Nervous System Function
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
Neural Networks.Chap..
... Rule 4: Prior information and invariance should be built into the design of a neural network, thereby simplifying the network design by not having to learn them. ...
... Rule 4: Prior information and invariance should be built into the design of a neural network, thereby simplifying the network design by not having to learn them. ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
Theoretical Neuroscience: From Single Neuron to Network Dynamics
... • EIF can be mapped to both LNP and Wilson-Cowan-type firing rate models, with a time constant that depends on intrinsic parameters of the cell, and on instantaneous rate itself ...
... • EIF can be mapped to both LNP and Wilson-Cowan-type firing rate models, with a time constant that depends on intrinsic parameters of the cell, and on instantaneous rate itself ...
Object Recognition and Learning using the BioRC Biomimetic Real
... Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the final output. Thus, we require N!/ ...
... Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the final output. Thus, we require N!/ ...
the cerebral cortex
... Efferents – thalamus (lateral geniculate body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area 7) Ventral stream – temporal cortex (whatcolors, form : cones, central area of retina, area 37, inferior. temporal cortex ...
... Efferents – thalamus (lateral geniculate body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area 7) Ventral stream – temporal cortex (whatcolors, form : cones, central area of retina, area 37, inferior. temporal cortex ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... The nerve impulse caused by a change in the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron ‘fires’, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. All-or-None Principal: ...
... The nerve impulse caused by a change in the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron ‘fires’, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. All-or-None Principal: ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
Brains, Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
... Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... • cells that have the ability to change their membrane potentials + neurons and muscle cells - resting potential (unexcited) + change from resting potential can result in active electrical impulse + gated ion channels - special channels that allow cell to change membrane potential + hyperpolarizatio ...
... • cells that have the ability to change their membrane potentials + neurons and muscle cells - resting potential (unexcited) + change from resting potential can result in active electrical impulse + gated ion channels - special channels that allow cell to change membrane potential + hyperpolarizatio ...
Nervous System - mr-youssef-mci
... Motor neuron 1 The reflex is initiated by tapping the tendon connected to the quadriceps (extensor) muscle. ...
... Motor neuron 1 The reflex is initiated by tapping the tendon connected to the quadriceps (extensor) muscle. ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
Slide ()
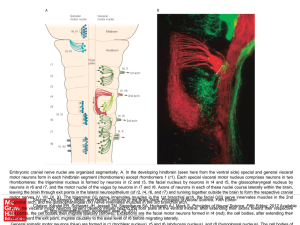
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... The cerebellar cortex is divided into three lobes: anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular. Each lobe consists of thin folds called folia. This sheet is laid over four cerebellar nuclei (CN) on each side. Three cerebellar peduncles on each side connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. The cortex c ...
... The cerebellar cortex is divided into three lobes: anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular. Each lobe consists of thin folds called folia. This sheet is laid over four cerebellar nuclei (CN) on each side. Three cerebellar peduncles on each side connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. The cortex c ...
collinsnervoussystem (1)
... Neural Bases of Psychology: Neural Communication • Within a neuron, communication occurs through an action potential (neural impulse that carries information along the axon of a neuron). ...
... Neural Bases of Psychology: Neural Communication • Within a neuron, communication occurs through an action potential (neural impulse that carries information along the axon of a neuron). ...
Powerpoint
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
neurons
... The transmission of information between two neurons occurs in one of two ways: electrically or chemically. ...
... The transmission of information between two neurons occurs in one of two ways: electrically or chemically. ...
Check Yourself
... 6. Chemical that affects a living organism 7. Powerful stimulant derived from a South American plant 10. An signal travels along the axon. 13. Drug that makes you drowsy, drunk, uncoordinated 14. Drug name used by several companies 17. Inactive or “fake” drug 18. Common term for opium, morphine, her ...
... 6. Chemical that affects a living organism 7. Powerful stimulant derived from a South American plant 10. An signal travels along the axon. 13. Drug that makes you drowsy, drunk, uncoordinated 14. Drug name used by several companies 17. Inactive or “fake” drug 18. Common term for opium, morphine, her ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.