nasal cavity
... region behind nasal cavity Oropharynx – Middle region behind mouth Laryngopharynx – Inferior region attached to larynx The oropharynx and laryngopharynx are common passageways for air and food Air then passes through the larynx, while food is directed into the esophagus posteriorly ...
... region behind nasal cavity Oropharynx – Middle region behind mouth Laryngopharynx – Inferior region attached to larynx The oropharynx and laryngopharynx are common passageways for air and food Air then passes through the larynx, while food is directed into the esophagus posteriorly ...
Steps to drawing Epithelial Histology diagrams. 1. Go to http://bit.ly
... instance, your stomach produces mucous which keeps the acid inside the stomach from affecting the lining or epithelium of the stomach. The average human body produces 1 liter of mucus per day. (Source: Wikipedia). ...
... instance, your stomach produces mucous which keeps the acid inside the stomach from affecting the lining or epithelium of the stomach. The average human body produces 1 liter of mucus per day. (Source: Wikipedia). ...
Measurement of Enzymes and Their Clinical Significance
... Measurement of Enzyme Activity • Often measured by catalytic activity then related to concentration • Enzyme concentration is best measured by its activity or its rate of activity by observing: ...
... Measurement of Enzyme Activity • Often measured by catalytic activity then related to concentration • Enzyme concentration is best measured by its activity or its rate of activity by observing: ...
VISCERAL X-RAYS – QUESTIONS
... B. epiglottis C. oropharynx D. laryngopharynx E. trachea (lumen) F. It’s a collapsed muscular tube, and thus poorly distinguishable from surrounding tissue. V-2 – Lower GI series A. cecum B. vermiform appendix C. ileum D. ascending colon E. hepatic (R. colic) flexure F. transverse colon G. splenic ( ...
... B. epiglottis C. oropharynx D. laryngopharynx E. trachea (lumen) F. It’s a collapsed muscular tube, and thus poorly distinguishable from surrounding tissue. V-2 – Lower GI series A. cecum B. vermiform appendix C. ileum D. ascending colon E. hepatic (R. colic) flexure F. transverse colon G. splenic ( ...
rat dissection guide
... Liver - is the large brown organ taking up most of the anterior portion of the cavity. I consists of four lobes. Its function is to manufacture bile, selectively remove and reintroduce nutrients into the blood, remove toxins, and manufacture needed proteins and carbohydrates. Gall Bladder - the rat ...
... Liver - is the large brown organ taking up most of the anterior portion of the cavity. I consists of four lobes. Its function is to manufacture bile, selectively remove and reintroduce nutrients into the blood, remove toxins, and manufacture needed proteins and carbohydrates. Gall Bladder - the rat ...
Anatomy/Physiology Syllabus Mrs. Tuggle Course Objectives To
... A chapter/body system is covered every two weeks. One or more labs will be conducted during that time and there are daily homework assignments. A multiple choice/ short answer test or a lab practical is given for each chapter/body system covered. School Grade Scale A 100-90 B 89-80 C 79-70 D 69-60 F ...
... A chapter/body system is covered every two weeks. One or more labs will be conducted during that time and there are daily homework assignments. A multiple choice/ short answer test or a lab practical is given for each chapter/body system covered. School Grade Scale A 100-90 B 89-80 C 79-70 D 69-60 F ...
ABDOMINAL CAVITY AND VISCERA
... vermiform appendix ascending colon transverse colon (cranial 2/3) Function: The gut as a whole (including the large intestine) has four primary functions: i) transportation by peristalsis, a muscular activity causing movement of food; ii) rhythmic contractions of the gut musculature for physical tre ...
... vermiform appendix ascending colon transverse colon (cranial 2/3) Function: The gut as a whole (including the large intestine) has four primary functions: i) transportation by peristalsis, a muscular activity causing movement of food; ii) rhythmic contractions of the gut musculature for physical tre ...
Special Senses - El Camino College
... 3. Vapors must ------------ before can stimulate olfactory cells. 4. --------- stimulate sour tasting = gustatory cells. 5. ----------stimulate salt tasting gustatory cells. 6. Facial nerve collects sensory information about taste from --- of tongue and glossopharyngeal nerve collects sensory input ...
... 3. Vapors must ------------ before can stimulate olfactory cells. 4. --------- stimulate sour tasting = gustatory cells. 5. ----------stimulate salt tasting gustatory cells. 6. Facial nerve collects sensory information about taste from --- of tongue and glossopharyngeal nerve collects sensory input ...
what breeders need to know about megaesophagus
... first among reported gastrointestinal disorders, with an 81 percent mortality rate. This disorder occurs in many lines, and though the mode of inheritance is not clearly understood, it is likely a genetic defect. While megaesophagus can occur in adult dogs secondary to diseases such as myasthenia gr ...
... first among reported gastrointestinal disorders, with an 81 percent mortality rate. This disorder occurs in many lines, and though the mode of inheritance is not clearly understood, it is likely a genetic defect. While megaesophagus can occur in adult dogs secondary to diseases such as myasthenia gr ...
