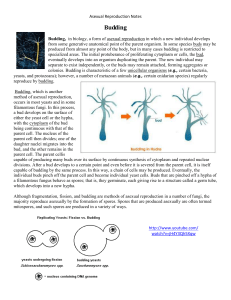
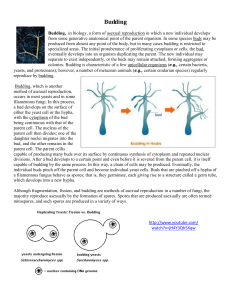
Life Science CRCT Study Guide 1
... desired traits or features. Heredity- is the passing of traits from parents to their offspring Characteristics –is a feature that has different forms Incomplete dominance– both parents influence the offspring/one white and one red and the offspring is pink Alleles –different versions of a gene Punne ...
... desired traits or features. Heredity- is the passing of traits from parents to their offspring Characteristics –is a feature that has different forms Incomplete dominance– both parents influence the offspring/one white and one red and the offspring is pink Alleles –different versions of a gene Punne ...
Chapter-12
... • Fusion of a sperm and egg at fertilization results in a zygote • Zygote first cell of a new individual ...
... • Fusion of a sperm and egg at fertilization results in a zygote • Zygote first cell of a new individual ...
Zoology
... System of classification that is based on phylogeny As groups of organisms diverge and evolve from a common ancestral group, they retain some unique inherited traits. Cladogram Branching diagram identifying a group’s derived traits. Similar to a pedigree or family tree. Two groups on div ...
... System of classification that is based on phylogeny As groups of organisms diverge and evolve from a common ancestral group, they retain some unique inherited traits. Cladogram Branching diagram identifying a group’s derived traits. Similar to a pedigree or family tree. Two groups on div ...
lfsc crct flashcards 2
... structure and function of cells; Explain that cells take in nutrients. ...
... structure and function of cells; Explain that cells take in nutrients. ...
No Slide Title - Effingham County Schools
... muscular/skeletal systems for movement or they have a way to move or circulate water for feeding. 7. Reproduction-most reproduction is sexual using haploid gametes ...
... muscular/skeletal systems for movement or they have a way to move or circulate water for feeding. 7. Reproduction-most reproduction is sexual using haploid gametes ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... cells, grow during periods of their lives. In a single-celled organism, the cell gets larger and divides, making other organisms. In organisms made of many cells, the number of cells gets larger, and the organism gets bigger. In addition to getting larger, living things may develop and change as the ...
... cells, grow during periods of their lives. In a single-celled organism, the cell gets larger and divides, making other organisms. In organisms made of many cells, the number of cells gets larger, and the organism gets bigger. In addition to getting larger, living things may develop and change as the ...
At fertilization the genetic traits of an individual are determined
... At fertilization the genetic traits of an individual are determined. Fertilization occurs when gametes, an egg and a sperm, join together. Each of the cells contributes a set of traits to the offspring. The task: In this activity you will use coins to represent the egg and sperm. The parents are het ...
... At fertilization the genetic traits of an individual are determined. Fertilization occurs when gametes, an egg and a sperm, join together. Each of the cells contributes a set of traits to the offspring. The task: In this activity you will use coins to represent the egg and sperm. The parents are het ...
Review Presentation
... • a form of asexual reproduction where a chromosome is copied before the cell divides to form two new cells • used by bacteria (which are unicellular and prokaryotes.) ...
... • a form of asexual reproduction where a chromosome is copied before the cell divides to form two new cells • used by bacteria (which are unicellular and prokaryotes.) ...
Insect Notes
... - Reproduction: external reproduction (water needed to transport sperm and eggs must be kept moist) - Circulation: 3 chambered heart. One chamber gets oxygen rich blood from lungs and skin. - Regulation: Ectotherms, variable body temperature- gets heat from outside source - Metamorphosis: eggs, tadp ...
... - Reproduction: external reproduction (water needed to transport sperm and eggs must be kept moist) - Circulation: 3 chambered heart. One chamber gets oxygen rich blood from lungs and skin. - Regulation: Ectotherms, variable body temperature- gets heat from outside source - Metamorphosis: eggs, tadp ...
HonoNameKEY Date Period Introduction to Living Things Notes
... There are many different types of organisms, each of which is organized into one of 3 major domains, and 6 major kingdoms. Each kingdom is subdivided into _phyla__________, which are subdivided into __classes__________, which are subdivided into __orders___________, which are subdivided into ___fami ...
... There are many different types of organisms, each of which is organized into one of 3 major domains, and 6 major kingdoms. Each kingdom is subdivided into _phyla__________, which are subdivided into __classes__________, which are subdivided into __orders___________, which are subdivided into ___fami ...
Health Unit 5 Vocabulary Chapter 7:
... Adolescence – the period between childhood and adulthood Endocrine system – a body system containing glands that regulate growth and other important activities Puberty – the time when you start developing physical characteristics of adults of your gender Lesson 2: Reproductive system – a body system ...
... Adolescence – the period between childhood and adulthood Endocrine system – a body system containing glands that regulate growth and other important activities Puberty – the time when you start developing physical characteristics of adults of your gender Lesson 2: Reproductive system – a body system ...
Asexual Reproduction Jigsaw
... Normal egg cells form after meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as their mother's body cells. Haploid individuals, however, are usually non-viable, and parthenogenetic offspring usually have the diploid chromosome number. If the chromosome number of the haploid egg cell is doubled ...
