Week 12 - CMS - Cerritos College
... A. SYMMETRY: Think "balance" – plane(s) by which an organism can be divided to give similar pieces. RADIAL - _________________________________________________________________________ BILATERAL - ______________________________________________________________________ ASYMMETRY - ______________________ ...
... A. SYMMETRY: Think "balance" – plane(s) by which an organism can be divided to give similar pieces. RADIAL - _________________________________________________________________________ BILATERAL - ______________________________________________________________________ ASYMMETRY - ______________________ ...
Chapter 5 Questions
... 8. What are the four major evolutionary groups of plants? What are the derived (unique) traits that exist between each other? The four major evolutionary groups are bryophytes (mosses), pteridophytes (ferns), gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Bryophytes do not have vascular tissue nor true roots. They ...
... 8. What are the four major evolutionary groups of plants? What are the derived (unique) traits that exist between each other? The four major evolutionary groups are bryophytes (mosses), pteridophytes (ferns), gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Bryophytes do not have vascular tissue nor true roots. They ...
theory of evolution
... • Parasitism: two organisms living together; one benefits at the expense of the other • Co-evolution: evolution of one species depends on part of another’s evolution • Succession and climax communities: gradual changes in vegetation over time ...
... • Parasitism: two organisms living together; one benefits at the expense of the other • Co-evolution: evolution of one species depends on part of another’s evolution • Succession and climax communities: gradual changes in vegetation over time ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology Overview Multicellular
... i. Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hormones are chemical messengers. Target tissues have cells with receptor proteins for hormones, so only some tissues are affected by specific hormones. ii. Blood glucose regulation including the role of insulin, glucagon, glycogen, pancrea ...
... i. Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hormones are chemical messengers. Target tissues have cells with receptor proteins for hormones, so only some tissues are affected by specific hormones. ii. Blood glucose regulation including the role of insulin, glucagon, glycogen, pancrea ...
Structure and Function
... Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this stimulus is called a response. Growth and Development Organisms have the ability to replace some cells that are worn out or damaged. As organisms grow and develop their body si ...
... Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this stimulus is called a response. Growth and Development Organisms have the ability to replace some cells that are worn out or damaged. As organisms grow and develop their body si ...
Review chapter 4 Organ Systems
... brings oxygen to the blood and the circulatory system moves the blood through the body. ...
... brings oxygen to the blood and the circulatory system moves the blood through the body. ...
INVESTIGATIVE SCIENCE
... Mr. Pomerantz__________________________________________________________________Page 2 of 2 3. Describe the difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis. Use the terms “chromosomes” and ...
... Mr. Pomerantz__________________________________________________________________Page 2 of 2 3. Describe the difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis. Use the terms “chromosomes” and ...
أسئلة مساعدة للطلاب للاختبار النهائى
... The movement of the sperm tail is due to the: a) fertilization b) primary spermatogenesis c) the large number of sperm d) spermatids e) ATP released from mitochondria ...
... The movement of the sperm tail is due to the: a) fertilization b) primary spermatogenesis c) the large number of sperm d) spermatids e) ATP released from mitochondria ...
IBO 1991 Theory_CCL - International Biology Olympiad
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
AP Biology - Cloudfront.net
... arrangement of all the chromosomes of a cell Homologous chromosomes are paired up, then they are put in order from the LARGEST chromosome pair to the smallest. ...
... arrangement of all the chromosomes of a cell Homologous chromosomes are paired up, then they are put in order from the LARGEST chromosome pair to the smallest. ...
10A Interactions in Animals
... 1. An animal’s body consists of organs and systems that are unified and interact to conduct the functions of life, including maintaining homeostasis, metabolizing nutrients, reproducing new organisms, and pursuing survival through defense and mobility. No single life process can be achieved without ...
... 1. An animal’s body consists of organs and systems that are unified and interact to conduct the functions of life, including maintaining homeostasis, metabolizing nutrients, reproducing new organisms, and pursuing survival through defense and mobility. No single life process can be achieved without ...
Chapter 20 – Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
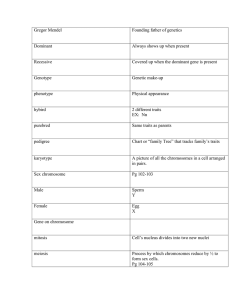
... Most of these circulatory changes are gradual and occur during the first ________________ after birth, although it may take up to a year for the foramen ovale to close. 20.5 Genetics (p. 540) A. The field of _________ investigates how genes confer specific characteristics and how genes are passed fr ...
... Most of these circulatory changes are gradual and occur during the first ________________ after birth, although it may take up to a year for the foramen ovale to close. 20.5 Genetics (p. 540) A. The field of _________ investigates how genes confer specific characteristics and how genes are passed fr ...
