The Life Cycle 12. - mt
... 2. If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower or another flower of the same plant, it is known as self pollination. 3. On the other hand, if pollen is transferred from one flower to the flower of another plant of the same species, it is known as cross pollination. The agents of cross polli ...
... 2. If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower or another flower of the same plant, it is known as self pollination. 3. On the other hand, if pollen is transferred from one flower to the flower of another plant of the same species, it is known as cross pollination. The agents of cross polli ...
PSEUDOCOELOMATE LABORATORY Phylum Gastrotricha 1
... lack any sort of excretory system, but larger species possess protonephridia with flame cells, just as do many rotifers. While there is no heart and no true circulatory system, a series of fluid-filled canals called a lacunar system extends through the tegument and even into body muscles. Contractio ...
... lack any sort of excretory system, but larger species possess protonephridia with flame cells, just as do many rotifers. While there is no heart and no true circulatory system, a series of fluid-filled canals called a lacunar system extends through the tegument and even into body muscles. Contractio ...
EOC Review 2011 #5
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck: Created the Theory of Use and Disuse and Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. He stated the more an organism uses a structure, the more developed it will become. If they are not using the structure, it will eventually disappear. He then stated that any trait/characterist ...
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck: Created the Theory of Use and Disuse and Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. He stated the more an organism uses a structure, the more developed it will become. If they are not using the structure, it will eventually disappear. He then stated that any trait/characterist ...
reproduction - Teaching Biology Project
... predators. Developing embryo not subject to environmental changes e.g. temperature. Young born fully developed, can feed and escape predators more easily. Occurs in some invertebrates, fish and ...
... predators. Developing embryo not subject to environmental changes e.g. temperature. Young born fully developed, can feed and escape predators more easily. Occurs in some invertebrates, fish and ...
REPRODUCTION - Teaching Biology Project
... predators. Developing embryo not subject to environmental changes e.g. temperature. Young born fully developed, can feed and escape predators more easily. Occurs in some invertebrates, fish and ...
... predators. Developing embryo not subject to environmental changes e.g. temperature. Young born fully developed, can feed and escape predators more easily. Occurs in some invertebrates, fish and ...
Child Development | Chapter 4
... females. These 22 pairs provide genetic information for both males and females, such as height and eye color. The chromosomes that make up the twenty-third pair are different for females and males. This pair is called the sex chromosomes. The sex of a child, however, is determined by this whole chro ...
... females. These 22 pairs provide genetic information for both males and females, such as height and eye color. The chromosomes that make up the twenty-third pair are different for females and males. This pair is called the sex chromosomes. The sex of a child, however, is determined by this whole chro ...
Kingdom_Animalia_Notes
... o Food is digested in a gut (gastrovascular cavity) and the resulting particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than its own cells. The extracellular digestion of food is an evolutionary development. o The single opening (mouth/anus) means that they have a tw ...
... o Food is digested in a gut (gastrovascular cavity) and the resulting particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than its own cells. The extracellular digestion of food is an evolutionary development. o The single opening (mouth/anus) means that they have a tw ...
File
... The Characteristics of Fungi • Cell wall present, composed of cellulose and/or chitin. • Food storage - generally in the form of lipids and glycogen. • Eukaryotes - true nucleus and other organelles present. • All fungi require water and oxygen (no obligate anaerobes). • Fungi grow in almost every ...
... The Characteristics of Fungi • Cell wall present, composed of cellulose and/or chitin. • Food storage - generally in the form of lipids and glycogen. • Eukaryotes - true nucleus and other organelles present. • All fungi require water and oxygen (no obligate anaerobes). • Fungi grow in almost every ...
Mate choice inside an egg cell.
... Gorelick and Carpinone 2009) and did not use sperm, but instead restored diploidy by either simply replicating all their chromosomes (endomitosis) or by the fusion of two haploid products of egg meiosis with one another. In such an ancestral condition, any invasion of the egg by another nucleus, a s ...