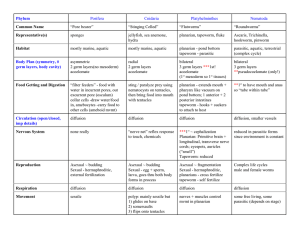
Phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Common
... bilateral 3 germ layers coelomate (**1st true coelom) ...
... bilateral 3 germ layers coelomate (**1st true coelom) ...
SESSION 5 - Oral Cavity - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 20. Why do we say that the vallate papillae, lying anterior to the sulcus terminalis, really belong to the posterior third of the tongue? ...
... 20. Why do we say that the vallate papillae, lying anterior to the sulcus terminalis, really belong to the posterior third of the tongue? ...
SESSION 5 - Oral Cavity - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 20. Why do we say that the vallate papillae, lying anterior to the sulcus terminalis, really belong to the posterior third of the tongue? ...
... 20. Why do we say that the vallate papillae, lying anterior to the sulcus terminalis, really belong to the posterior third of the tongue? ...
Endocrine System
... The thyroid glands and parathyroid gland are located together in the neck. The thyroid glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and calcium levels. The parathyroid gland also secretes hormones that regulate calcium levels. The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that ...
... The thyroid glands and parathyroid gland are located together in the neck. The thyroid glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and calcium levels. The parathyroid gland also secretes hormones that regulate calcium levels. The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that ...
Lecture No. 8
... • They are free aminoacids in Brassicaceae family plants • It is S-methylcysteinsulfoxide (SMCO) and its precursor Smethylcystein (necessary for cystein and methionin synthesis) • High concentration of SMCO is in young tissues and represents a storage reservoir of sulphur in an organism. Its product ...
... • They are free aminoacids in Brassicaceae family plants • It is S-methylcysteinsulfoxide (SMCO) and its precursor Smethylcystein (necessary for cystein and methionin synthesis) • High concentration of SMCO is in young tissues and represents a storage reservoir of sulphur in an organism. Its product ...
Greater omentum
... kidney, suprarenal gland, pancreas, descending and ascending colon, upper 3rd of rectum duodenum, and ureter, aorta and I.V.C Since the Aorta is retroperitoneal, if we have a ruptured aorta the bleeding will be outside the peritoneal cavity in the back, so the patient will have pain in his back. ...
... kidney, suprarenal gland, pancreas, descending and ascending colon, upper 3rd of rectum duodenum, and ureter, aorta and I.V.C Since the Aorta is retroperitoneal, if we have a ruptured aorta the bleeding will be outside the peritoneal cavity in the back, so the patient will have pain in his back. ...
Human Anatomy - Perry Local Schools
... Science Course of Study Course Description Human Anatomy is designed to provide a solid base for students intending to pursue a career in a diversified health field and/or the field of cosmetology. It is a study into the structures and systems of the human body. The eleven systems of the body are ex ...
... Science Course of Study Course Description Human Anatomy is designed to provide a solid base for students intending to pursue a career in a diversified health field and/or the field of cosmetology. It is a study into the structures and systems of the human body. The eleven systems of the body are ex ...
1050. All of the following increase gastric secretion
... Encephalopathy is associated with liver failure and increased nitrogenous products being absorbed into the circulation. There is no relationship between pancreatic ascites and encephalopathy. d. Painless abdominal enlargement Pancreatic ascites is almost always associated with a disruption of the pa ...
... Encephalopathy is associated with liver failure and increased nitrogenous products being absorbed into the circulation. There is no relationship between pancreatic ascites and encephalopathy. d. Painless abdominal enlargement Pancreatic ascites is almost always associated with a disruption of the pa ...
glycocholic acid
... 8. Surrounding smooth muscle start to secrete a range of small peptides, which stimulate smooth muscle cells to proliferate and to migrate toward the lumen side of the arterial wall. 9. In the same time, smooth muscle cells start synthesizing extracellular matrix, such as collagen. 10. Relocated sm ...
... 8. Surrounding smooth muscle start to secrete a range of small peptides, which stimulate smooth muscle cells to proliferate and to migrate toward the lumen side of the arterial wall. 9. In the same time, smooth muscle cells start synthesizing extracellular matrix, such as collagen. 10. Relocated sm ...
Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS
... Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve Ventral ramus of spinal nerve Gray ramus communicans White ramus communicans To effector ...
... Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve Ventral ramus of spinal nerve Gray ramus communicans White ramus communicans To effector ...
Pig Dissection
... • Using your scapel – separate the skin of the chest area off of the rib cage. – You will have to cut through muscle and connective tissue to do this – It’s like skinning raw chicken! ...
... • Using your scapel – separate the skin of the chest area off of the rib cage. – You will have to cut through muscle and connective tissue to do this – It’s like skinning raw chicken! ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.