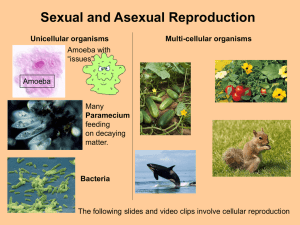
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... strawberry plants. When they touch the ground they form new plants Daffodil Bulbs. These increase in number each year. Producing Clones of the original plant. Plant Cuttings. If you take a cutting from a Geranium Plant and place it in soil it may grow to produce a new Geranium Plant ...
... strawberry plants. When they touch the ground they form new plants Daffodil Bulbs. These increase in number each year. Producing Clones of the original plant. Plant Cuttings. If you take a cutting from a Geranium Plant and place it in soil it may grow to produce a new Geranium Plant ...
Animal Kingdom
... Six Kingdoms: two for bacteria (Archaebacteria & Eubacteria) protists fungi plants animals Scientists study both the internal and external structures of living things; individual cells; chemical processes inside cells. The evidence suggests shared histories and common ancestors. Scientists ...
... Six Kingdoms: two for bacteria (Archaebacteria & Eubacteria) protists fungi plants animals Scientists study both the internal and external structures of living things; individual cells; chemical processes inside cells. The evidence suggests shared histories and common ancestors. Scientists ...
science - dav hzl senior secondary school
... by not wasting them Recycle Segregate the waste that can be recycled and use to make required things. Reuse use the things again and gain. Reuse is better than recycling as it saves energy. Management of Natural Resources is necessary so that these may last for the generations to come and are not ex ...
... by not wasting them Recycle Segregate the waste that can be recycled and use to make required things. Reuse use the things again and gain. Reuse is better than recycling as it saves energy. Management of Natural Resources is necessary so that these may last for the generations to come and are not ex ...
Lecture Notes to Accompany Labs 8 and 9
... •Shoot systems •Vascular tissues •Waxy cuticle •Stomata Alternation of Generations: •Sporophyte: Diploid (2N) spore producing body of the plant or algae. Undergoes meiosis to produce haplod (1N) gametes. •Gametophyte: The haploid (1N), body in which gametes form during the life cycle via mitosis. Br ...
... •Shoot systems •Vascular tissues •Waxy cuticle •Stomata Alternation of Generations: •Sporophyte: Diploid (2N) spore producing body of the plant or algae. Undergoes meiosis to produce haplod (1N) gametes. •Gametophyte: The haploid (1N), body in which gametes form during the life cycle via mitosis. Br ...
doc
... In rotifers, as well as some insects, fish, amphibians and reptiles the eggs produced by females develop directly into adults without being fertilized by sperm This process is called parthenogenesis E.g., aphids, some whiptail lizards, honeybee production of fertile males (drones) Sexual reproductio ...
... In rotifers, as well as some insects, fish, amphibians and reptiles the eggs produced by females develop directly into adults without being fertilized by sperm This process is called parthenogenesis E.g., aphids, some whiptail lizards, honeybee production of fertile males (drones) Sexual reproductio ...
File eoct review with answers
... 64. What are biotic and abiotic factors? Give examples of each. Biotic Factors: all living things in an ecosystem. Ex: plants, animals, fungus, bacteria. Abiotic Factors: all nonliving things in an ecosystem. Ex. rocks, temperature, water. 65. Define: species, organism, population, community, ecosys ...
... 64. What are biotic and abiotic factors? Give examples of each. Biotic Factors: all living things in an ecosystem. Ex: plants, animals, fungus, bacteria. Abiotic Factors: all nonliving things in an ecosystem. Ex. rocks, temperature, water. 65. Define: species, organism, population, community, ecosys ...
Reproductive System Interactions
... • Kidneys dispose of nitrogenous wastes and maintain acid—base balance of blood of mother and fetus; semen exits the body through the urethra of the male ...
... • Kidneys dispose of nitrogenous wastes and maintain acid—base balance of blood of mother and fetus; semen exits the body through the urethra of the male ...
11 Big Fish, Little Fish
... simple source of sperm? Why work and feed, and grow large and complex? Why not exploit the feeding female? All her offspring will still be 50 percent you. Indeed, this strategy is quite common, although little ap preciated by sentient mammals of dife f rent status, among marine invertebrates that e ...
... simple source of sperm? Why work and feed, and grow large and complex? Why not exploit the feeding female? All her offspring will still be 50 percent you. Indeed, this strategy is quite common, although little ap preciated by sentient mammals of dife f rent status, among marine invertebrates that e ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.