10:4 Review Test
... successful animal phylum. Arthropods are characterized by an exoskeleton made of ________, __________ appendages, a ___________ body, and a well developed ________ with ________ organs. Their ___________ body allows them to divide labor between segments with _____________ functions. The hard exoskel ...
... successful animal phylum. Arthropods are characterized by an exoskeleton made of ________, __________ appendages, a ___________ body, and a well developed ________ with ________ organs. Their ___________ body allows them to divide labor between segments with _____________ functions. The hard exoskel ...
L to J PowerPoint
... A scientific law stating that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object ...
... A scientific law stating that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
Lecture
... -union of sperm and egg nuclei (zygote) -> first cell division within 24 hours to form the embryo - cell division continues -> formation of the morula at day 4 - morula = a mass of tiny, uniformly sized cells with equal amounts of cytoplasm - cells of the embryo = blastomeres ...
... -union of sperm and egg nuclei (zygote) -> first cell division within 24 hours to form the embryo - cell division continues -> formation of the morula at day 4 - morula = a mass of tiny, uniformly sized cells with equal amounts of cytoplasm - cells of the embryo = blastomeres ...
eoc powerpoint # 2
... • Genes – chemical factors that determine traits • Alleles – different forms of genes ...
... • Genes – chemical factors that determine traits • Alleles – different forms of genes ...
1. The animals which possess backbones are a. Insects b. Birds c
... The unique feature of the DNA is its property of duplicating itself during cell division, this property is known as a. Addition ...
... The unique feature of the DNA is its property of duplicating itself during cell division, this property is known as a. Addition ...
Cell Reproduction
... Some organisms look and act exactly like their parent. Others share many similar traits, but they are definitely unique individuals. Some species have two parents, whereas others have just one. How an organism reproduces determines the amount of similarity the organism will have to its parent. Repro ...
... Some organisms look and act exactly like their parent. Others share many similar traits, but they are definitely unique individuals. Some species have two parents, whereas others have just one. How an organism reproduces determines the amount of similarity the organism will have to its parent. Repro ...
Benchmark Review
... Ovaries – house the ovules Ovules – make the eggs Style – the long tube that leads from the outside of the flower to the ovules Stigma – the sticky top of the flower that is used to catch pollen grains Pollen grains – produce sperm (the male sex cell) Egg – the female sex cell Seed – an undeveloped ...
... Ovaries – house the ovules Ovules – make the eggs Style – the long tube that leads from the outside of the flower to the ovules Stigma – the sticky top of the flower that is used to catch pollen grains Pollen grains – produce sperm (the male sex cell) Egg – the female sex cell Seed – an undeveloped ...
File
... If one of these abnormal gametes participates in fertilization, a zygote with an abnormal chromosome number is produced. Since the zygote is the first cell of the new organism, when this cell undergoes cell division, all the new cells will be identical to it. Therefore, all the cells in the organism ...
... If one of these abnormal gametes participates in fertilization, a zygote with an abnormal chromosome number is produced. Since the zygote is the first cell of the new organism, when this cell undergoes cell division, all the new cells will be identical to it. Therefore, all the cells in the organism ...
File
... - the process by which living things take in materials from its environment for growth and repair; there are 2 types 1) autotrophic nutrition - where a living ...
... - the process by which living things take in materials from its environment for growth and repair; there are 2 types 1) autotrophic nutrition - where a living ...
On the mechanism of haploid production by RWS Haploids have
... triploid endosperm and a haploid embryo. Second, the normal double fertilization events would take place, and then the chromosomes contributed by the female parent are eliminated from the embryo after fertilization. The following experiment was performed to distinguish between these two hypotheses. ...
... triploid endosperm and a haploid embryo. Second, the normal double fertilization events would take place, and then the chromosomes contributed by the female parent are eliminated from the embryo after fertilization. The following experiment was performed to distinguish between these two hypotheses. ...
EOC Review Powerpoint
... • Sex Cell division • Produces four different haploid daughter cells called GAMETES • Male gamete = sperm • Female = egg Fertilization: Egg + sperm = zygote ...
... • Sex Cell division • Produces four different haploid daughter cells called GAMETES • Male gamete = sperm • Female = egg Fertilization: Egg + sperm = zygote ...
Dictyostelium discoideum, an interesting model organism for
... which are too complex in e.g. chickens or dogs and can give us a hint, how these processes might work in higher organisms. Moreover, higher organisms are more difficult to keep under laboratory conditions. Dictyostelium discoideum (Dictyostelium hereafter) is an eukaryotic organism (this domain incl ...
... which are too complex in e.g. chickens or dogs and can give us a hint, how these processes might work in higher organisms. Moreover, higher organisms are more difficult to keep under laboratory conditions. Dictyostelium discoideum (Dictyostelium hereafter) is an eukaryotic organism (this domain incl ...
Section 18.2 - CPO Science
... – Skin is the first line of defense for blocking moisture and invaders like bacteria. – Skin contains sweat glands that help regulate your body temperature. – Skin contains nerve endings that allow you to sense your environment through touch and pressure. ...
