File
... attraction on each other increases. • This pulls more nearby particles toward an area of increasing mass, and regions of dense matter begin to build up within the nebula. ...
... attraction on each other increases. • This pulls more nearby particles toward an area of increasing mass, and regions of dense matter begin to build up within the nebula. ...
test - Scioly.org
... 1. Consider an object of .2 solar masses orbiting the Sun. The object’s orbit has a semimajor axis of 6 AU. a. How long is its period in years? b. Consider the points A, B, C, D on the orbit of the object. The arc length from point A to point B is .225 AU. The arc length from point C to D is .556 AU ...
... 1. Consider an object of .2 solar masses orbiting the Sun. The object’s orbit has a semimajor axis of 6 AU. a. How long is its period in years? b. Consider the points A, B, C, D on the orbit of the object. The arc length from point A to point B is .225 AU. The arc length from point C to D is .556 AU ...
Population synthesis view of gravitational waves - Astro-PF
... Galactic supernova rate, Galactic blue luminosity + blue luminosity density in the local Universe: ...
... Galactic supernova rate, Galactic blue luminosity + blue luminosity density in the local Universe: ...
Extreme Optics and the Search for Earth-Like Planets
... • Are there Earth-like planets? • Are they common? • Is there life on some of them? ...
... • Are there Earth-like planets? • Are they common? • Is there life on some of them? ...
PH607lec12
... QSOs, we have speculated on whether the centre of our galaxy might contain a black hole "Galactic Centre" here will mean the central ~10 parsecs of the Galaxy. It contains: 1. Young stars: the stellar population including evidence for star formation there in the last 50 million years or even less 2 ...
... QSOs, we have speculated on whether the centre of our galaxy might contain a black hole "Galactic Centre" here will mean the central ~10 parsecs of the Galaxy. It contains: 1. Young stars: the stellar population including evidence for star formation there in the last 50 million years or even less 2 ...
Question 1
... spiral arms formed first. globular clusters formed first. disk component started out thin and grew. spiral density waves formed first. bar in the bulge formed first. ...
... spiral arms formed first. globular clusters formed first. disk component started out thin and grew. spiral density waves formed first. bar in the bulge formed first. ...
Extrasolar Kuiper Belt Dust Disks
... (Backman and Paresce, 1993). Because all the above timescales are generally much shorter than the age of the disk, it is inferred that the observed dust is not primordial but is likely produced by a reservoir of undetected kilometersized planetesimals producing dust by mutual collisions or by evapor ...
... (Backman and Paresce, 1993). Because all the above timescales are generally much shorter than the age of the disk, it is inferred that the observed dust is not primordial but is likely produced by a reservoir of undetected kilometersized planetesimals producing dust by mutual collisions or by evapor ...
Chapter 16 Lives of the Stars (Low Mass)
... M ) can burn hydrogen for extremely long and we haven't observed them running out yet • Observations of star clusters show that intermediate mass stars ( 0.2 M to 8 M ) becomes larger, redder, more luminous after their time on the main sequence is over: they become first subgiants, then red giants S ...
... M ) can burn hydrogen for extremely long and we haven't observed them running out yet • Observations of star clusters show that intermediate mass stars ( 0.2 M to 8 M ) becomes larger, redder, more luminous after their time on the main sequence is over: they become first subgiants, then red giants S ...
Dynamical evolution of planetary systems
... Lambrechts and Johansen (2012) argued that, if the mass in the disk is originally dominated by ...
... Lambrechts and Johansen (2012) argued that, if the mass in the disk is originally dominated by ...
The Life Cycle of A Star
... is only a few thousand miles in diameter. It has become a white dwarf. White dwarfs are stable because the inward pull of gravity is balanced by the electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space ...
... is only a few thousand miles in diameter. It has become a white dwarf. White dwarfs are stable because the inward pull of gravity is balanced by the electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space ...
Astronomy (C) - North Carolina Science Olympiad
... Black hole: so dense nothing opposes collapse Nothing – even light – can escape after getting too close (“event horizon”) Can’t be directly observed – must be inferred from presence of accretion disk and/or jet ...
... Black hole: so dense nothing opposes collapse Nothing – even light – can escape after getting too close (“event horizon”) Can’t be directly observed – must be inferred from presence of accretion disk and/or jet ...
Lecture 13 Local group chapter 4 of S+G
... which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are satellites of MW, M31 or M33 The gravitational interaction between these systems is complex but the local group is apparently bound. Major advantages – close and bright- all nearby enough that individual stars can be well measured as ...
... which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are satellites of MW, M31 or M33 The gravitational interaction between these systems is complex but the local group is apparently bound. Major advantages – close and bright- all nearby enough that individual stars can be well measured as ...
4. The Solar System
... but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
... but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
More detailed notes - Particle Physics and Particle Astrophysics
... that the Sun was completely dark for the first billion years of its life—it just means that only one in a billion pairs of protons will fuse in any given year. There are side branches of the pp chain which involve less probable reactions, e.g. the sequence 3He + 4He → 7Be + γ; 7Be + e− → 7Li + νe; 7 ...
... that the Sun was completely dark for the first billion years of its life—it just means that only one in a billion pairs of protons will fuse in any given year. There are side branches of the pp chain which involve less probable reactions, e.g. the sequence 3He + 4He → 7Be + γ; 7Be + e− → 7Li + νe; 7 ...
HW1-6
... changeable objects must be earthly. Since this star just suddenly appeared, the old system said it must be earthly (under the sphere of the moon). Tycho’s observations indicated that the star could not be close. If it were close, it would have shifted (parallax). ...
... changeable objects must be earthly. Since this star just suddenly appeared, the old system said it must be earthly (under the sphere of the moon). Tycho’s observations indicated that the star could not be close. If it were close, it would have shifted (parallax). ...
Light and shadow from distant worlds
... of momentum—the planet mass times the sine of the orbital inclination. Given an astronomical estimate of the stellar mass, the semimajor axis of the planet’s orbit follows from Kepler’s law. At an orbital distance of 0.05 astronomical units (1 AU is the Earth–Sun distance), 51 Peg b should be heated ...
... of momentum—the planet mass times the sine of the orbital inclination. Given an astronomical estimate of the stellar mass, the semimajor axis of the planet’s orbit follows from Kepler’s law. At an orbital distance of 0.05 astronomical units (1 AU is the Earth–Sun distance), 51 Peg b should be heated ...
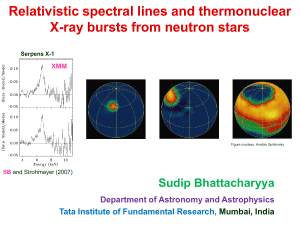
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
... common among various kinds of objects, such as proto-stars, Xray binaries and AGN. (b) Accretion onto black holes and neutron stars is possibly the most efficient energy source in the universe. (c) A study of accretion-ejection in X-ray binaries provides an important tool to probe the strong gravity ...
... common among various kinds of objects, such as proto-stars, Xray binaries and AGN. (b) Accretion onto black holes and neutron stars is possibly the most efficient energy source in the universe. (c) A study of accretion-ejection in X-ray binaries provides an important tool to probe the strong gravity ...
View PDF - Sara Seager
... a more detailed list, see (30)]. Many other factors are relevant to habitability, including the radiation environment from the star, especially the energy distribution as a function of wavelength and the EUV radiation that destroys molecules and determines their atmospheric lifetime, and x-ray flux ...
... a more detailed list, see (30)]. Many other factors are relevant to habitability, including the radiation environment from the star, especially the energy distribution as a function of wavelength and the EUV radiation that destroys molecules and determines their atmospheric lifetime, and x-ray flux ...