Untitled - Dommelroute
... of growing from the size of a large pinhead to a mountain may have taken one hundred thousand years or so. Then the process began to slow down. The original dust and gas had been used up, and the cloud thinned. Several stars—such as Beta Pictoris—have been observed with large, thin disks of dust sur ...
... of growing from the size of a large pinhead to a mountain may have taken one hundred thousand years or so. Then the process began to slow down. The original dust and gas had been used up, and the cloud thinned. Several stars—such as Beta Pictoris—have been observed with large, thin disks of dust sur ...
Teacher notes and student sheets
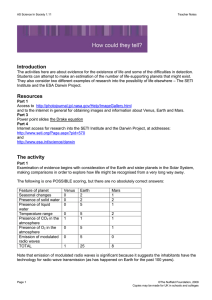
... presence of life. However, while oxygen on other planets might be consistent with the presence of life based on photosynthesis there may be other unknown causes. This means that the level of confidence in supposing that life is the ‘cause’ of the oxygen is reduced. Part 2 There is then some work on ...
... presence of life. However, while oxygen on other planets might be consistent with the presence of life based on photosynthesis there may be other unknown causes. This means that the level of confidence in supposing that life is the ‘cause’ of the oxygen is reduced. Part 2 There is then some work on ...
UCSD Students` Presentation on Star Formation
... Stages 6 and 7—A Newborn Star -After 10 million years, the protostar evolves into a true star. -Stage 6 = The radius of the star will be larger than an avg. sun, but b/c it has a lower surface temperature which means that its luminosity is only about 2/3 of its actual solar value. -What occurs in S ...
... Stages 6 and 7—A Newborn Star -After 10 million years, the protostar evolves into a true star. -Stage 6 = The radius of the star will be larger than an avg. sun, but b/c it has a lower surface temperature which means that its luminosity is only about 2/3 of its actual solar value. -What occurs in S ...
Stellar Evolution
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
Reminder: Assignments are due back to teachers within 2 school days.
... very dense plasma forms. If the initial star had mass of less than 1.4 solar masses (1.4 times the mass of our sun), the process ceases at the density of 1,000 tons per cubic inch, and the star becomes the white dwarf. However, if the star was originally more massive, the white dwarf plasma can’t re ...
... very dense plasma forms. If the initial star had mass of less than 1.4 solar masses (1.4 times the mass of our sun), the process ceases at the density of 1,000 tons per cubic inch, and the star becomes the white dwarf. However, if the star was originally more massive, the white dwarf plasma can’t re ...
talk - University of Southampton
... IV. Discussion We have shown how BZ-mechanism could drive GRB explosions. However, this requires both fast rotation and strong magnetic field of stellar cores of GRB progenitors. This is problematic for solitary stars: • Evolutionary models of solitary massive stars show that even much weaker magne ...
... IV. Discussion We have shown how BZ-mechanism could drive GRB explosions. However, this requires both fast rotation and strong magnetic field of stellar cores of GRB progenitors. This is problematic for solitary stars: • Evolutionary models of solitary massive stars show that even much weaker magne ...
Document
... have the mass of more than 1 Million Suns put together. Stellar Black Holes are formed when the center of a very large star collapses and forms a supernova. The Earth will never be destroyed by a Black Hole. 1. www.nasa.gov 2. www.desura.com ...
... have the mass of more than 1 Million Suns put together. Stellar Black Holes are formed when the center of a very large star collapses and forms a supernova. The Earth will never be destroyed by a Black Hole. 1. www.nasa.gov 2. www.desura.com ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... Plenary: What is the correct order for these sentences about how a star is formed? This causes the ‘nebula’ to collapse. ...
... Plenary: What is the correct order for these sentences about how a star is formed? This causes the ‘nebula’ to collapse. ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... • Hubble found globulars in Andromeda; they were roughly spherically distributed, and centered on the center of the galaxy. • In our own sky, we’d known for over a hundred years that globulars are strongly concentrated in the summer sky; hardly any in the winter sky. Ergo We must be far from the ce ...
... • Hubble found globulars in Andromeda; they were roughly spherically distributed, and centered on the center of the galaxy. • In our own sky, we’d known for over a hundred years that globulars are strongly concentrated in the summer sky; hardly any in the winter sky. Ergo We must be far from the ce ...
Intelligent life in the Universe
... Ps = percentage of stars that can have planets (~20% late type only) Pp = percentage of star that actually have planets (~80%) Ph = percentage of stars with habitable zones (~10%) Pg = percentage of planets with stable circular orbits PI = percentage of planets where life has evolved Pe = percentage ...
... Ps = percentage of stars that can have planets (~20% late type only) Pp = percentage of star that actually have planets (~80%) Ph = percentage of stars with habitable zones (~10%) Pg = percentage of planets with stable circular orbits PI = percentage of planets where life has evolved Pe = percentage ...
Scientists classify stars by
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
The phenomena of astrophysical masers are not new by any means
... The discovery of naturally occurring masers has created new opportunities for exploring the universe. They provide the ability to see into the center of some galaxies obscured by dust and gas. The discovery of water masers in galaxies billions of light years away showed that water molecules existed ...
... The discovery of naturally occurring masers has created new opportunities for exploring the universe. They provide the ability to see into the center of some galaxies obscured by dust and gas. The discovery of water masers in galaxies billions of light years away showed that water molecules existed ...
Powerpoint
... when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force (remember, stars are ~1020 x denser than a molecular cloud). As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense ...
... when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force (remember, stars are ~1020 x denser than a molecular cloud). As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense ...