Neuron Testing Activity Teacher Key
... b. Bring lots of paper clips in case of students taking or breaking them 2. Lab a. Watch that students do not press extremely hard b. Graph will vary from person to person, but the fingers will generally be more sensitive c. Collect paper clips after Review Questions 1. No, or at least student’s sho ...
... b. Bring lots of paper clips in case of students taking or breaking them 2. Lab a. Watch that students do not press extremely hard b. Graph will vary from person to person, but the fingers will generally be more sensitive c. Collect paper clips after Review Questions 1. No, or at least student’s sho ...
File
... Myelin sheath White fatty casing on axon Acts as an electrical insulator Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Myelin sheath White fatty casing on axon Acts as an electrical insulator Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
Neurons
... the greatest density of voltage-dependent Na+ channels the most easily-excited part of the neuron receives inputs from other neurons ...
... the greatest density of voltage-dependent Na+ channels the most easily-excited part of the neuron receives inputs from other neurons ...
Flash cards
... electrical charge that travels down the axon (depolarizes the neuron as it travels through). ...
... electrical charge that travels down the axon (depolarizes the neuron as it travels through). ...
Unit 6 Day 5 Anatomy
... MORE likely to fire. (raise) • Inhibitory Postsynaptic potentials make the neuron LESS likey to fire.(more -) ...
... MORE likely to fire. (raise) • Inhibitory Postsynaptic potentials make the neuron LESS likey to fire.(more -) ...
Slide ()
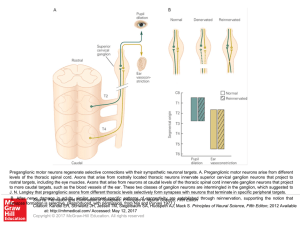
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
A1990DM11000002
... to be an ideal candidate for qualifying as a command in BBS,~’ and the comments indicate that indeed neuron. The neuron had been reported to have a very our conceptualization is not without problems but extensive synaptic output, exerting different types that a number of investigators have found it ...
... to be an ideal candidate for qualifying as a command in BBS,~’ and the comments indicate that indeed neuron. The neuron had been reported to have a very our conceptualization is not without problems but extensive synaptic output, exerting different types that a number of investigators have found it ...
Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 Motor neurons are located in the
... depolarization because the axon changes from negative to positive. The second part is the Potassium gates opening, this is when the potassium channels open and K+ flows to the outside of the axon. This is repolarization because the inside of the axon resumes a negative charge from positive. ...
... depolarization because the axon changes from negative to positive. The second part is the Potassium gates opening, this is when the potassium channels open and K+ flows to the outside of the axon. This is repolarization because the inside of the axon resumes a negative charge from positive. ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... The nerve cells and their axons, dendrites, and synapses form the most important components of the nervous system and as such are the foundation for rehabilitation. A nerve cell (neuron) is the structural unit of the nervous system. Axons and dendrites are the parts of the neuron that make contact w ...
... The nerve cells and their axons, dendrites, and synapses form the most important components of the nervous system and as such are the foundation for rehabilitation. A nerve cell (neuron) is the structural unit of the nervous system. Axons and dendrites are the parts of the neuron that make contact w ...
Laminar analysis of excitatory local circuits in vibrissal motor
... adeno-associated virus expressing ChR2. We prepared brain slices and recorded from ChR2positive neurons using loose-seal cell-attached recordings. CPP and NBQX were added to prevent feed-forward excitation between neurons. We stimulated axonal arbors in a grid pattern on the slice using a short puls ...
... adeno-associated virus expressing ChR2. We prepared brain slices and recorded from ChR2positive neurons using loose-seal cell-attached recordings. CPP and NBQX were added to prevent feed-forward excitation between neurons. We stimulated axonal arbors in a grid pattern on the slice using a short puls ...
Neural Development - Peoria Public Schools
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
The Nervous System
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... Thus, there is first an influx of sodium ions (leading to massive depolarization) followed by a rapid efflux of potassium ions from the neuron (leading to repolarisation). Above critical threshold, the feedback of sodium current activates even more channels to open, thus the cell ‘fires’ producing t ...
