Ox bile, dried
... salts. The bile salts in fresh bile are mainly totally conjugated as peptides formed from bile acid, glycine or taurine. The selective activity of fully conjugated bile acids is less than that of free acids. Deoxycholic acid is the most active of the bile acids. Bacterial enzymes hydrolyse bile conj ...
... salts. The bile salts in fresh bile are mainly totally conjugated as peptides formed from bile acid, glycine or taurine. The selective activity of fully conjugated bile acids is less than that of free acids. Deoxycholic acid is the most active of the bile acids. Bacterial enzymes hydrolyse bile conj ...
Lecture notes File
... sensory perception, integration of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems and respiratory function” (RCSLT 2006) ...
... sensory perception, integration of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems and respiratory function” (RCSLT 2006) ...
Is your digestive system not feeling quite right? Did you know? Good
... bacteria inside your digestive system and they weigh up to 3kg? In fact, you have more bacteria living inside you than you have cells in your entire body! There are approximately 100 trillion bacteria in your digestive system, the vast majority of which live in your bowel. The balance of all these b ...
... bacteria inside your digestive system and they weigh up to 3kg? In fact, you have more bacteria living inside you than you have cells in your entire body! There are approximately 100 trillion bacteria in your digestive system, the vast majority of which live in your bowel. The balance of all these b ...
BHS 116.2: Physiology II Date: 1/23/13 Notetaker: Stephanie Cullen
... o The bile salts are recycled into the pool of bile for another round Reused o Most is recycled Very small amount is made from new cholesterol o Bile sequestering drug: binds bile in intestine to prevent it from being absorbed Excreted in feces Reduce cholesterol levels by forcing the body t ...
... o The bile salts are recycled into the pool of bile for another round Reused o Most is recycled Very small amount is made from new cholesterol o Bile sequestering drug: binds bile in intestine to prevent it from being absorbed Excreted in feces Reduce cholesterol levels by forcing the body t ...
Human body
... (windpipe) into the bronchi and bronchioles, and ends in little air pockets called alveoli within the lungs. The used blood is cleansed of carbon dioxide, which is expelled in the process known as expiration. The cleansed blood is then oxygenated and redistributed along the circulatory system. The e ...
... (windpipe) into the bronchi and bronchioles, and ends in little air pockets called alveoli within the lungs. The used blood is cleansed of carbon dioxide, which is expelled in the process known as expiration. The cleansed blood is then oxygenated and redistributed along the circulatory system. The e ...
Respiratory Anatomy - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Nasal/oral cavity -> pharynx -> epiglottis -> larynx -> trachea -> bronchi -> bronchioles -> alveoli The pharynx also opens into the esophagus where food travels to the stomach. When food is chewed, it is forced to the top of the mouth, and pushed backwards. This forces the epiglottis to close, al ...
... Nasal/oral cavity -> pharynx -> epiglottis -> larynx -> trachea -> bronchi -> bronchioles -> alveoli The pharynx also opens into the esophagus where food travels to the stomach. When food is chewed, it is forced to the top of the mouth, and pushed backwards. This forces the epiglottis to close, al ...
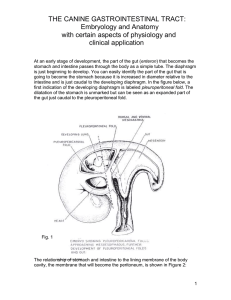
caninegastrointesttract
... dilatation of the stomach is unmarked but can be seen as an expanded part of the gut just caudal to the pleuroperitoneal fold. ...
... dilatation of the stomach is unmarked but can be seen as an expanded part of the gut just caudal to the pleuroperitoneal fold. ...
TCM Spleen
... – food into Qi and Blood – keeps Blood in vessels to prevent bruising – gives ability to build and nourish muscles – to keep us supple and adaptable – to make us think when we should – direct us to food/experiences that nourish – sends Pure essence of Food up to Lungs – controls suspensory ligaments ...
