Terminology
... The rectum is the lowest portion of the large intestine, terminating at the anus. Rib In anatomy, the ribs are elastic arches of bone which are connected behind with the vertebral column and form a large part of the skeleton of the thorax. Saliva Saliva is a secretion from the salivary glands in the ...
... The rectum is the lowest portion of the large intestine, terminating at the anus. Rib In anatomy, the ribs are elastic arches of bone which are connected behind with the vertebral column and form a large part of the skeleton of the thorax. Saliva Saliva is a secretion from the salivary glands in the ...
SALIVARY GLANDS
... • It is the most superficial structure. • It enters the gland through its posteromedial surface. • It breaks within the gland into terminal branches that leave it through; upper end, lower end and anteromedial surface. • These terminal branches are 5; Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular ...
... • It is the most superficial structure. • It enters the gland through its posteromedial surface. • It breaks within the gland into terminal branches that leave it through; upper end, lower end and anteromedial surface. • These terminal branches are 5; Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular ...
Mollusca - Net Start Class
... the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
... the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
Legend Ectoderm – covering cells, sensory and nerve cells, cells
... as is the pharnx). All have parapodia –muscular extensions of the body wall, serve to aid swimming and as a primitive gill. This requires circulation into the parapodia. Benthic types have secondary radial symmetry due to the expansion of a circular array of feathery arms extending out from near the ...
... as is the pharnx). All have parapodia –muscular extensions of the body wall, serve to aid swimming and as a primitive gill. This requires circulation into the parapodia. Benthic types have secondary radial symmetry due to the expansion of a circular array of feathery arms extending out from near the ...
Anatomical Language - Mrs. Reid's Webpage
... separated from the abdominal cavity by diaphragm • Pleural (right and left) – each contains small amount of fluid and one lung • Pericardial – fluid filled space the surrounds heart • Mediastinum – medial to the lungs; extends from the sternum to the vertebral column and from the neck to the diaphra ...
... separated from the abdominal cavity by diaphragm • Pleural (right and left) – each contains small amount of fluid and one lung • Pericardial – fluid filled space the surrounds heart • Mediastinum – medial to the lungs; extends from the sternum to the vertebral column and from the neck to the diaphra ...
Organs of the Respiratory System
... ▫ Carbon dioxide diffuses from blood through walls and enters alveoli ▫ Adult lung: about 300 million alveoli, total surface area half the size of a tennis court ...
... ▫ Carbon dioxide diffuses from blood through walls and enters alveoli ▫ Adult lung: about 300 million alveoli, total surface area half the size of a tennis court ...
Oral clinical examination
... Palatine rugae: just behind the incisive papilla Palatine raphe: whitish band of tissue in the midline of the palate from the incisive papilla to the uvula Vibrating line or ahh line: the junction of the hard and soft palate Foveae palatinae: just anterior the vibrating line, on either side ...
... Palatine rugae: just behind the incisive papilla Palatine raphe: whitish band of tissue in the midline of the palate from the incisive papilla to the uvula Vibrating line or ahh line: the junction of the hard and soft palate Foveae palatinae: just anterior the vibrating line, on either side ...
Signs and Symptoms of the Hepatobiliary Tract and Pancreas
... – The liver is one of the largest organs in the human body and has many functions including: processing food and changing it into energy; breaking down toxic substances in the body and their excretion; storing iron reserves, as well as vitamins and minerals; creating bile, which aids in digestion, g ...
... – The liver is one of the largest organs in the human body and has many functions including: processing food and changing it into energy; breaking down toxic substances in the body and their excretion; storing iron reserves, as well as vitamins and minerals; creating bile, which aids in digestion, g ...
Chapter 03
... The scarcity of pre-Cambrian fossils led systematists to search for clues about the evolutionary history of animals by examining features of • Anatomy • Embryological development • DNA sequences ...
... The scarcity of pre-Cambrian fossils led systematists to search for clues about the evolutionary history of animals by examining features of • Anatomy • Embryological development • DNA sequences ...
WHY - rcastilho.pt
... divisions, the embryo is a zygote shortly before the first between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just completed the second surrounded by the fertilization by the fertilization envelope. cleavage division. envelope. The blastocoel cavity The nu ...
... divisions, the embryo is a zygote shortly before the first between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just completed the second surrounded by the fertilization by the fertilization envelope. cleavage division. envelope. The blastocoel cavity The nu ...
anatomy_lec18_19_4_2011
... 1-intrensic muscles: which alter the shape of the tongue while inside the oral cavity….for example flattening the tongue. 2-extrensic muscles:come from outside of the oral cavity…..which move the tongue: a-genioglossus:originates from superior mental spine which forms most of the body of the tongue. ...
... 1-intrensic muscles: which alter the shape of the tongue while inside the oral cavity….for example flattening the tongue. 2-extrensic muscles:come from outside of the oral cavity…..which move the tongue: a-genioglossus:originates from superior mental spine which forms most of the body of the tongue. ...