... – Skin is the first line of defense for blocking moisture and invaders like bacteria. – Skin contains sweat glands that help regulate your body temperature. – Skin contains nerve endings that allow you to sense your environment through touch and pressure. ...
reproduction
... Use what you know about asexual and sexual reproduction to sort the following terms into the correct column. If the term is related to asexual reproduction, write it in the column on the left. If the term is related to sexual reproduction, write it in the column on the right. If the term is related ...
... Use what you know about asexual and sexual reproduction to sort the following terms into the correct column. If the term is related to asexual reproduction, write it in the column on the left. If the term is related to sexual reproduction, write it in the column on the right. If the term is related ...
Zoology Semester Exam Study Guide
... Zoology Semester Exam Chapters 26-34 1. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have __________ __________. 2. If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, it is _______________________. 3. An animal is: unicellular or multicellular; autotrophic or heterotrophic; prokaryotic or eukary ...
... Zoology Semester Exam Chapters 26-34 1. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have __________ __________. 2. If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, it is _______________________. 3. An animal is: unicellular or multicellular; autotrophic or heterotrophic; prokaryotic or eukary ...
Reproduction
... Bacteria, fungi, and plants are not the only organisms that reproduce asexually. In some animals, like fish, reptiles, and amphibians, an unfertilized egg can develop into a full-grown adult. This offspring would only have a copy of the female’s DNA. For example, in some insects called aphids, asexua ...
... Bacteria, fungi, and plants are not the only organisms that reproduce asexually. In some animals, like fish, reptiles, and amphibians, an unfertilized egg can develop into a full-grown adult. This offspring would only have a copy of the female’s DNA. For example, in some insects called aphids, asexua ...
1.2 From Cells to Organisms
... the plant. The flesh of fruit is another example of plant tissue. It protects the plant’s seeds. B. Plant and animals tissues that come together for a specific purpose form organs a. Examples of plant organs are stems, fruit, onions (store water). b. Examples of animal organs are brains, lungs, hear ...
... the plant. The flesh of fruit is another example of plant tissue. It protects the plant’s seeds. B. Plant and animals tissues that come together for a specific purpose form organs a. Examples of plant organs are stems, fruit, onions (store water). b. Examples of animal organs are brains, lungs, hear ...
100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the
... FOR HUMANS 46 SPECIES is a group of closely related organisms that share certain characteristics and can produce new individuals through reproduction. TOPIC 4 47. Differences between mitosis and meiosis Mitotic division Meiotic division asexual sexual ONE cell division TWO cell divisions # functioni ...
... FOR HUMANS 46 SPECIES is a group of closely related organisms that share certain characteristics and can produce new individuals through reproduction. TOPIC 4 47. Differences between mitosis and meiosis Mitotic division Meiotic division asexual sexual ONE cell division TWO cell divisions # functioni ...
100 Things to Know About Biology
... 60. Two different types of reproduction exist: Asexual (without sex) and sexual (meaning with sex). Remember, sex is not an act, in the biological sense, but rather a conjoining of the actual male and female reproductive cells. 61. Asexual: many eukaryotic organisms that are asexual reproduce by mea ...
... 60. Two different types of reproduction exist: Asexual (without sex) and sexual (meaning with sex). Remember, sex is not an act, in the biological sense, but rather a conjoining of the actual male and female reproductive cells. 61. Asexual: many eukaryotic organisms that are asexual reproduce by mea ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Refreshers April 2015
... reflection questions that correlate with an Amoeba Sisters video. Please note that these refreshers are brief so they only cover major video points. Terms of Use: This may be reproduced, uploaded on websites, and used for educational purposes. There are 4 pages total (not counting this one) which ca ...
... reflection questions that correlate with an Amoeba Sisters video. Please note that these refreshers are brief so they only cover major video points. Terms of Use: This may be reproduced, uploaded on websites, and used for educational purposes. There are 4 pages total (not counting this one) which ca ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragment into a host Genetic engineering organism of the same or different species Genetics Branch of biology that studies heredity Mitochondria ...
... Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragment into a host Genetic engineering organism of the same or different species Genetics Branch of biology that studies heredity Mitochondria ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction & Animal Development
... is passed onto the next Sexual Reproduction – genetic material of two individuals are combined In sexual reproduction an egg and sperm unite and some traits come from each parent, so the offspring is never identical to either of its parents produced in ...
... is passed onto the next Sexual Reproduction – genetic material of two individuals are combined In sexual reproduction an egg and sperm unite and some traits come from each parent, so the offspring is never identical to either of its parents produced in ...
document
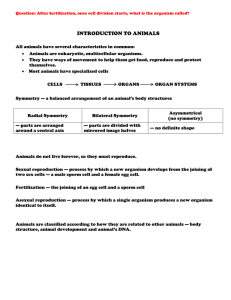
... Animals do not live forever, so they must reproduce. Sexual reproduction — process by which a new organism develops from the joining of two sex cells — a male sperm cell and a female egg cell. Fertilization — the joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell Asexual reproduction — process by which a singl ...
... Animals do not live forever, so they must reproduce. Sexual reproduction — process by which a new organism develops from the joining of two sex cells — a male sperm cell and a female egg cell. Fertilization — the joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell Asexual reproduction — process by which a singl ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.