From Hot Jupiters to Hot Neptunes and Below
... The saga of the detection of exoplanets has been constantly driven by the evenincreasing accuracy of the radial velocity determination. Until the end of the eighties, the most accurate radial velocities were obtained with cross-correlation spectrographs like CORAVEL with a precision on individual me ...
... The saga of the detection of exoplanets has been constantly driven by the evenincreasing accuracy of the radial velocity determination. Until the end of the eighties, the most accurate radial velocities were obtained with cross-correlation spectrographs like CORAVEL with a precision on individual me ...
Document
... clouds and the interstellar material must be the same Pressure depends on density and temperature These clouds are embedded in a thin gas with a temperature of 1 million K from exploding stars The outer layers can be heated to a few 1000 K If the could is large enough, the inner core can stay cool a ...
... clouds and the interstellar material must be the same Pressure depends on density and temperature These clouds are embedded in a thin gas with a temperature of 1 million K from exploding stars The outer layers can be heated to a few 1000 K If the could is large enough, the inner core can stay cool a ...
13_Lecture_Outline
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Types of Stars http://space.about.com/od/stars/tp/What-Are
... the ensuing supernova drives the outer part of the star outward, leaving only the core behind. The core will have become so dense that not even light can escape its grasp. These objects are so exotic that the laws of physics break down. 6. Brown Dwarfs ...
... the ensuing supernova drives the outer part of the star outward, leaving only the core behind. The core will have become so dense that not even light can escape its grasp. These objects are so exotic that the laws of physics break down. 6. Brown Dwarfs ...
A dust ring around Epsilon Eridani: analogue to the young Solar
... even if the star is as old as 1 Gyr. Thus it would be difficult to reproduce clearing out to the observed 35 AU. Also, P-R drag naturally produces a 1/r density distribution as small grains spiral in towards the star, and this is not seen. Thus it appears unlikely that sublimation of grain mantles o ...
... even if the star is as old as 1 Gyr. Thus it would be difficult to reproduce clearing out to the observed 35 AU. Also, P-R drag naturally produces a 1/r density distribution as small grains spiral in towards the star, and this is not seen. Thus it appears unlikely that sublimation of grain mantles o ...
A Universe of Galaxies - Pennsylvania State University
... do not produce much radio emission). They were named quasistellar radio sources (quasars, or QSOs): ...
... do not produce much radio emission). They were named quasistellar radio sources (quasars, or QSOs): ...
Our solar system
... • Four inner planets – terrestrial planets – are rocky, small, and dense. • Four outer planets – Jovian planets – are gaseous and large. • Nebular theory of solar system formation: Cloud of gas and dust gradually collapsed under its own gravity, spinning faster as it shrank. • Condensation theory sa ...
... • Four inner planets – terrestrial planets – are rocky, small, and dense. • Four outer planets – Jovian planets – are gaseous and large. • Nebular theory of solar system formation: Cloud of gas and dust gradually collapsed under its own gravity, spinning faster as it shrank. • Condensation theory sa ...
Lecture 10: Interstellar gas
... simpler molecules (at least H2). Their surfaces act as catalysts by allowing atoms (or simple molecules) to stick to them so that there is time for a second atom to land, interact, and form a molecule that then evaporates back into the gas. Dust grains also shield molecules from dissociation by UV r ...
... simpler molecules (at least H2). Their surfaces act as catalysts by allowing atoms (or simple molecules) to stick to them so that there is time for a second atom to land, interact, and form a molecule that then evaporates back into the gas. Dust grains also shield molecules from dissociation by UV r ...
Solar System
... • These planets are named terrestrial because of their solid, rocky surfaces. • These planets are sometimes called the inner planets. ...
... • These planets are named terrestrial because of their solid, rocky surfaces. • These planets are sometimes called the inner planets. ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution
... Stellar Evolution How stars are born, age and die Study stars of different ages ...
... Stellar Evolution How stars are born, age and die Study stars of different ages ...
Galaxies * Island universes
... Galaxies formed by gravitational infall of proto-galactic clumps which were already forming stars by the time they came together, forming spheroid, and bulge Disk formed from later infalling gas of higher angular momentum, which dissipates against itself to settle into a thin disk A Galaxy’s color e ...