... Gorelick and Carpinone 2009) and did not use sperm, but instead restored diploidy by either simply replicating all their chromosomes (endomitosis) or by the fusion of two haploid products of egg meiosis with one another. In such an ancestral condition, any invasion of the egg by another nucleus, a s ...
cnidarian key
... A. Introduction •most cnidarians are found in marine environments, but some live in fresh water (eg. Hydra) •phylum Cnidaria gets its name from the stinging cell (cnidocyte) that is found all members •the cnidocyte contains a stinging structure called a nematocyst •all cnidarians are soft-bodied ani ...
... A. Introduction •most cnidarians are found in marine environments, but some live in fresh water (eg. Hydra) •phylum Cnidaria gets its name from the stinging cell (cnidocyte) that is found all members •the cnidocyte contains a stinging structure called a nematocyst •all cnidarians are soft-bodied ani ...
PHYLUM ASCHELMINTHES
... blastula stage and the inner cavity the blastocoel. Blastula by invagination forms a gastrula. A juvenile develops in 10-14 days. The juvenile has an alimentary canal, a lateral excretory system and a nerve ring. This stage is called rhabditiform larva or rhabditoid (because of its resemblance to a ...
... blastula stage and the inner cavity the blastocoel. Blastula by invagination forms a gastrula. A juvenile develops in 10-14 days. The juvenile has an alimentary canal, a lateral excretory system and a nerve ring. This stage is called rhabditiform larva or rhabditoid (because of its resemblance to a ...
Class Body Types Skeletal Type
... adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels humans. Schistosomes are long, slim worms with a tegument that bears a large number of small tubercules. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: humans where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single in ...
... adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels humans. Schistosomes are long, slim worms with a tegument that bears a large number of small tubercules. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: humans where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single in ...
Animals Part I - CCRI Faculty Web
... Asexual reproduction single parent gives rise to an offspring that will be genetically identical to the parent Asexual reproduction of a body part!! Fertilization /Copulation Internal fertilization External fertilization Development of a fetus Internal External ...
... Asexual reproduction single parent gives rise to an offspring that will be genetically identical to the parent Asexual reproduction of a body part!! Fertilization /Copulation Internal fertilization External fertilization Development of a fetus Internal External ...
Circulatory system
... • Most animals reproduce sexually, by means of differentiated haploid cells (eggs and sperm). •Most animals are diploid, meaning that the cells of adults contain two copies of the genetic material. •Some animals can reproduce asexually through ...
... • Most animals reproduce sexually, by means of differentiated haploid cells (eggs and sperm). •Most animals are diploid, meaning that the cells of adults contain two copies of the genetic material. •Some animals can reproduce asexually through ...
Evolution of Metabolism Puzzle Race
... Larger animals also need more energy, so the stomach pocket elongated to form a passageway through the center of their entire bodies called the gut or digestive tube. This digestive tube allows the outside environment—the ocean and all its nutrients—to pass through the animal in a safe way while giv ...
... Larger animals also need more energy, so the stomach pocket elongated to form a passageway through the center of their entire bodies called the gut or digestive tube. This digestive tube allows the outside environment—the ocean and all its nutrients—to pass through the animal in a safe way while giv ...
Document
... constant composition and the dynamic properties of the internal environment. The metabolism – the set of chemical reactions in living organisms that support them. Reproduction – the ability of organisms to reproduce themselves. ...
... constant composition and the dynamic properties of the internal environment. The metabolism – the set of chemical reactions in living organisms that support them. Reproduction – the ability of organisms to reproduce themselves. ...
Y10 Biology Mock Exam Revision Mind Maps – Set 1 ONLY
... large area •Roots deep – collect water because surface likely to dry out quickly •No leaves – reduce surface area from which water can be lost •Stem able to swell – store water ...
... large area •Roots deep – collect water because surface likely to dry out quickly •No leaves – reduce surface area from which water can be lost •Stem able to swell – store water ...
I. Review of Genetics
... B. Anatomy of Fungi Main body is a mesh (mycelium) made of many smaller units (hypha). Hypha is a single cell, surrounded by a cell wall of chitin. Mushroom is one example of a fruiting body, used for reproduction. ...
