Chapter21
... binary stars in a single coherent chapter. First, most stars are in binary or multiple systems, so it isn’t reasonable to treat single stars as if they were ordinary and binary stars as if they were unusual. Second, we now have a clear enough picture of the evolution of close binary systems that it ...
... binary stars in a single coherent chapter. First, most stars are in binary or multiple systems, so it isn’t reasonable to treat single stars as if they were ordinary and binary stars as if they were unusual. Second, we now have a clear enough picture of the evolution of close binary systems that it ...
Formation of Globular Clusters: In and Out of Dwarf Galaxies
... The gas in early halos is not dense enough to form the observed globular clusters In addition, the cosmic time is less than 0.4 Gyr Moore et al. (2006) ...
... The gas in early halos is not dense enough to form the observed globular clusters In addition, the cosmic time is less than 0.4 Gyr Moore et al. (2006) ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or old? 12. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.20 In the formation of a star cluster with a wide range of stellar mas ...
... Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or old? 12. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.20 In the formation of a star cluster with a wide range of stellar mas ...
deduction of the gravity law and quantum mechanical model of
... the angular velocities as the vector, what is the most often ignored. As the result on this way were obtained the possibility to calculate planetary circular velocities, with important detail - faster decreasing of the velocity by increasing of the distance. Kepler held his attention on this detail ...
... the angular velocities as the vector, what is the most often ignored. As the result on this way were obtained the possibility to calculate planetary circular velocities, with important detail - faster decreasing of the velocity by increasing of the distance. Kepler held his attention on this detail ...
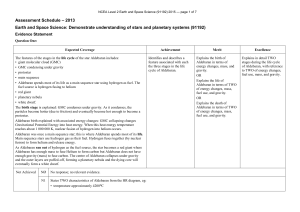
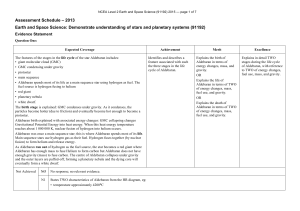
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192)
... After the Sun had formed, there were leftover gas and dust particles. These particles began to rotate around the young sun and flattened into a disk shape called a protoplanetary disk. Inside the swirling disk, rocky particles began to collide and formed bigger masses. This increase in mass attracte ...
... After the Sun had formed, there were leftover gas and dust particles. These particles began to rotate around the young sun and flattened into a disk shape called a protoplanetary disk. Inside the swirling disk, rocky particles began to collide and formed bigger masses. This increase in mass attracte ...
All_Stars
... • Medium-mass stars burn H He in their cores while on the main sequence and He C and O while on the horizontal branch • They are not massive enough to ignite C-burning once their He is gone. Their cores contract and heat up until the contraction is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure • At th ...
... • Medium-mass stars burn H He in their cores while on the main sequence and He C and O while on the horizontal branch • They are not massive enough to ignite C-burning once their He is gone. Their cores contract and heat up until the contraction is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure • At th ...
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2013
... After the Sun had formed, there were leftover gas and dust particles. These particles began to rotate around the young sun and flattened into a disk shape called a protoplanetary disk. Inside the swirling disk, rocky particles began to collide and formed bigger masses. This increase in mass attracte ...
... After the Sun had formed, there were leftover gas and dust particles. These particles began to rotate around the young sun and flattened into a disk shape called a protoplanetary disk. Inside the swirling disk, rocky particles began to collide and formed bigger masses. This increase in mass attracte ...
A Story about a Star`s Life
... • Brightest stars had magnitude 1 and dimmest had magnitude 6 • The system is still used today and units of measurement are called apparent magnitudes to emphasize how bright a star looks to an observer ...
... • Brightest stars had magnitude 1 and dimmest had magnitude 6 • The system is still used today and units of measurement are called apparent magnitudes to emphasize how bright a star looks to an observer ...
AST1001.ch13
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (also known as the Chandrasekhar limit). ...
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (also known as the Chandrasekhar limit). ...
A Planetary System Around Our Nearest Star is Emerging
... Today, a team of European scientists announces the discovery of the first planet around a star in the Alpha Centau planet is as massive as Earth, only 13% more massive, although too hot for life. This new result opens the possibilit might be other Earth-size planets in the Alpha Centauri system, inc ...
... Today, a team of European scientists announces the discovery of the first planet around a star in the Alpha Centau planet is as massive as Earth, only 13% more massive, although too hot for life. This new result opens the possibilit might be other Earth-size planets in the Alpha Centauri system, inc ...
The Parent Stars of New Extrasolar Planet System Candidates
... it is possible that an inward-migrating planet was accreted by the star, thus changing the stellar surface and explaining the odd abundances observed. Unlike Gliese 876, the two stars HR 810 and HR 7875 are very similar to the sun. They are each close to one solar mass and are slightly younger than ...