... Normal egg cells form after meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as their mother's body cells. Haploid individuals, however, are usually non-viable, and parthenogenetic offspring usually have the diploid chromosome number. If the chromosome number of the haploid egg cell is doubled ...
Life Science
... they have a backbone • Another is to determine whether they make their own food – animals do NOT make their own food, they must get energy from eating something, whereas plants do make their own food (photosynthesis) ...
... they have a backbone • Another is to determine whether they make their own food – animals do NOT make their own food, they must get energy from eating something, whereas plants do make their own food (photosynthesis) ...
Review for structures
... Ovaries - FEMALE reproductive gland in which EGGS are formed and hormones are produced. Testes -- MALE reproductive gland that produces SPERM and TESTOSTERONE. Sex Cells Contain HALF the normal number of chromosomes Female Reproductive Cell - EGG (OVULE) Male Reproductive Cell - SPERM Semen - the fl ...
... Ovaries - FEMALE reproductive gland in which EGGS are formed and hormones are produced. Testes -- MALE reproductive gland that produces SPERM and TESTOSTERONE. Sex Cells Contain HALF the normal number of chromosomes Female Reproductive Cell - EGG (OVULE) Male Reproductive Cell - SPERM Semen - the fl ...
Final Exam Review - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Cell plate, cleavage furrow~ occurs during cytokinesis • Autosomes~ body chromosomes/somatic chromosomes (44) • Sex chromosomes: XX (girl)or XY (boy) (2) ...
... Cell plate, cleavage furrow~ occurs during cytokinesis • Autosomes~ body chromosomes/somatic chromosomes (44) • Sex chromosomes: XX (girl)or XY (boy) (2) ...
Final Exam Review
... Cell plate, cleavage furrow~ occurs during cytokinesis • Autosomes~ body chromosomes/somatic chromosomes (44) • Sex chromosomes: XX (girl)or XY (boy) (2) ...
... Cell plate, cleavage furrow~ occurs during cytokinesis • Autosomes~ body chromosomes/somatic chromosomes (44) • Sex chromosomes: XX (girl)or XY (boy) (2) ...
Cells
... Type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only ...
... Type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only ...
DOMAINS AND KINGDOMS
... food from outside. Besides fungi these are the main decomposers. Cyanobacteria have Chlorophyll a for photosynthesis like algae and plants (photoautotrophs). Others use hydrogen sulfide instead of water and release sulfur instead of oxygen. Still others can gain electrons from inorganic chemicals to ...
... food from outside. Besides fungi these are the main decomposers. Cyanobacteria have Chlorophyll a for photosynthesis like algae and plants (photoautotrophs). Others use hydrogen sulfide instead of water and release sulfur instead of oxygen. Still others can gain electrons from inorganic chemicals to ...
Behavioral, Structural, and Reproductive Adaptations
... Autotrophs- organisms that can make their own food (photosynthesis). Heterotrophs- organisms that consume food or decompose food. ...
... Autotrophs- organisms that can make their own food (photosynthesis). Heterotrophs- organisms that consume food or decompose food. ...
development
... Reproduction is the formation of new individuals The reproductive system could be thought of as the single most important system for the continuation of a species—without it, no species could produce another generation ...
... Reproduction is the formation of new individuals The reproductive system could be thought of as the single most important system for the continuation of a species—without it, no species could produce another generation ...
Amphibians Notes
... They are _______________, meaning cold-blooded. During extreme environmental conditions they either _______________ (winter) or ________________ (summer). ...
... They are _______________, meaning cold-blooded. During extreme environmental conditions they either _______________ (winter) or ________________ (summer). ...
What is an organism?
... the blood sugar level by moving sugar into the cells. Once blood sugar levels reach homeostasis the pancreas ...
... the blood sugar level by moving sugar into the cells. Once blood sugar levels reach homeostasis the pancreas ...
ch_1-4 - WordPress.com
... - Unicellular (eg. Yeast) to multicellular filamentous body called mycelium. - One unit of mycelium called hypha . - Mycelia maybe coenocytic (no septum) or septate. - Lichens – Symbiotic association of fungus and algae. - Mycorrhiza – Symbiotic association of fungi with root of higher plants eg. Pi ...
... - Unicellular (eg. Yeast) to multicellular filamentous body called mycelium. - One unit of mycelium called hypha . - Mycelia maybe coenocytic (no septum) or septate. - Lichens – Symbiotic association of fungus and algae. - Mycorrhiza – Symbiotic association of fungi with root of higher plants eg. Pi ...
Reproduction and Development - Mahopac Central School District
... 6. In humans, the fertilized egg (called an embryo) undergoes many cell divisions a. eventually, three layers of cells develop b. these three layers produce cells which are different from each of the other layers c. they will become different tissues, organs, and organ systems 7. In humans, all orga ...
... 6. In humans, the fertilized egg (called an embryo) undergoes many cell divisions a. eventually, three layers of cells develop b. these three layers produce cells which are different from each of the other layers c. they will become different tissues, organs, and organ systems 7. In humans, all orga ...
Asexual Reproduction Jigsaw
... Normal egg cells form after meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as their mother's body cells. Haploid individuals, however, are usually non-viable, and parthenogenetic offspring usually have the diploid chromosome number. If the chromosome number of the haploid egg cell is doubled ...
... Normal egg cells form after meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as their mother's body cells. Haploid individuals, however, are usually non-viable, and parthenogenetic offspring usually have the diploid chromosome number. If the chromosome number of the haploid egg cell is doubled ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.