Asteroids and Comets II
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... It is caused by the motion of the atoms. Or in a star, it is mostly the free electrons that cause pressure, since it is too hot for atoms to hold onto their electrons. In a normal gas, the electrons’ motion is caused by heat. But at very high densities, the wave properties of the electrons become im ...
... It is caused by the motion of the atoms. Or in a star, it is mostly the free electrons that cause pressure, since it is too hot for atoms to hold onto their electrons. In a normal gas, the electrons’ motion is caused by heat. But at very high densities, the wave properties of the electrons become im ...
white dwarf supernova
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
Life in the galactic danger zone
... giant planets to inhibit these terrestrial planets. The danger posed by high metallicity environments in the work of Lineweaver is higher than that of our work.” So, if you believe Gowanlock, the higher metallicity coupled with the high density of stars near the galactic centre means that although m ...
... giant planets to inhibit these terrestrial planets. The danger posed by high metallicity environments in the work of Lineweaver is higher than that of our work.” So, if you believe Gowanlock, the higher metallicity coupled with the high density of stars near the galactic centre means that although m ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in ce ...
... billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in ce ...
PDF format
... a) the recycling of stellar material from stars into the interstellar medium which then forms new stars b) the transfer of material from one star through an accretion disk to another star in a binary star system c) the shockwave from a supernova triggering gas clouds to condense into new stars d) ...
... a) the recycling of stellar material from stars into the interstellar medium which then forms new stars b) the transfer of material from one star through an accretion disk to another star in a binary star system c) the shockwave from a supernova triggering gas clouds to condense into new stars d) ...
Lecture 39: Life in the Universe The Main Point Simple Life vs
... N = Number of civilizations in the Galaxy capable of communicating with us R* = The rate of star formation in the Galaxy (stars/year) fs = fraction of stars that are Sun-like Np = number of planets per star fe = fraction of "environmentally correct" planets fL = fraction of planets where life develo ...
... N = Number of civilizations in the Galaxy capable of communicating with us R* = The rate of star formation in the Galaxy (stars/year) fs = fraction of stars that are Sun-like Np = number of planets per star fe = fraction of "environmentally correct" planets fL = fraction of planets where life develo ...
The chemical history of molecules in circumstellar disks I: Ices
... thus necessarily ignore the circumstellar disk. As the protostar turns on and heats up the surrounding material, all models agree that frozen-out species return to the gas phase if the dust temperature surpasses their evaporation temperature. The higher temperatures can further drive a hot-core–like ...
... thus necessarily ignore the circumstellar disk. As the protostar turns on and heats up the surrounding material, all models agree that frozen-out species return to the gas phase if the dust temperature surpasses their evaporation temperature. The higher temperatures can further drive a hot-core–like ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Unit 33: The Origin of the Solar System Describe the three basic ingredients of the “cosmic cupboard” and how these three ingredients and the thermal structure of the solar nebula create the distribution of planets that we see in our solar system. Describe the steps in the formation of solar sy ...
... Unit 33: The Origin of the Solar System Describe the three basic ingredients of the “cosmic cupboard” and how these three ingredients and the thermal structure of the solar nebula create the distribution of planets that we see in our solar system. Describe the steps in the formation of solar sy ...
English Summary
... is called radiation and gives the star a colour. The colour of a star is related to its temperature. For instance, Rigel in the constellation Orion is very blue (and hot) while Betelgeuse is red (and cool). This concept is easier if we think of a wire that is being heated up. As it gets hotter (radi ...
... is called radiation and gives the star a colour. The colour of a star is related to its temperature. For instance, Rigel in the constellation Orion is very blue (and hot) while Betelgeuse is red (and cool). This concept is easier if we think of a wire that is being heated up. As it gets hotter (radi ...
charts_set_9
... and computer simulations show this situation can be maintained for a long time. ...
... and computer simulations show this situation can be maintained for a long time. ...
Surveys of Stars, The interstellar medium
... where UV radiation is completely absorbed. “Molecular ...
... where UV radiation is completely absorbed. “Molecular ...
Extragalactic Astrophysics 1 AA 2011-2012 Prof. LA Antonelli
... orbits with random orientations, and with negligible total angular momentum Bulge stars are younger than globular clusters (age < ~8-10 Gyr). they could have been formed in the densest region of the protogalactic gas, or in a dense region of the disk, or they could be remnants of globular clusters f ...
... orbits with random orientations, and with negligible total angular momentum Bulge stars are younger than globular clusters (age < ~8-10 Gyr). they could have been formed in the densest region of the protogalactic gas, or in a dense region of the disk, or they could be remnants of globular clusters f ...
che
... eclipse is extremely variable (presumably due to gaseous streams from ther star and stellar wind from the disk) Ingress to the primary eclipse is much more stable Interpretation of the primary eclipse by geometrical model should be based on the upper envelope of the eclipse ingress ...
... eclipse is extremely variable (presumably due to gaseous streams from ther star and stellar wind from the disk) Ingress to the primary eclipse is much more stable Interpretation of the primary eclipse by geometrical model should be based on the upper envelope of the eclipse ingress ...
Advanced Interactive PPT
... Our sun and its nine planets are only a small part o a huge system, the galaxy called the Milky Way. We know that our solar system is near the edge of the Milky Way, a huge galaxy which is about 100,000 light years in diameter. The Milky Way has a spiral shape and its stars are arranged in long, cur ...
... Our sun and its nine planets are only a small part o a huge system, the galaxy called the Milky Way. We know that our solar system is near the edge of the Milky Way, a huge galaxy which is about 100,000 light years in diameter. The Milky Way has a spiral shape and its stars are arranged in long, cur ...
Nova
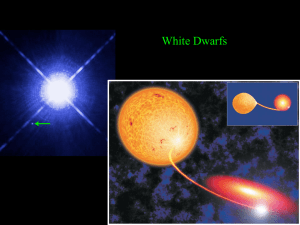
... inner Lagrangian point (L1), where the two Roche lobes touch. This gas stream free-falls onto the companion star, much like rocks dropped from a building. However, the path of the gas stream becomes curved because it feels the orbital motion of the binary (or the Coriolis force) as it falls. ...
... inner Lagrangian point (L1), where the two Roche lobes touch. This gas stream free-falls onto the companion star, much like rocks dropped from a building. However, the path of the gas stream becomes curved because it feels the orbital motion of the binary (or the Coriolis force) as it falls. ...
Life cycle of low mass stars
... All element greater than iron require energy, instead of releasing it. When a Red Supergiant reaches this stage the core condenses to attempt to create the energy need. The star collapses rapidly, creating a supernova Supernova = the explosion of a massive star that occurs when its core runs out of ...
... All element greater than iron require energy, instead of releasing it. When a Red Supergiant reaches this stage the core condenses to attempt to create the energy need. The star collapses rapidly, creating a supernova Supernova = the explosion of a massive star that occurs when its core runs out of ...
SPECTRAL WORKSHOP
... In the last 15 years or so, telescopes have become powerful enough to observe planets orbiting distant stars. When the planet moves in front of the star, it hides some of the star's light – this can be observed with a back-garden telescope as a periodic decrease in the light from the star. ...
... In the last 15 years or so, telescopes have become powerful enough to observe planets orbiting distant stars. When the planet moves in front of the star, it hides some of the star's light – this can be observed with a back-garden telescope as a periodic decrease in the light from the star. ...