... it is possible that an inward-migrating planet was accreted by the star, thus changing the stellar surface and explaining the odd abundances observed. Unlike Gliese 876, the two stars HR 810 and HR 7875 are very similar to the sun. They are each close to one solar mass and are slightly younger than ...
Chapter 15: The Deaths of Massive Stars
... 3. The source of the Crab pulsar’s energy and that of the surrounding nebula is the rotational energy of the pulsar. This was implied by the observation that the Crab pulsar is slowing down. As the magnetic field of the pulsar propels electrons out into the nebula, the electrons slow down the pulsar ...
... 3. The source of the Crab pulsar’s energy and that of the surrounding nebula is the rotational energy of the pulsar. This was implied by the observation that the Crab pulsar is slowing down. As the magnetic field of the pulsar propels electrons out into the nebula, the electrons slow down the pulsar ...
A Planetary Overview
... few years of other objects at about the same distance made it obvious that things were not this simple. The Titius-Bode law could not account for the large number of “planets” between Mars and Jupiter. (However, it is possible that tidal interactions from Jupiter did not allow all these objects to c ...
... few years of other objects at about the same distance made it obvious that things were not this simple. The Titius-Bode law could not account for the large number of “planets” between Mars and Jupiter. (However, it is possible that tidal interactions from Jupiter did not allow all these objects to c ...
Program and Abstract Book - European Southern Observatory
... Mike Dunham (SUNY Fredonia, NY, USA) Stars form from the gravitational collapse of dense molecular cloud cores. In the protostellar phase, mass both accretes from the core onto a protostar, likely through an accretion disk, and is ejected in the form of jets and outflows. It is during this protostel ...
... Mike Dunham (SUNY Fredonia, NY, USA) Stars form from the gravitational collapse of dense molecular cloud cores. In the protostellar phase, mass both accretes from the core onto a protostar, likely through an accretion disk, and is ejected in the form of jets and outflows. It is during this protostel ...
Unit 1
... before becoming white dwarfs • Higher mass stars move rapidly off the main sequence and into the giant stages, eventually exploding in a supernova ...
... before becoming white dwarfs • Higher mass stars move rapidly off the main sequence and into the giant stages, eventually exploding in a supernova ...
The Intricate Role of Cold Gas and Dust in Galaxy Evolution at Early
... - idea: z>4 galaxy dust spectral energy distributions peak beyond 500 µm! ! can use (sub)mm colors to determine reasonable photometric redshifts! ! “red” sources are strong candidates for starbursts at the earliest epochs Systematic approach, but…how well does it work?! ...
... - idea: z>4 galaxy dust spectral energy distributions peak beyond 500 µm! ! can use (sub)mm colors to determine reasonable photometric redshifts! ! “red” sources are strong candidates for starbursts at the earliest epochs Systematic approach, but…how well does it work?! ...
Free floating planets
... transit the disk of their parent stars, allowing for a determination of planetary radii. The 14 confirmed transiting planets observed to date are all more massive than Saturn, have orbital periods of only a few days, and orbit stars bright enough such that radial velocities can be determined, allowi ...
... transit the disk of their parent stars, allowing for a determination of planetary radii. The 14 confirmed transiting planets observed to date are all more massive than Saturn, have orbital periods of only a few days, and orbit stars bright enough such that radial velocities can be determined, allowi ...
PH607 – Galaxies 2
... monitored. However, in spite of all efforts, no unambiguous NIR counterpart of SgrA* could be detected up to 2003. On the 9th of May, during routine observations of the GC star cluster at 1.7 microns with NAOS/CONICA at the VLT, we witnessed a powerful flare at the location of the black hole. Within ...
... monitored. However, in spite of all efforts, no unambiguous NIR counterpart of SgrA* could be detected up to 2003. On the 9th of May, during routine observations of the GC star cluster at 1.7 microns with NAOS/CONICA at the VLT, we witnessed a powerful flare at the location of the black hole. Within ...
Powerpoint slides - Earth & Planetary Sciences
... • Hypothesis 1) can’t explain why the gas/ice giants are so different to the original nebular composition, and require an enormous initial nebula mass (~1 solar mass) • Hypothesis 2) is reasonable, and can explain why Uranus and Neptune are smaller with less H/He – they must have been forming as the ...
... • Hypothesis 1) can’t explain why the gas/ice giants are so different to the original nebular composition, and require an enormous initial nebula mass (~1 solar mass) • Hypothesis 2) is reasonable, and can explain why Uranus and Neptune are smaller with less H/He – they must have been forming as the ...