... B. Anatomy of Fungi Main body is a mesh (mycelium) made of many smaller units (hypha). Hypha is a single cell, surrounded by a cell wall of chitin. Mushroom is one example of a fruiting body, used for reproduction. ...
AP Biology Syllabus - Mr. Multhaupt`s Biology Page
... Do not feel overwhelmed. Yes there is a lot of information that we will be covered, but I have had numerous students tell me that they felt very prepared for the AP exam. I have also been told by most of the students that despite the amount of work the class entails, they very much enjoyed the cours ...
... Do not feel overwhelmed. Yes there is a lot of information that we will be covered, but I have had numerous students tell me that they felt very prepared for the AP exam. I have also been told by most of the students that despite the amount of work the class entails, they very much enjoyed the cours ...
Lab 1
... Plant Mitosis Models skip Onion Root Tip Slide 1. Identify a cell in anaphase on a slide under a microscope and put the pointer on it. Call me over to check it and ask for my initials here: ________ Summary of Mitosis: Read about Cytokinesis on the next page (p. 70), before filling in the chart. sig ...
... Plant Mitosis Models skip Onion Root Tip Slide 1. Identify a cell in anaphase on a slide under a microscope and put the pointer on it. Call me over to check it and ask for my initials here: ________ Summary of Mitosis: Read about Cytokinesis on the next page (p. 70), before filling in the chart. sig ...
Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have
... a solid ball of cells. a hollow ball of cells. a flat sheet of cells. a folded sheet of cells. ...
... a solid ball of cells. a hollow ball of cells. a flat sheet of cells. a folded sheet of cells. ...
Kingdom Animalia 1. Several characteristics are used to classify
... Circulatory System of Birds and Mammals (a) Birds and mammals (also crocodilians) have a four-chambered heart which acts as two separate pumps. After passing through the body, blood is pumped under high pressure to the lungs. Upon returning from the lungs, it is pumped under high pressure to the bod ...
... Circulatory System of Birds and Mammals (a) Birds and mammals (also crocodilians) have a four-chambered heart which acts as two separate pumps. After passing through the body, blood is pumped under high pressure to the lungs. Upon returning from the lungs, it is pumped under high pressure to the bod ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology: Learning Outcomes
... Each topic of biology requires you to learn and understand a variety of subject specific vocabulary. The words you will be expected to define are in bold. To help you learn these words you could produce a topic glossary or flashcards. ...
... Each topic of biology requires you to learn and understand a variety of subject specific vocabulary. The words you will be expected to define are in bold. To help you learn these words you could produce a topic glossary or flashcards. ...
Unit 11.2 Anatomy and Physiology
... For students with disabilities, the instructor should refer to the student's IEP to be sure that the accommodations specified are being provided. Instructors should also familiarize themselves with the provisions of Behavior Intervention Plans that may be part of a student's IEP. Frequent consultati ...
... For students with disabilities, the instructor should refer to the student's IEP to be sure that the accommodations specified are being provided. Instructors should also familiarize themselves with the provisions of Behavior Intervention Plans that may be part of a student's IEP. Frequent consultati ...
Diapositiva 1 - Holy Family Catholic Regional Division No. 37
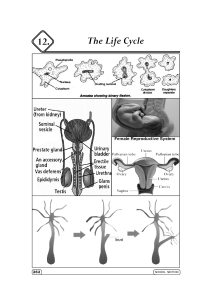
... tubules consist of diploid spermatogonia, stem cells that are the precursors of sperm. divide by mitosis to produce more spermatogonia The Meiosis of each spermatocyte produces 4 haploid spermatids. These then differentiate into sperm, losing most of their cytoplasm and gaining motility in the proce ...
... tubules consist of diploid spermatogonia, stem cells that are the precursors of sperm. divide by mitosis to produce more spermatogonia The Meiosis of each spermatocyte produces 4 haploid spermatids. These then differentiate into sperm, losing most of their cytoplasm and gaining motility in the proce ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.























