endocrine glands
... The endocrin system •The general description Composition endocrine glands (ductless glands ) have no ducts, their secretions (hormone ) release directly into circulation and trave to its target organs ...
... The endocrin system •The general description Composition endocrine glands (ductless glands ) have no ducts, their secretions (hormone ) release directly into circulation and trave to its target organs ...
SALC07 Biological Sciences Head & Neck 4: Normal Swallow
... sensory perception, integration of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems and respiratory function” (RCSLT 2006) ...
... sensory perception, integration of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems and respiratory function” (RCSLT 2006) ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Anatomical characterizations – Origin: craniosacral or thoracolumbar regions – Length of fibers: long preganglionic, short post- or opposite – Location of ganglia: in effectors or close to spinal cord ...
... • Anatomical characterizations – Origin: craniosacral or thoracolumbar regions – Length of fibers: long preganglionic, short post- or opposite – Location of ganglia: in effectors or close to spinal cord ...
File
... 2. Geniohyoid muscles: 2 cord-like muscles above mylohyoid, run from mandible in front to hyoid bone behind. 3. Tongue: located superior to geniohyoid & mouth floor is formed largely by anterior 2/3 of tongue & reflection of mucous membrane from sides of the tongue to gums. Frenulum of tongue: is a ...
... 2. Geniohyoid muscles: 2 cord-like muscles above mylohyoid, run from mandible in front to hyoid bone behind. 3. Tongue: located superior to geniohyoid & mouth floor is formed largely by anterior 2/3 of tongue & reflection of mucous membrane from sides of the tongue to gums. Frenulum of tongue: is a ...
Competency
... Be able to state the conditions necessary for evolution to occur. Be able to discuss the evidences for evolution. Be able to define what a species is, how speciation occurs and isolating mechanisms.. Be able to trace the evolutionary lineage of Homo sapiens.. Recognize and classify common examples o ...
... Be able to state the conditions necessary for evolution to occur. Be able to discuss the evidences for evolution. Be able to define what a species is, how speciation occurs and isolating mechanisms.. Be able to trace the evolutionary lineage of Homo sapiens.. Recognize and classify common examples o ...
LIPIDS - Biochemistry Notes
... acid-stable lingual lipase (originates at the back of the tongue) that acts on TAG molecules particularly on those containing FA of short and medium-chain length (<12C such as those in milk fat); they are also degraded by gastric lipase (secreted by the gastric mucosa); both enzymes are acid stable ...
... acid-stable lingual lipase (originates at the back of the tongue) that acts on TAG molecules particularly on those containing FA of short and medium-chain length (<12C such as those in milk fat); they are also degraded by gastric lipase (secreted by the gastric mucosa); both enzymes are acid stable ...
25 The peritoneum
... !1 The superior wall of the abdominal cavity, separating it from the thoracic cavity, is: the diaphragm #the transverse colon the lesser omentum the liver ! The anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is formed by: the tendinous expansions of the three broad abdominal muscles and the rectus abdominis ...
... !1 The superior wall of the abdominal cavity, separating it from the thoracic cavity, is: the diaphragm #the transverse colon the lesser omentum the liver ! The anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is formed by: the tendinous expansions of the three broad abdominal muscles and the rectus abdominis ...
Pharynx
... Oropharyngeal isthmus closed by contraction of styloglossus – pull tongue upward & backward Palatoglossus – narrow palatoglossal arch & pull root of tongue upward to soft palate Pharyngeal isthmus closed by Elevation of soft palate – levator palatini Tightning of Soft Palate – Tensor veli palatini S ...
... Oropharyngeal isthmus closed by contraction of styloglossus – pull tongue upward & backward Palatoglossus – narrow palatoglossal arch & pull root of tongue upward to soft palate Pharyngeal isthmus closed by Elevation of soft palate – levator palatini Tightning of Soft Palate – Tensor veli palatini S ...
Peritoneum and abdominal cavity
... which comes directly off the aorta. These structures include: oesophagus, stomach, and proximal part of the duodenum, liver and pancreas. Derivatives of midgut The derivatives of midgut are supplied by the superior mesenteric artery (or branches off) which comes directly from the aorta. The structur ...
... which comes directly off the aorta. These structures include: oesophagus, stomach, and proximal part of the duodenum, liver and pancreas. Derivatives of midgut The derivatives of midgut are supplied by the superior mesenteric artery (or branches off) which comes directly from the aorta. The structur ...
lee_mervin_mentoor - University of Western Cape
... Have may features that they share, but some important once that separate them Seperated on basis of symmetry from other metazoan organisms ...
... Have may features that they share, but some important once that separate them Seperated on basis of symmetry from other metazoan organisms ...
branches of the thoracoacromial trunk
... Relative Position of Ureters “Water under the bridge” The ureters (which carry water), are posterior to the ovarian/testicular artery Lobes of the Liver “VC goes with VC” The Venosum and Caudate is on same side as Vena Cava [posterior]. Therefore, quadrate and teres must be on anterior by default. ...
... Relative Position of Ureters “Water under the bridge” The ureters (which carry water), are posterior to the ovarian/testicular artery Lobes of the Liver “VC goes with VC” The Venosum and Caudate is on same side as Vena Cava [posterior]. Therefore, quadrate and teres must be on anterior by default. ...
File
... - are true vocal cordsモbecause they produce sound when air passes between them Superior ligaments are called the vestibular folds. - are false vocal cordsモbecause they have no function in sound production, but protect the vocal ...
... - are true vocal cordsモbecause they produce sound when air passes between them Superior ligaments are called the vestibular folds. - are false vocal cordsモbecause they have no function in sound production, but protect the vocal ...
Phylum Cnidaria - Solon City Schools
... • Ex- Hydra •both asexual polyps and sexual medusa stages •Spends most of its life in the polyp stage Reproduction: •Sexual: eggs and sperm are shed into the water and form fertilized eggs; planula is by passed with eggs hatching into young hydras •Asexual reproduction via budding ...
... • Ex- Hydra •both asexual polyps and sexual medusa stages •Spends most of its life in the polyp stage Reproduction: •Sexual: eggs and sperm are shed into the water and form fertilized eggs; planula is by passed with eggs hatching into young hydras •Asexual reproduction via budding ...
Biliary Anatomy and Physiology
... Fundus of the gall bladder project a little beyond the sharp lower border of the liver and touches the parietal peritoneum at the tip of the 9th costal cartilage where the transpyloric plan crosses the right costal margin at the lateral border of the right rectus sheath(surface marking for ...
... Fundus of the gall bladder project a little beyond the sharp lower border of the liver and touches the parietal peritoneum at the tip of the 9th costal cartilage where the transpyloric plan crosses the right costal margin at the lateral border of the right rectus sheath(surface marking for ...
Gastro40-HALabPracticalReview
... The tail of the pancreas especially the part that abuts against the spleen is at T12. In the event of discrepancies between the computer-based dissector and the written checklist follow the written checklist. I – Embryology a. ...
... The tail of the pancreas especially the part that abuts against the spleen is at T12. In the event of discrepancies between the computer-based dissector and the written checklist follow the written checklist. I – Embryology a. ...
Porifera
... except porifera (sponges) Bilateria: symmetry; all phyla except cnidaria and porifera Deuterostomia: blastopore = anus; only echinodermata, chordata ...
... except porifera (sponges) Bilateria: symmetry; all phyla except cnidaria and porifera Deuterostomia: blastopore = anus; only echinodermata, chordata ...
Launch Activity
... Production of BILE……… BILE is composed of water & BILE SALTS. BILE SALTS emulsify fats, then LIPASE can act on the larger surface area. BILE SALTS also contain cholesterol – if there is too much cholesterol or not enough water, gall stones can form. They can block bile duct and interfere with lipas ...
... Production of BILE……… BILE is composed of water & BILE SALTS. BILE SALTS emulsify fats, then LIPASE can act on the larger surface area. BILE SALTS also contain cholesterol – if there is too much cholesterol or not enough water, gall stones can form. They can block bile duct and interfere with lipas ...
