Semantical evaluations as monadic second-order
... Nullary operations denote basic graphs : the connected graphs with at most one edge. For dealing with hypergraphs one takes more nullary symbols for denoting hyperedges. More precise algebraic framework : a many sorted algebra where each finite set of source labels is a sort. The above operations ar ...
... Nullary operations denote basic graphs : the connected graphs with at most one edge. For dealing with hypergraphs one takes more nullary symbols for denoting hyperedges. More precise algebraic framework : a many sorted algebra where each finite set of source labels is a sort. The above operations ar ...
MA154 - Academics
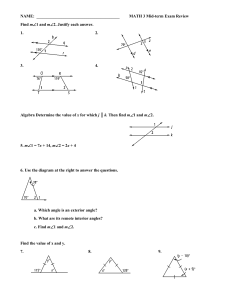
... 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. B 6. C 7. D 8. B 9. B 10. C 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. D 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. C 21. B 22. B 23. B 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. A 28. D 29. A 30. A 31. D 32. D 33. A 34. D 35. C ...
... 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. B 6. C 7. D 8. B 9. B 10. C 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. D 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. C 21. B 22. B 23. B 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. A 28. D 29. A 30. A 31. D 32. D 33. A 34. D 35. C ...
Math 30-1 Learning Outcomes
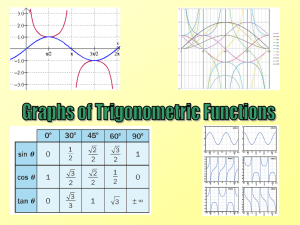
... Determine, using a unit circle or reference triangle, the exact value of a trigonometric ratio for angles expressed in degrees that are multiples of 0º, 30º, 45º, 60º or 90º, or for angles expressed in radians that are multiples of 0, π/6, π/4, π/3, or π/2 , and explain the ...
... Determine, using a unit circle or reference triangle, the exact value of a trigonometric ratio for angles expressed in degrees that are multiples of 0º, 30º, 45º, 60º or 90º, or for angles expressed in radians that are multiples of 0, π/6, π/4, π/3, or π/2 , and explain the ...
Activity 6.5.5 Constructive and Destructive Interference
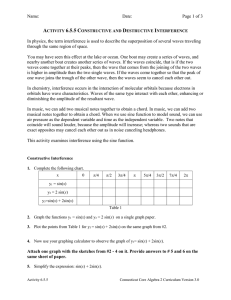
... ACTIVITY 6.5.5 CONSTRUCTIVE AND DESTRUCTIVE INTERFERENCE In physics, the term interference is used to describe the superposition of several waves traveling through the same region of space. You may have seen this effect at the lake or ocean. One boat may create a series of waves, and nearby another ...
... ACTIVITY 6.5.5 CONSTRUCTIVE AND DESTRUCTIVE INTERFERENCE In physics, the term interference is used to describe the superposition of several waves traveling through the same region of space. You may have seen this effect at the lake or ocean. One boat may create a series of waves, and nearby another ...
Coloring k-colorable graphs using smaller palletes
... an odd cycle cancel each other! We effectively sum only over even cycle covers. A graph contains a perfect matching iff it contains an even cycle cover. ...
... an odd cycle cancel each other! We effectively sum only over even cycle covers. A graph contains a perfect matching iff it contains an even cycle cover. ...
mgraph - The University of Kansas
... injection f: V(G) -> V(H) such that uv ε E(G) if and only if f(u)f(v) ε E(G). In other words: A graph G is sub-isomorphic to graph H iff graph G is isomorphic to at least one subgraph of H. ...
... injection f: V(G) -> V(H) such that uv ε E(G) if and only if f(u)f(v) ε E(G). In other words: A graph G is sub-isomorphic to graph H iff graph G is isomorphic to at least one subgraph of H. ...
Chapter 1
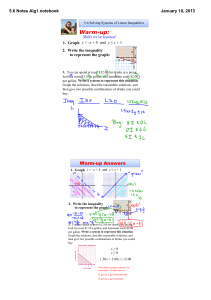
... 1.2 Sketching Graphs of Linear Equations A number, or an ordered pair of numbers, is said to satisfy an equation if substituting the number(s) into the equation results in a true statement. An ordered pair (a, b) is a solution of an equation in two variables if the ordered pair satisfies the equati ...
... 1.2 Sketching Graphs of Linear Equations A number, or an ordered pair of numbers, is said to satisfy an equation if substituting the number(s) into the equation results in a true statement. An ordered pair (a, b) is a solution of an equation in two variables if the ordered pair satisfies the equati ...
Scale-free networks - Chair of Computational Biology
... Aim: allow a power-law degree distribution in a graph while leaving all other aspects as in the random graph model. Given a degree sequence (e.g. power-law distribution) one can generate a random graph by assigning to a vertex i a degree ki from the given degree sequence. Then choose pairs of vert ...
... Aim: allow a power-law degree distribution in a graph while leaving all other aspects as in the random graph model. Given a degree sequence (e.g. power-law distribution) one can generate a random graph by assigning to a vertex i a degree ki from the given degree sequence. Then choose pairs of vert ...
Proportional vs. Non-proportional
... A proportional graph will always go through the origin (0,0) A proportional graph will be a straight line. If you list points (ordered pairs) from a graph, you can create ratios and see if they are constant (equal). ...
... A proportional graph will always go through the origin (0,0) A proportional graph will be a straight line. If you list points (ordered pairs) from a graph, you can create ratios and see if they are constant (equal). ...
Median graph
In graph theory, a division of mathematics, a median graph is an undirected graph in which every three vertices a, b, and c have a unique median: a vertex m(a,b,c) that belongs to shortest paths between each pair of a, b, and c.The concept of median graphs has long been studied, for instance by Birkhoff & Kiss (1947) or (more explicitly) by Avann (1961), but the first paper to call them ""median graphs"" appears to be Nebeský (1971). As Chung, Graham, and Saks write, ""median graphs arise naturally in the study of ordered sets and discrete distributive lattices, and have an extensive literature"". In phylogenetics, the Buneman graph representing all maximum parsimony evolutionary trees is a median graph. Median graphs also arise in social choice theory: if a set of alternatives has the structure of a median graph, it is possible to derive in an unambiguous way a majority preference among them.Additional surveys of median graphs are given by Klavžar & Mulder (1999), Bandelt & Chepoi (2008), and Knuth (2008).