... – food into Qi and Blood – keeps Blood in vessels to prevent bruising – gives ability to build and nourish muscles – to keep us supple and adaptable – to make us think when we should – direct us to food/experiences that nourish – sends Pure essence of Food up to Lungs – controls suspensory ligaments ...
4. DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION OF LIPIDS
... • Foods are enzymatically digested to prepare them for absorption. • During digestion in the gastrointestinal tract of mammals, the three major nutrients (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) undergo enzymatic hydrolysis into their building block components. • This is necessary for their absorption, ...
... • Foods are enzymatically digested to prepare them for absorption. • During digestion in the gastrointestinal tract of mammals, the three major nutrients (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) undergo enzymatic hydrolysis into their building block components. • This is necessary for their absorption, ...
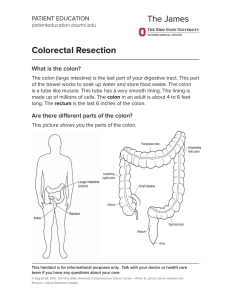
Colorectal Resection - OSU Patient Education Materials
... The colon (large intestine) is the last part of your digestive tract. This part of the bowel works to soak up water and store food waste. The colon is a tube like muscle. This tube has a very smooth lining. The lining is made up of millions of cells. The colon in an adult is about 4 to 6 feet long. ...
... The colon (large intestine) is the last part of your digestive tract. This part of the bowel works to soak up water and store food waste. The colon is a tube like muscle. This tube has a very smooth lining. The lining is made up of millions of cells. The colon in an adult is about 4 to 6 feet long. ...
Suprarenal Glands
... the neural crest. • These cells invade the cortex on its medial side, occupy the central position and differentiate into the secretory cells. • Preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers grow into the medulla, release Epinephrine and Norepinephrine upon sympathetic stimulation, and influence the activit ...
... the neural crest. • These cells invade the cortex on its medial side, occupy the central position and differentiate into the secretory cells. • Preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers grow into the medulla, release Epinephrine and Norepinephrine upon sympathetic stimulation, and influence the activit ...
File - Mrs. Rosewitz
... 10. What are the upper chambers of the heart called? What are the lower chambers of the heart called? (1 pt) 11. How many chambers are there in a rat’s heart? (1 pt) ...
... 10. What are the upper chambers of the heart called? What are the lower chambers of the heart called? (1 pt) 11. How many chambers are there in a rat’s heart? (1 pt) ...
Three-Field Lymphadenectomy for Esophageal Cancer
... towards the neck and upper mediastinum, although there is also some drainage to the nodes along the left gastric artery. In 1981, the first reported study of three-field lymphadenectomy in Japan noted that 10 of 36 patients with esophagectomy had skip metastases to the neck or abdominal lymph nodes in ...
... towards the neck and upper mediastinum, although there is also some drainage to the nodes along the left gastric artery. In 1981, the first reported study of three-field lymphadenectomy in Japan noted that 10 of 36 patients with esophagectomy had skip metastases to the neck or abdominal lymph nodes in ...
Ch.24Pt.4_000
... Typical body fuel reserves are: fat: 100,000 kcal. protein: 25,000 kcal. carbohydrate: 650 kcal. Provides 60% of energy needs for body at rest TAG reserves would enable someone to survive starvation for ~30 days ...
... Typical body fuel reserves are: fat: 100,000 kcal. protein: 25,000 kcal. carbohydrate: 650 kcal. Provides 60% of energy needs for body at rest TAG reserves would enable someone to survive starvation for ~30 days ...
ORAL CAVITY The oral cavity (O.C) and its accessory organs
... ducts connect the oral cavity and the nasal cavity. The duct opens on the incisive papillae. The mucus membrane of the O.C. is usually pink but may be pigmented (black) in some places. It is well supplied with blood vessels and in its sub mucosa it contains serous or mucous gland know as the labial, ...
