Lesson Overviews and Content Standards
... begin with a discussion of why Uranus, Neptune, and all of the dwarf planets in our own solar system weren’t discovered until after the invention of telescopes. Turning to the search for extrasolar planets, students will draw upon knowledge from the previous lessons, and some new demonstrations, as ...
... begin with a discussion of why Uranus, Neptune, and all of the dwarf planets in our own solar system weren’t discovered until after the invention of telescopes. Turning to the search for extrasolar planets, students will draw upon knowledge from the previous lessons, and some new demonstrations, as ...
A Binary Mass-Orbit Nomenclature for Planetary Bodies
... These general ideas have led to problems as astronomy progressed. The largest satellite of a giant planet can easily match for size the smallest independently orbiting planet in the system; in our own Solar System, Ganymede and Titan are both larger than Mercury, though in terms of mass the planet i ...
... These general ideas have led to problems as astronomy progressed. The largest satellite of a giant planet can easily match for size the smallest independently orbiting planet in the system; in our own Solar System, Ganymede and Titan are both larger than Mercury, though in terms of mass the planet i ...
PDF format
... • The nebular theory predicts that massive Jupiterlike planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. ...
... • The nebular theory predicts that massive Jupiterlike planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. ...
Constraining the formation of the Milky Way: Ages
... with a last significant merger concluding ∼9 − 8 Gyr ago; (v) the disc gas-to-total mass ratio at the final time is ∼0.12, consistent with the estimate of ∼0.14 for the solar vicinity, and (vi) the radial and vertical velocity dispersions at r ≈ 8 kpc are ∼40 and ∼20 km/s, in good agreement with obs ...
... with a last significant merger concluding ∼9 − 8 Gyr ago; (v) the disc gas-to-total mass ratio at the final time is ∼0.12, consistent with the estimate of ∼0.14 for the solar vicinity, and (vi) the radial and vertical velocity dispersions at r ≈ 8 kpc are ∼40 and ∼20 km/s, in good agreement with obs ...
habitability - Dr. Jonti Horner
... for detection. As a main sequence star ages, its luminosity gradually increases. Indeed, our Sun is currently thought to be some 30 % more luminous than it was when it first joined the main sequence. All other things being equal, this means that the region around that star in which water could be liq ...
... for detection. As a main sequence star ages, its luminosity gradually increases. Indeed, our Sun is currently thought to be some 30 % more luminous than it was when it first joined the main sequence. All other things being equal, this means that the region around that star in which water could be liq ...
The Milky Way
... • Theoretical H-R diagrams have the higher mass stars reaching ZAMS first; It takes 107 years before 2-3 M stars reach ZAMS; • meanwhile highest mass stars have left MS to become SN • by 108 years many high mass stars have become RGs and SGs, but lowest mass stars still not on ZAMS. • By 109 yr all ...
... • Theoretical H-R diagrams have the higher mass stars reaching ZAMS first; It takes 107 years before 2-3 M stars reach ZAMS; • meanwhile highest mass stars have left MS to become SN • by 108 years many high mass stars have become RGs and SGs, but lowest mass stars still not on ZAMS. • By 109 yr all ...
Stellar-mass Black Hole Formation
... Masses greater than the maximum NS mass: 1.5-2.5 Msun (from detailed EOS calculations); 3.2 Msun (upper limit from causality; Lattimer & Prakash ) ~109 SMBHs in the Galaxy, from stellar popn modeling (Brown & Bethe 1994) 20 confirmed black holes in X-ray binaries, with secure masses (as of 2006) mas ...
... Masses greater than the maximum NS mass: 1.5-2.5 Msun (from detailed EOS calculations); 3.2 Msun (upper limit from causality; Lattimer & Prakash ) ~109 SMBHs in the Galaxy, from stellar popn modeling (Brown & Bethe 1994) 20 confirmed black holes in X-ray binaries, with secure masses (as of 2006) mas ...
Project Icarus: Astronomical Considerations Relating to the Choice
... Within 15 light-years of the Sun there are approximately 56 stars, in 38 separate stellar systems. The number is approximate for several reasons. Firstly, at the outer boundary the errors on the distances can amount to a few tenths of a light-year, which could mean that some stars notionally just be ...
... Within 15 light-years of the Sun there are approximately 56 stars, in 38 separate stellar systems. The number is approximate for several reasons. Firstly, at the outer boundary the errors on the distances can amount to a few tenths of a light-year, which could mean that some stars notionally just be ...
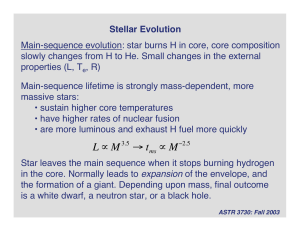
Stellar Evolution
... • “White dwarf” cools but does not contract because core is degenerate • No energy from fusion, no energy from gravitational contraction • White dwarf slowly fades away… ...
... • “White dwarf” cools but does not contract because core is degenerate • No energy from fusion, no energy from gravitational contraction • White dwarf slowly fades away… ...
$doc.title
... thick structures around solar-type stars equals ∼3 to 10 Myr. The shorter of the two times applies to β Pic as an intermediate-mass star (Strom et al 1993). After that time, photoevaporation and other processes are believed to remove the bulk of gas and fine dust. ...
... thick structures around solar-type stars equals ∼3 to 10 Myr. The shorter of the two times applies to β Pic as an intermediate-mass star (Strom et al 1993). After that time, photoevaporation and other processes are believed to remove the bulk of gas and fine dust. ...
Dynamical relaxation and the orbits of low
... protostellar envelope on a scale of 100 au. Such a system then underwent dynamical relaxation on a time-scale of hundreds of orbits which resulted in ejection of most of the objects. It was found that the characteristics of massive eccentric extrasolar planets and the massive ‘hot Jupiter’ observed ...
... protostellar envelope on a scale of 100 au. Such a system then underwent dynamical relaxation on a time-scale of hundreds of orbits which resulted in ejection of most of the objects. It was found that the characteristics of massive eccentric extrasolar planets and the massive ‘hot Jupiter’ observed ...
CHAPTER 8 Survey of Solar Systems
... the same direction as the planets’ orbital motion around the Sun (again, counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s North Pole), and the tilt of the rotation axes relative to the plane of planetary orbits is generally not far from the perpendicular. However, there are two exceptions: Venus and ...
... the same direction as the planets’ orbital motion around the Sun (again, counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s North Pole), and the tilt of the rotation axes relative to the plane of planetary orbits is generally not far from the perpendicular. However, there are two exceptions: Venus and ...
Chapter 20: Stellar Evolution: The Death of Stars PowerPoint
... Helix Nebula: 140 pc From Earth ...
... Helix Nebula: 140 pc From Earth ...
Document
... Synchrotron radiation of magnetized plasma, which is heated during accretion up to 1012 K (here the temperature means the average energy of electrons motion perpendicular to magnetic field lines). (Development of this approach see in astro-ph/0403649) ...
... Synchrotron radiation of magnetized plasma, which is heated during accretion up to 1012 K (here the temperature means the average energy of electrons motion perpendicular to magnetic field lines). (Development of this approach see in astro-ph/0403649) ...
Disk Galaxies and problem 3
... increases as a function of radius, implying a large amount of dark matter in the outer part. Rotation curves are only approximately flat. Numerical simulations finds the so-called Navarro, Frenk and White profile ...
... increases as a function of radius, implying a large amount of dark matter in the outer part. Rotation curves are only approximately flat. Numerical simulations finds the so-called Navarro, Frenk and White profile ...
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...