... Thus, there is first an influx of sodium ions (leading to massive depolarization) followed by a rapid efflux of potassium ions from the neuron (leading to repolarisation). Above critical threshold, the feedback of sodium current activates even more channels to open, thus the cell ‘fires’ producing t ...
BehNeuro11#2 (2) - Biology Courses Server
... d) The arcuate N. cells shown above release NPY & AgRP. What roles do the arcuate neurons that contain MSH & CART play (how does their activity influence the PV and lateral hypothalamic areas?). Use a diagram like the one shown above. ...
... d) The arcuate N. cells shown above release NPY & AgRP. What roles do the arcuate neurons that contain MSH & CART play (how does their activity influence the PV and lateral hypothalamic areas?). Use a diagram like the one shown above. ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Drugs and other chemicals affect brain chemistry at synapses, often by either amplifying or blocking a neurotransmitter’s activity a. Agonists are molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor and mimic its effects i. Some opiate drugs are agonists and produce a tem ...
... Drugs and other chemicals affect brain chemistry at synapses, often by either amplifying or blocking a neurotransmitter’s activity a. Agonists are molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor and mimic its effects i. Some opiate drugs are agonists and produce a tem ...
Slide ()
... a set ofER, interneurons cross the midline and ascend in the left medial longitudinal fasciculus to the oculomotor nucleus,2012 where they Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; Available excite the neurons at: thathttp://mhmedical.co ...
... a set ofER, interneurons cross the midline and ascend in the left medial longitudinal fasciculus to the oculomotor nucleus,2012 where they Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; Available excite the neurons at: thathttp://mhmedical.co ...
How Antidepressants Work - Rainsville Family Practice
... This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites adequately on the next neuron, therefore the signal is muted. ...
... This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites adequately on the next neuron, therefore the signal is muted. ...
ppt
... B. An action potential reaches the end of the axon C. An action potential reaches the end of the dendrite D. You take morphine or other narcotic ...
... B. An action potential reaches the end of the axon C. An action potential reaches the end of the dendrite D. You take morphine or other narcotic ...
Neurons
... body (soma) that sends and receives information between cells. Can be thought of as the brain's traffic cops routing messages to their desired cell target ...
... body (soma) that sends and receives information between cells. Can be thought of as the brain's traffic cops routing messages to their desired cell target ...
Luis V. Colom, MD, PhD VP of Research Center for Biomedical Studies
... Center for Biomedical Studies Phone: 956-882-5048 Email: luis.colom@utb.edu ...
... Center for Biomedical Studies Phone: 956-882-5048 Email: luis.colom@utb.edu ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... Dopamine creates the feelings of pleasure we get from enjoyable activities such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere from five to 15 minutes. But then the drug begins to wear off, leaving t ...
... Dopamine creates the feelings of pleasure we get from enjoyable activities such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere from five to 15 minutes. But then the drug begins to wear off, leaving t ...
Power Point
... refractory period. If the stimulus is sufficient to initiate an action potential the entire fiber will fire. This is called the, “all or none principle,” for nerve fibers. ...
... refractory period. If the stimulus is sufficient to initiate an action potential the entire fiber will fire. This is called the, “all or none principle,” for nerve fibers. ...
Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... Glutamate: Major neurotransmitter in the brain ● learning, memory, plasticity ● Open/allows entry (synaptic connects) Na+,Ca+2 channels into receiving or post-synaptic neuron. This is an excitatory signal because it makes inside of cell positive and thus excitatory. ● K+ channels may also close whic ...
... Glutamate: Major neurotransmitter in the brain ● learning, memory, plasticity ● Open/allows entry (synaptic connects) Na+,Ca+2 channels into receiving or post-synaptic neuron. This is an excitatory signal because it makes inside of cell positive and thus excitatory. ● K+ channels may also close whic ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.