Clinical Notes of Head & Neck
... At the junction of the mouth with the oral part of the pharynx, and the nose with the nasal part of the pharynx, are collections of lymphoid tissue of considerable clinical importance The palatine tonsils and the nasopharyngeal tonsils are the most important ...
... At the junction of the mouth with the oral part of the pharynx, and the nose with the nasal part of the pharynx, are collections of lymphoid tissue of considerable clinical importance The palatine tonsils and the nasopharyngeal tonsils are the most important ...
shark dissection - Uplift Luna / Overview
... The heart is located in the head region of the shark, just above and to the inside of the pectoral girdle. The heart is almost totally incased in the cartilaginous pectoral girdle and the muscles that surround it. The heart lies in its cavity called the pericardial cavity. To reach the pericardial c ...
... The heart is located in the head region of the shark, just above and to the inside of the pectoral girdle. The heart is almost totally incased in the cartilaginous pectoral girdle and the muscles that surround it. The heart lies in its cavity called the pericardial cavity. To reach the pericardial c ...
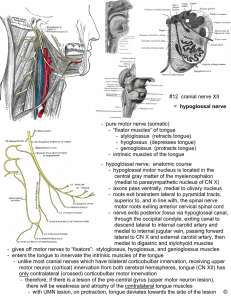
- pure motor nerve (somatic) - “fixator muscles” of tongue
... - roots exit brainstem lateral to pyramidal tracts, superior to, and in line with, the spinal nerve motor roots exiting anterior cervical spinal cord - nerve exits posterior fossa via hypoglossal canal, through the occipital condyle, exiting canal to descend lateral to internal carotid artery and me ...
... - roots exit brainstem lateral to pyramidal tracts, superior to, and in line with, the spinal nerve motor roots exiting anterior cervical spinal cord - nerve exits posterior fossa via hypoglossal canal, through the occipital condyle, exiting canal to descend lateral to internal carotid artery and me ...
Chapter 17
... The fossil record of the vertebrates is relatively well documented because they were so common. they lived in shallow water, where fossils often are found. there were few scavengers at that time to disrupt the skeletons. they had hard body parts. All of the choices are correct. ...
... The fossil record of the vertebrates is relatively well documented because they were so common. they lived in shallow water, where fossils often are found. there were few scavengers at that time to disrupt the skeletons. they had hard body parts. All of the choices are correct. ...
Ch 13 Structures of the Respiratory System
... Gas exchange occurs between: blood & external environment Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs ...
... Gas exchange occurs between: blood & external environment Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs ...
Oral Cavity
... ultimately come from spinal cord level T1, synapse in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion, and are eventually distributed to the oral cavity along branches of the trigeminal nerve [V] or directly along blood vessels. ...
... ultimately come from spinal cord level T1, synapse in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion, and are eventually distributed to the oral cavity along branches of the trigeminal nerve [V] or directly along blood vessels. ...
PERITONEUM and TORSION of GUT TUBE
... Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
... Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
PERITONEUM and TORSION of GUT TUBE
... Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
... Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
Mollusks
... • HEMOLYMPH (blood in an organism with open circulation) does not remain in vessels 1. Collected from gills or lungs 2. Pumped through heart 3. Released directly into spaces in the tissues a) Fluid filled spaces or blood cavity ...
... • HEMOLYMPH (blood in an organism with open circulation) does not remain in vessels 1. Collected from gills or lungs 2. Pumped through heart 3. Released directly into spaces in the tissues a) Fluid filled spaces or blood cavity ...
Worms
... The nervous system in an earthworm consists of a ventral nerve cord and two cerebral __________________ GANGLIA ...
... The nervous system in an earthworm consists of a ventral nerve cord and two cerebral __________________ GANGLIA ...
Cholecystitis - RadiologyInfo.org
... Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, the pear-shaped organ beneath the liver that serves as a storage reservoir for bile. When the gallbladder is inflamed, patients experience pain in the upper right or mid-portion of the abdomen. A normal functioning gallbladder stores bile (which is m ...
... Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, the pear-shaped organ beneath the liver that serves as a storage reservoir for bile. When the gallbladder is inflamed, patients experience pain in the upper right or mid-portion of the abdomen. A normal functioning gallbladder stores bile (which is m ...
Cholecystitis - RadiologyInfo.org
... Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, the pear-shaped organ beneath the liver that serves as a storage reservoir for bile. When the gallbladder is inflamed, patients experience pain in the upper right or mid-portion of the abdomen. A normal functioning gallbladder stores bile (which is m ...
... Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, the pear-shaped organ beneath the liver that serves as a storage reservoir for bile. When the gallbladder is inflamed, patients experience pain in the upper right or mid-portion of the abdomen. A normal functioning gallbladder stores bile (which is m ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.