Introduction to Neural Networks
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
... should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. ...
1: Nervous System II: Anatomy Review
... (on soma). They carry input signals to the other neuron. Axons from one neuron can synapse with the axon terminal of another neuron. These synapses are called ________________________, and they regulate the amount of ________________________ released by the other neuron. ...
... (on soma). They carry input signals to the other neuron. Axons from one neuron can synapse with the axon terminal of another neuron. These synapses are called ________________________, and they regulate the amount of ________________________ released by the other neuron. ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs i ...
... throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs i ...
HPA Axis Activation and Hippocampal Atrophy
... resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal neurons in monkeys. This effect differs for various areas in hippocampus according to the type of stressor. The decrease in hippocampal volume related to glucocorticoid and stress ca ...
... resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal neurons in monkeys. This effect differs for various areas in hippocampus according to the type of stressor. The decrease in hippocampal volume related to glucocorticoid and stress ca ...
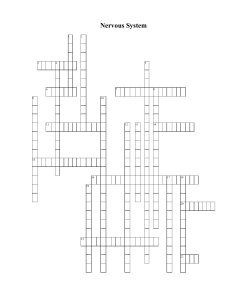
Nervous System - Crossword Labs
... 3. respond to efferent signals 6. Area where a neuron communicates with another cell 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All ...
... 3. respond to efferent signals 6. Area where a neuron communicates with another cell 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All ...
Final review quiz
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
ch4_1 - Homework Market
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Physiology of Perception
... Effect of excitatory (E) and inhibitory (I) input on the firing rate of a neuron. The amount of excitatory and inhibitory input to the neuron is indicated by the size of the arrows at the synapse. As inhibition becomes stronger relative to excitation, firing rate decreases, until eventually the neur ...
... Effect of excitatory (E) and inhibitory (I) input on the firing rate of a neuron. The amount of excitatory and inhibitory input to the neuron is indicated by the size of the arrows at the synapse. As inhibition becomes stronger relative to excitation, firing rate decreases, until eventually the neur ...
A1985AUW1100002
... These papers are probably cited often for several reasons. First, together with the2studies of Phillips on the pyra’ midal cells ot the neocorten, they were the lirst systematic study ol neurons above the spinal cord. They showed that the electrophysiological techniques that were so uselul in the sp ...
... These papers are probably cited often for several reasons. First, together with the2studies of Phillips on the pyra’ midal cells ot the neocorten, they were the lirst systematic study ol neurons above the spinal cord. They showed that the electrophysiological techniques that were so uselul in the sp ...
1. The main function of myelin is to a. form a protective coating over
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
In Pursuit of Ecstasy - Heartland Community College
... • Action potential in one part of an axon brings neighboring region to threshold • Action potential moves from one patch of membrane to another ...
... • Action potential in one part of an axon brings neighboring region to threshold • Action potential moves from one patch of membrane to another ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... Sensory Neuron 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles o ...
... Sensory Neuron 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles o ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission - Milton
... stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, and all attempts at a vaccine or cure have failed. Scientific and industrial infrastructure is rapidly faltering. Early attempts at controll ...
... stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, and all attempts at a vaccine or cure have failed. Scientific and industrial infrastructure is rapidly faltering. Early attempts at controll ...
The Biological Perspective - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... Sending the message to other cells: The Synapse Axon Terminals Synaptic Knob Synaptic Vesicles Neurotransmitters Synaptic Gap or Synapse Receptor Sites How do Neurotransmitters get across the synapse Video ...
... Sending the message to other cells: The Synapse Axon Terminals Synaptic Knob Synaptic Vesicles Neurotransmitters Synaptic Gap or Synapse Receptor Sites How do Neurotransmitters get across the synapse Video ...
Slide 1
... The goals of neural computation 1. To understand how the brain actually works Neuroscience is hard! ...
... The goals of neural computation 1. To understand how the brain actually works Neuroscience is hard! ...
Slide ()
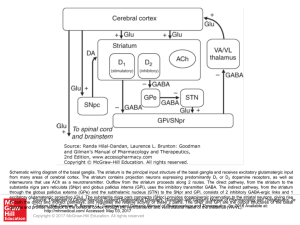
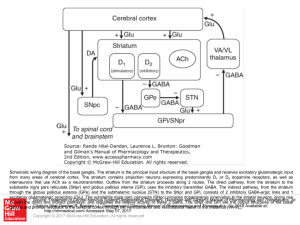
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... • Humans born with all our neurons that slowly die over our lifetime. • What two areas of the brain does new research suggest can regrow? – Hippocampus and olfactory bulb ...
... • Humans born with all our neurons that slowly die over our lifetime. • What two areas of the brain does new research suggest can regrow? – Hippocampus and olfactory bulb ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... ________________ – Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential ...
... ________________ – Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Neural Communication • After a neuron fires there is a Refractory Period – a period of inactivity after it has fired. ...
... Neural Communication • After a neuron fires there is a Refractory Period – a period of inactivity after it has fired. ...
Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission
... Information in the form of an electrical impulse is carried away from the neuron’s cell body along the axon of a presynaptic neuron toward the axon terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the synaptic space, or synaptic cleft, to reach the postsynaptic neuron. Ins ...
... Information in the form of an electrical impulse is carried away from the neuron’s cell body along the axon of a presynaptic neuron toward the axon terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the synaptic space, or synaptic cleft, to reach the postsynaptic neuron. Ins ...
Brain & Behavior
... “jump” from one Node of Ranvier to the next • Multiple Sclerosis – myelin sheath destroyed ...
... “jump” from one Node of Ranvier to the next • Multiple Sclerosis – myelin sheath destroyed ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.