... Galaxies formed by gravitational infall of proto-galactic clumps which were already forming stars by the time they came together, forming spheroid, and bulge Disk formed from later infalling gas of higher angular momentum, which dissipates against itself to settle into a thin disk A Galaxy’s color e ...
Lecture 6-1: Schematic Evolution of Stars as seen from the core
... Ignoring for the moment shell burning ,for larger mass, when the core is hot enough, He will ignite with another phase of stable burning. If this happens near the degenerate border, a thermal instability happens (g-4/3; P independent of T). This story continues with the lower mass stars developing a ...
... Ignoring for the moment shell burning ,for larger mass, when the core is hot enough, He will ignite with another phase of stable burning. If this happens near the degenerate border, a thermal instability happens (g-4/3; P independent of T). This story continues with the lower mass stars developing a ...
The Kuiper Belt and Other Debris Disks - UCLA
... they are certainly not solid bodies but are merely composed of molecules which, if they were much colder, would be simple ices. In terms of their mode of formation, the difference between the ice giants and the gas giants may be largely one of timescale. It is widely thought that the ice giants corr ...
... they are certainly not solid bodies but are merely composed of molecules which, if they were much colder, would be simple ices. In terms of their mode of formation, the difference between the ice giants and the gas giants may be largely one of timescale. It is widely thought that the ice giants corr ...
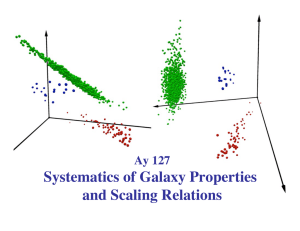
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... Virial Theorem connects mass, density, and kinetic temperature, and is thus an equation of a plane in that (theoretical) parameter space. Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured ...
... Virial Theorem connects mass, density, and kinetic temperature, and is thus an equation of a plane in that (theoretical) parameter space. Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured ...
The Anglo-Australian Planet Search – XXI. A Gas-Giant
... 8.5 m s−1 , which is substantially higher (by almost a factor of two) than would be expected based on measurement precision (the median value of the internal uncertainty produced by our iodine velocity fitting is 1.9 m s−1 ) and stellar jitter (3.0 m s−1 ). Preliminary analysis of these velocities i ...
... 8.5 m s−1 , which is substantially higher (by almost a factor of two) than would be expected based on measurement precision (the median value of the internal uncertainty produced by our iodine velocity fitting is 1.9 m s−1 ) and stellar jitter (3.0 m s−1 ). Preliminary analysis of these velocities i ...
G-stars - Gemini Astronomie
... It is interesting to see that every star “moves” on a certain path represented in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, which helps to scientifically classify stars according to their spectral characteristics and brightness. Mekbuda has a very special development in its near future. Supergiants tend to e ...
... It is interesting to see that every star “moves” on a certain path represented in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, which helps to scientifically classify stars according to their spectral characteristics and brightness. Mekbuda has a very special development in its near future. Supergiants tend to e ...
Stephen Ashworth
... These general ideas have led to problems as astronomy progressed. The largest satellite of a giant planet can easily match for size the smallest independently orbiting planet in the system; in our own Solar System, Ganymede and Titan are both larger than Mercury, though in terms of mass the planet i ...
... These general ideas have led to problems as astronomy progressed. The largest satellite of a giant planet can easily match for size the smallest independently orbiting planet in the system; in our own Solar System, Ganymede and Titan are both larger than Mercury, though in terms of mass the planet i ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
... Enormous, cold clouds of gas and dust, called giant molecular clouds, are scattered about the disk of the Galaxy. Star formation begins when gravitational attraction causes clumps of gas and dust, called protostars, to coalesce in Bok globules within a giant molecular cloud. As a protostar contr ...
... Enormous, cold clouds of gas and dust, called giant molecular clouds, are scattered about the disk of the Galaxy. Star formation begins when gravitational attraction causes clumps of gas and dust, called protostars, to coalesce in Bok globules within a giant molecular cloud. As a protostar contr ...