Creating 3-Dimensional Graph Structures with DNA
... 4. If a path remains, a Hamiltonian cycle exists. The rst step presumably generates an exponential number of paths that contain the result. Steps 2 and 3 are used to isolate and detect the result generated by step 1. Step 3 of this algorithm must be repeated n times for a graph of n vertices. The l ...
... 4. If a path remains, a Hamiltonian cycle exists. The rst step presumably generates an exponential number of paths that contain the result. Steps 2 and 3 are used to isolate and detect the result generated by step 1. Step 3 of this algorithm must be repeated n times for a graph of n vertices. The l ...
Solutions - SD308.org
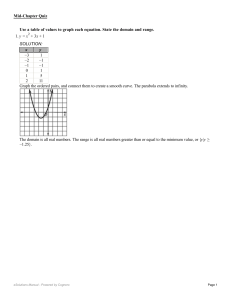
... The domain is all real numbers. The range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the minimum value, or {y|y ≥ Mid-Chapter ...
... The domain is all real numbers. The range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the minimum value, or {y|y ≥ Mid-Chapter ...
Revision Quadratic Functions
... Diagrams 2, 3 and 4 show a part of the graph of y = x2 after it has been moved parallel to the x-axis, or parallel to the y-axis, or parallel to one axis, then the other. y ...
... Diagrams 2, 3 and 4 show a part of the graph of y = x2 after it has been moved parallel to the x-axis, or parallel to the y-axis, or parallel to one axis, then the other. y ...
Graphing exponential and logarithmic functions Exponential function
... Because k 0 , the horizontal asymptote is y 0. Because a 1 0 , the graph lies above the horizontal asymptote and the range is (0, ) . f (0) 201 2 , so the y-intercept is (0, 2) . To find the reference point: a. Set the expression in the exponent equal to 0 and solve for x: x 1 0 ...
... Because k 0 , the horizontal asymptote is y 0. Because a 1 0 , the graph lies above the horizontal asymptote and the range is (0, ) . f (0) 201 2 , so the y-intercept is (0, 2) . To find the reference point: a. Set the expression in the exponent equal to 0 and solve for x: x 1 0 ...
Graphing A Linear Inequality
... 1. Graph the corresponding equation, using a dashed (< or >) line or a solid ( < or >) line. You may need to write the equation in slope-intercept form to graph the boundary line. 2. Test the coordinates of a point in one of the half-planes. You can use any point that is not on the line as a test po ...
... 1. Graph the corresponding equation, using a dashed (< or >) line or a solid ( < or >) line. You may need to write the equation in slope-intercept form to graph the boundary line. 2. Test the coordinates of a point in one of the half-planes. You can use any point that is not on the line as a test po ...
Algebra 2 - Mrs. Schneider MathClawson High School
... A linear equation has no operations other than addition, subtraction, and multiplication of a variable by a constant. The variables may not be multiplied together or appear in a denominator. It does not contain variables with exponents other than 1. The graph of a linear equation is always a line. ...
... A linear equation has no operations other than addition, subtraction, and multiplication of a variable by a constant. The variables may not be multiplied together or appear in a denominator. It does not contain variables with exponents other than 1. The graph of a linear equation is always a line. ...
Investigating Compound Inequalities Packet
... 4. Now graph |x – 1| < 3 on a number line and write a corresponding compound inequality. What changes between the graph in step 2 and the compound inequality in step 3? ...
... 4. Now graph |x – 1| < 3 on a number line and write a corresponding compound inequality. What changes between the graph in step 2 and the compound inequality in step 3? ...
Show all work on a separate sheet of work paper
... $200 per day plus expenses for his services. If expenses are expected to be $1500, for how many days can I hire Mr. Rockford and still remain within my budget of $3,300? 22. Suzie has an interesting job. She sells seashells (by the seashore). She makes $50 per day plus $0.25 for each seashell she se ...
... $200 per day plus expenses for his services. If expenses are expected to be $1500, for how many days can I hire Mr. Rockford and still remain within my budget of $3,300? 22. Suzie has an interesting job. She sells seashells (by the seashore). She makes $50 per day plus $0.25 for each seashell she se ...
MA.8.A.4.2 Solve and graph one
... MA.8.A.4.2 Solve and graph one- and two-step inequalities in one variable. An inequality is a mathematical sentence that contains > or < to compare or describe a range of values. Some inequalities use the symbols ≤ or ≥. The symbol ≤ is read is less than or equal to. The symbol ≥ is read is greater ...
... MA.8.A.4.2 Solve and graph one- and two-step inequalities in one variable. An inequality is a mathematical sentence that contains > or < to compare or describe a range of values. Some inequalities use the symbols ≤ or ≥. The symbol ≤ is read is less than or equal to. The symbol ≥ is read is greater ...
A topological approach to evasiveness | SpringerLink
... original version of the conjecture, which Aanderaa disproved, did not assume monotonicity.) The Aanderaa--Rosenberg conjecture was proved by Rivest and Vuillemin [12]. Their value of e= 1/16 was subsequently improved by Kleitman and Kwiatkowski [8] to e=l/9. (Note: These papers and most later work d ...
... original version of the conjecture, which Aanderaa disproved, did not assume monotonicity.) The Aanderaa--Rosenberg conjecture was proved by Rivest and Vuillemin [12]. Their value of e= 1/16 was subsequently improved by Kleitman and Kwiatkowski [8] to e=l/9. (Note: These papers and most later work d ...
9_5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing
... STEP 1 Write the equation in the standard for ax2 +bx + c = 0 STEP 2 Sketch the graph of the related quadratic function y = ax2 +bx + c STEP 3 Estimate the values of the x-intercepts, if any. The solutions, or roots, of ax2 +bx + c = 0 are the x-intercepts of the graph. ...
... STEP 1 Write the equation in the standard for ax2 +bx + c = 0 STEP 2 Sketch the graph of the related quadratic function y = ax2 +bx + c STEP 3 Estimate the values of the x-intercepts, if any. The solutions, or roots, of ax2 +bx + c = 0 are the x-intercepts of the graph. ...
Median graph
In graph theory, a division of mathematics, a median graph is an undirected graph in which every three vertices a, b, and c have a unique median: a vertex m(a,b,c) that belongs to shortest paths between each pair of a, b, and c.The concept of median graphs has long been studied, for instance by Birkhoff & Kiss (1947) or (more explicitly) by Avann (1961), but the first paper to call them ""median graphs"" appears to be Nebeský (1971). As Chung, Graham, and Saks write, ""median graphs arise naturally in the study of ordered sets and discrete distributive lattices, and have an extensive literature"". In phylogenetics, the Buneman graph representing all maximum parsimony evolutionary trees is a median graph. Median graphs also arise in social choice theory: if a set of alternatives has the structure of a median graph, it is possible to derive in an unambiguous way a majority preference among them.Additional surveys of median graphs are given by Klavžar & Mulder (1999), Bandelt & Chepoi (2008), and Knuth (2008).