Multicellular organisms meet their needs in different ways.
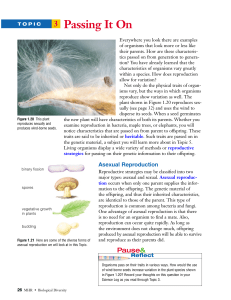
... organism grows off, or buds, from another. Organisms that reproduce asexually can reproduce more often. Asexual reproduction limits genetic diversity within a group because offspring have the same genetic material as the parent. ...
... organism grows off, or buds, from another. Organisms that reproduce asexually can reproduce more often. Asexual reproduction limits genetic diversity within a group because offspring have the same genetic material as the parent. ...
Reproduction in Organisms
... 1. The time period for which an organism is functional from birth to natural death is called its lifespan. 2. During its lifespan an organism grows, develops, attains maturity and gives rise to new individuals of the same type. 3. All the reproductive methods of living organisms are broadly ...
... 1. The time period for which an organism is functional from birth to natural death is called its lifespan. 2. During its lifespan an organism grows, develops, attains maturity and gives rise to new individuals of the same type. 3. All the reproductive methods of living organisms are broadly ...
5.4 Asexual Reproduction
... so they will respond to their environment in the same way. If conditions stay the same, this is not a problem. If the environment changes, and the organisms cannot live with the changes, the entire population could die off. In contrast, offspring from sexual reproduction are genetically different fr ...
... so they will respond to their environment in the same way. If conditions stay the same, this is not a problem. If the environment changes, and the organisms cannot live with the changes, the entire population could die off. In contrast, offspring from sexual reproduction are genetically different fr ...
Asexual Reproduction
... Disadvantages: Asexual Reproduction Because their offspring are identical, there is no genetic variation that can give an organism a better chance for survival Example: If a weed killer can kill the parent, it will also kill the offspring A whole species can be wiped out from a ...
... Disadvantages: Asexual Reproduction Because their offspring are identical, there is no genetic variation that can give an organism a better chance for survival Example: If a weed killer can kill the parent, it will also kill the offspring A whole species can be wiped out from a ...
3) ALL LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO A STIMULUS
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
Characteristics of life
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism e.g. urea and carbon dioxide from the body. These waste products can become toxic to the cell if allowed to accumulate. The organism tries to maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis). Plants have less need for excretion because t ...
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism e.g. urea and carbon dioxide from the body. These waste products can become toxic to the cell if allowed to accumulate. The organism tries to maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis). Plants have less need for excretion because t ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
Reproductive cells
... • Binary fission- organism splits directly into two equal-sized offspring, each with the parent’s genetic material. – Occurs in bacteria and other single-celled organisms ...
... • Binary fission- organism splits directly into two equal-sized offspring, each with the parent’s genetic material. – Occurs in bacteria and other single-celled organisms ...
Animal Kingdom Test Study Guide
... Starfish, mammals, fish, sharks, amphibians, birds Sexual Reproduction Process by which two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism Chordates, earthworms, mammals, some worms, clams, squid, insects ...
... Starfish, mammals, fish, sharks, amphibians, birds Sexual Reproduction Process by which two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism Chordates, earthworms, mammals, some worms, clams, squid, insects ...
7th Grade Science Standards—Life Science (one semester)
... and muscle cells) to the function that the cell performs. Explain the relationship between tissues that make up individual organs and the functions the organ performs (e.g., valves in the heart control blood flow, air sacs in the lungs maximize surface area for transfer of gases). Describe the compo ...
... and muscle cells) to the function that the cell performs. Explain the relationship between tissues that make up individual organs and the functions the organ performs (e.g., valves in the heart control blood flow, air sacs in the lungs maximize surface area for transfer of gases). Describe the compo ...
29.2 Form and Function in Invertebrates
... annelids, mollusks, arthropods, and echinoderms Food enters through mouth and waste leave through ...
... annelids, mollusks, arthropods, and echinoderms Food enters through mouth and waste leave through ...
Chapter 2 Parents & Offspring
... The fertilized egg cell contains genetic material from both parents. The fertilized egg goes on to develop into a new individual who will have some characteristics, or traits from each parent. ...