... ducts connect the oral cavity and the nasal cavity. The duct opens on the incisive papillae. The mucus membrane of the O.C. is usually pink but may be pigmented (black) in some places. It is well supplied with blood vessels and in its sub mucosa it contains serous or mucous gland know as the labial, ...
ORAL CAVITY, TONGUE & PALATE
... The tonge is the most important articulator for speech production. During speech, the tongue can make amazing range of movements The primary function of the tongue is to provide a mechanism for taste. Taste buds are located on different areas of the tongue, but are generally found around the edges. ...
... The tonge is the most important articulator for speech production. During speech, the tongue can make amazing range of movements The primary function of the tongue is to provide a mechanism for taste. Taste buds are located on different areas of the tongue, but are generally found around the edges. ...
ORAL CAVITY
... The muscular diaphragm separates the upper from the lower ventrali:>ody cavity. The upper is the thoracic, the lower is the abdominal cavity. We shall study the abdominal area first and later consider the thorax in relation to the study of the heart and circulatory system. With your fingertips locat ...
... The muscular diaphragm separates the upper from the lower ventrali:>ody cavity. The upper is the thoracic, the lower is the abdominal cavity. We shall study the abdominal area first and later consider the thorax in relation to the study of the heart and circulatory system. With your fingertips locat ...
GENERAL SPLANCHNOLOGY
... Some systems, for instance, the bony system is a set of bones with common structure, functions, and development. There are organs and systems of organs that differ in structure and development but they are united for the performance of a common function. Such functional collection of heterogeneous o ...
... Some systems, for instance, the bony system is a set of bones with common structure, functions, and development. There are organs and systems of organs that differ in structure and development but they are united for the performance of a common function. Such functional collection of heterogeneous o ...
1 - BrainMass
... deuterostomes in which the coelom forms. The stage starts with the gastrula; as the archenteron forms, pockets of migrating cells also form, creating another layer between the endoderm and ectoderm, the mesoderm. These pockets gradually expand to form the coelom. Enterocelous development is advance ...
... deuterostomes in which the coelom forms. The stage starts with the gastrula; as the archenteron forms, pockets of migrating cells also form, creating another layer between the endoderm and ectoderm, the mesoderm. These pockets gradually expand to form the coelom. Enterocelous development is advance ...
BIO 104 - Jefferson State Community College
... Internal anatomy: heart, right atrium, left atrium, ventrical, lungs, mouth, tongue, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, urinary bladder, mesentery, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, ovary, kidney, oviduct, fat body, and colon. List 2 characteristics by which amphibians and reptiles may ...
... Internal anatomy: heart, right atrium, left atrium, ventrical, lungs, mouth, tongue, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, urinary bladder, mesentery, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, ovary, kidney, oviduct, fat body, and colon. List 2 characteristics by which amphibians and reptiles may ...
529773.FEBS_abstract__Ana_Savic
... investigated by quantitative real-time PCR (TaqMan). The outcome of the first treatment course was studied in one patient after 3 months. Results: There is regional variation of ABC transporters in gastrointestinal tract, but in general localization did not differ between IBD patients and controls. ...
... investigated by quantitative real-time PCR (TaqMan). The outcome of the first treatment course was studied in one patient after 3 months. Results: There is regional variation of ABC transporters in gastrointestinal tract, but in general localization did not differ between IBD patients and controls. ...
PARTS OF THE PHARYNX THE PHARYNX Skeleton THE
... Reflex is triggered when the bolus touches the oropharynx (CN IX) The longitudinal muscles contract Raising the larynx (helping to fold the epiglottis and seal off the airway) Pulling the pharynx up over the bolus Then circular/constrictor muscles contract and the longitudinal ones relax Carrying th ...
... Reflex is triggered when the bolus touches the oropharynx (CN IX) The longitudinal muscles contract Raising the larynx (helping to fold the epiglottis and seal off the airway) Pulling the pharynx up over the bolus Then circular/constrictor muscles contract and the longitudinal ones relax Carrying th ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.