of ligand basicity on a metal c ...
... the properties and observed reactivity of transition metal complexes. Indeed, gaining the ability to “tune” the properties of metal complexes is a primary goal in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. Unfortunately, a detailed understanding of the fundamental impact of ligand basicity on a metal c ...
Quantum properties of atomic
... not the case. Guided by this knowledge, in experiments on gold we have discovered that during the contact breaking process the atoms in the contact form stable chains of single atoms being up to 7 atoms long. Such chains constitute the ultimate one-dimensional metallic nanowires. The mechanism behin ...
... not the case. Guided by this knowledge, in experiments on gold we have discovered that during the contact breaking process the atoms in the contact form stable chains of single atoms being up to 7 atoms long. Such chains constitute the ultimate one-dimensional metallic nanowires. The mechanism behin ...
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, markers in protein assays, and as tools for determining coordination of metal-binding sites in proteins. Our main goal is to study the structural and spectroscopic characteristics of these systems employing Monte Carlo techniques.As a preli ...
... agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, markers in protein assays, and as tools for determining coordination of metal-binding sites in proteins. Our main goal is to study the structural and spectroscopic characteristics of these systems employing Monte Carlo techniques.As a preli ...