Unit 24: Abdominal and Peritoneal Cavities
... dorsal body wall was called the dorsal mesogastrium. Locate the portion of the mesentery which attaches the fundus of the stomach to the diaphragm. This is called the gastrophrenic ligament. The spleen developed in the dorsal mesogastrium. In the adult, the spleen is located posterior and lateral in ...
... dorsal body wall was called the dorsal mesogastrium. Locate the portion of the mesentery which attaches the fundus of the stomach to the diaphragm. This is called the gastrophrenic ligament. The spleen developed in the dorsal mesogastrium. In the adult, the spleen is located posterior and lateral in ...
7.Development of mid..
... When the intestines return back to the abdominal cavity during the 10th week and then herniate through an imperfectly closed umbilicus, an umbilical hernia forms ...
... When the intestines return back to the abdominal cavity during the 10th week and then herniate through an imperfectly closed umbilicus, an umbilical hernia forms ...
7. Development of digestive system I. Yolk sac. Primitive gut
... vesicle → blindly ending entoderm-lined blind-ending cavity named primitive gut (archenteron) − the vitelline duct (ductus omphaloentericus) connects the middle part of the primitive gut with the yolk sac − both ends of the primitive gut are temporarily closed by membranes, which represent boundarie ...
... vesicle → blindly ending entoderm-lined blind-ending cavity named primitive gut (archenteron) − the vitelline duct (ductus omphaloentericus) connects the middle part of the primitive gut with the yolk sac − both ends of the primitive gut are temporarily closed by membranes, which represent boundarie ...
Honors Biology Unit 1 Objectives: The Chemistry of Life
... (temperature, salinity, and pH). 5. Analyze and draw meaningful conclusions from graphs depicting enzyme activity in various conditions. 6. Give the functions of and locate the following organs/structures in a drawing and/or dissection specimen: mouth, esophagus, cardiac sphincter, stomach, pyloric ...
... (temperature, salinity, and pH). 5. Analyze and draw meaningful conclusions from graphs depicting enzyme activity in various conditions. 6. Give the functions of and locate the following organs/structures in a drawing and/or dissection specimen: mouth, esophagus, cardiac sphincter, stomach, pyloric ...
As described in the previous paper, gallstones can form in the
... decrease after incision, but for unknown reasons. During the healing process, hormone, immune, and mineral levels return to normal. These short-term physiological changes are coupled with several long-term changes to the physiology of the biliary and gastrointestinal systems after cholecystectomy. N ...
... decrease after incision, but for unknown reasons. During the healing process, hormone, immune, and mineral levels return to normal. These short-term physiological changes are coupled with several long-term changes to the physiology of the biliary and gastrointestinal systems after cholecystectomy. N ...
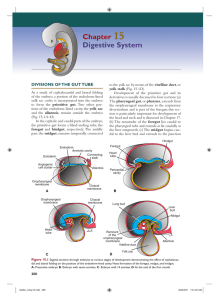
Chapter 15 Digestive System
... (Fig. 15.2D). Once the mesoderm is specified by this code, then it instructs the endoderm to form the various components of the mid- and hindgut regions, including part of the small intestine, cecum, colon, and cloaca (Fig. 15.2). ...
... (Fig. 15.2D). Once the mesoderm is specified by this code, then it instructs the endoderm to form the various components of the mid- and hindgut regions, including part of the small intestine, cecum, colon, and cloaca (Fig. 15.2). ...
AandPExam3takehomecC7sf7Y
... parameters of the vibrating object. 4. The paired muscles called the orbicularis oris muscle controls labial movement such as puckering. 5. Micrognathia is a congenital madibular hypoplasia that can lead to cleft palate. 6. The tongue is covered in mechanoreceptors which assist with feeling, maintai ...
... parameters of the vibrating object. 4. The paired muscles called the orbicularis oris muscle controls labial movement such as puckering. 5. Micrognathia is a congenital madibular hypoplasia that can lead to cleft palate. 6. The tongue is covered in mechanoreceptors which assist with feeling, maintai ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.