... The fertilized egg cell contains genetic material from both parents. The fertilized egg goes on to develop into a new individual who will have some characteristics, or traits from each parent. ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... Some fungi, such as mushrooms, can reproduce asexually by forming single-celled, reproductive structures called spores. When asexual spores are formed, only one parent organism supplies the genetic material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, ...
... Some fungi, such as mushrooms, can reproduce asexually by forming single-celled, reproductive structures called spores. When asexual spores are formed, only one parent organism supplies the genetic material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... Some fungi, such as mushrooms, can reproduce asexually by forming single-celled, reproductive structures called spores. When asexual spores are formed, only one parent organism supplies the genetic material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, ...
... Some fungi, such as mushrooms, can reproduce asexually by forming single-celled, reproductive structures called spores. When asexual spores are formed, only one parent organism supplies the genetic material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, ...
LIVING ENVIRONMENT SUMMER PACKET Ecology
... system to produce antibodies, so the afflicted individual is unable to cope with infections and cancer cells which arise within the body. 50) _________________________________ is a group of diseases resulting from gene mutations which cause cells to divide uncontrollably. Exposure of cells to certai ...
... system to produce antibodies, so the afflicted individual is unable to cope with infections and cancer cells which arise within the body. 50) _________________________________ is a group of diseases resulting from gene mutations which cause cells to divide uncontrollably. Exposure of cells to certai ...
Bacteria protist fungi insect mammal
... sometimes flagella. Reproduction: Binary fission (asexual) Can be photosynthetic or heterotrophic ...
... sometimes flagella. Reproduction: Binary fission (asexual) Can be photosynthetic or heterotrophic ...
Insects - OG Science Pages
... • Insects have a hindgut and their food moves through it and then exits their body through their anal ...
... • Insects have a hindgut and their food moves through it and then exits their body through their anal ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction? Of internal and external fertilization? Asexual reproduction produces identical clones of one individual and is advantageous in an environment that does not change much over time. Sexual reproduction requires two parent ...
... 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction? Of internal and external fertilization? Asexual reproduction produces identical clones of one individual and is advantageous in an environment that does not change much over time. Sexual reproduction requires two parent ...
List and tell the function of the parts of a cell
... • Ovules – make the eggs • Style – the long tube that leads from the outside of the flower to the ovules • Stigma – the sticky top of the flower that is used to catch pollen grains c. Pollen grains – produce sperm (the male sex cell) d. Egg – the female sex cell e. Seed – an undeveloped plant, a zyg ...
... • Ovules – make the eggs • Style – the long tube that leads from the outside of the flower to the ovules • Stigma – the sticky top of the flower that is used to catch pollen grains c. Pollen grains – produce sperm (the male sex cell) d. Egg – the female sex cell e. Seed – an undeveloped plant, a zyg ...
Fertilization and Development
... Gestation (AKA Pregnancy) • In humans, this typically lasts 40 weeks • Premature birth – babies born prior to completing 37 weeks of development – Increase chance of lung and brain problems – Typically, the earliest survivable birth is 24 weeks ...
... Gestation (AKA Pregnancy) • In humans, this typically lasts 40 weeks • Premature birth – babies born prior to completing 37 weeks of development – Increase chance of lung and brain problems – Typically, the earliest survivable birth is 24 weeks ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
Characteristics of Life Notes Packet
... DNA deoxyribonucleic acid – the molecule which makes up the “genetic blueprint” of each organism How does DNA work? DNA codes for RNA which codes for proteins which determine traits. *All DNA uses the same type of coding system (‘language’) – thus the term “universal” Prokaryotic: Smaller, simpler, ...
... DNA deoxyribonucleic acid – the molecule which makes up the “genetic blueprint” of each organism How does DNA work? DNA codes for RNA which codes for proteins which determine traits. *All DNA uses the same type of coding system (‘language’) – thus the term “universal” Prokaryotic: Smaller, simpler, ...
REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE
... in the ovule to form a zygote. The other sperm nucleus combines with another bigger nucleus in the ovule which develops into the endosperm. Sexual Reproduction in Humans and Animals Humans (and all animals that reproduce sexually) have cells called gametes. Gametes are formed during meiosis and come ...
... in the ovule to form a zygote. The other sperm nucleus combines with another bigger nucleus in the ovule which develops into the endosperm. Sexual Reproduction in Humans and Animals Humans (and all animals that reproduce sexually) have cells called gametes. Gametes are formed during meiosis and come ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.