FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
www.translationalneuromodeling.org
... Jansen and Rit model Post-synaptic potential (PSP) model: convolution of impulse response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
... Jansen and Rit model Post-synaptic potential (PSP) model: convolution of impulse response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
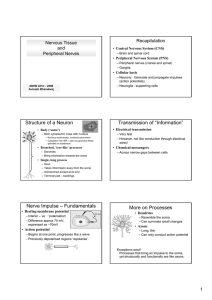
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
... Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... Surround suppression in the cortex can be explained by normalization models in which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation o ...
... Surround suppression in the cortex can be explained by normalization models in which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation o ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... o Memory items: a pattern of synapses (between excitatory cells) o Different kinds of memory, different kinds of learning → different brain structures The hippocampus: short term memory o Basic anatomy: the tri-synaptic circuit o Long-term potentiation o Long-term depression o Rat hippocampus (12.4) ...
... o Memory items: a pattern of synapses (between excitatory cells) o Different kinds of memory, different kinds of learning → different brain structures The hippocampus: short term memory o Basic anatomy: the tri-synaptic circuit o Long-term potentiation o Long-term depression o Rat hippocampus (12.4) ...
Psychology 210
... Now which way do the ions want to go? Sodium: Which way does equilibrium push? What about the charge? At rest Resting potential -70mV Potassium ________________________________ the membrane Sodium and Chloride ________________ cross the membrane Stimulation When stimulated by another neuron, some __ ...
... Now which way do the ions want to go? Sodium: Which way does equilibrium push? What about the charge? At rest Resting potential -70mV Potassium ________________________________ the membrane Sodium and Chloride ________________ cross the membrane Stimulation When stimulated by another neuron, some __ ...
Biological Bases of Behavior, Barron`s Neuroanatomy, pages 78
... 10. Why are neurotransmitters important ? - enable neurons to communicate 11. What does it take for a neuron to fire? - terminal buttons on one neuron are stimulated and release transmitters into the synapse - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron ce ...
... 10. Why are neurotransmitters important ? - enable neurons to communicate 11. What does it take for a neuron to fire? - terminal buttons on one neuron are stimulated and release transmitters into the synapse - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron ce ...
deep learning with different types of neurons
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
Sensory Physiology
... firing can increase or decrease in frequency known as “On” pathway and “Off” pathway. • Secondary neurons can receive inputs from both “on” and “off” neurons and that leads to more sensitivity. ...
... firing can increase or decrease in frequency known as “On” pathway and “Off” pathway. • Secondary neurons can receive inputs from both “on” and “off” neurons and that leads to more sensitivity. ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... membrane of the axon • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
... membrane of the axon • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
Like crumpled paper balls: the evolution of the mammalian cerebral
... Prof. Suzana Herculano-Houzel - Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil Larger brains tend to have larger and more folded cortices, and gyrification has long been considered a mechanism that allows for larger neurons in the cerebral cortex – but why is the cetacean cortex much more folded tha ...
... Prof. Suzana Herculano-Houzel - Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil Larger brains tend to have larger and more folded cortices, and gyrification has long been considered a mechanism that allows for larger neurons in the cerebral cortex – but why is the cetacean cortex much more folded tha ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
Neural Transmission Project
... Synapse/synaptic gap: space between neurons. When neurotransmitters are floating between cells, you get the effect of the neuron. Dendrites: These grabby guys hold the receptors in their fingertips. Dendrites can be blocked or mimicked - Prozac works here to help depressed people feel better. Neurot ...
... Synapse/synaptic gap: space between neurons. When neurotransmitters are floating between cells, you get the effect of the neuron. Dendrites: These grabby guys hold the receptors in their fingertips. Dendrites can be blocked or mimicked - Prozac works here to help depressed people feel better. Neurot ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... • Synapse is the point of communication between one neuron and another. • Synaptic cleft is the gap between neurons at the synapse. ...
... • Synapse is the point of communication between one neuron and another. • Synaptic cleft is the gap between neurons at the synapse. ...
Nervous System - Wando High School
... body: contains the nucleus and all other cellular organelles along with the bulk of cytoplasm ...
... body: contains the nucleus and all other cellular organelles along with the bulk of cytoplasm ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
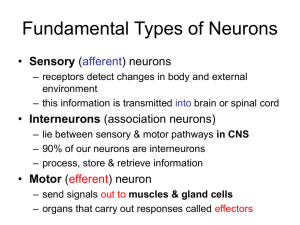
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Neuron Stations
... 3) Dendrites: take 2 short pipe cleaners (1/3 length) of the same color and push them through the "cell body" on the side opposite the axon. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons! Q4: What would ha ...
... 3) Dendrites: take 2 short pipe cleaners (1/3 length) of the same color and push them through the "cell body" on the side opposite the axon. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons! Q4: What would ha ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... Carl Wernicke (1848-1905): describes patient who cannot comprehend language but CAN produce it Damage to an area in the left TEMPORAL lobe Wernicke’s Aphasia ...
... Carl Wernicke (1848-1905): describes patient who cannot comprehend language but CAN produce it Damage to an area in the left TEMPORAL lobe Wernicke’s Aphasia ...
Nerve Cell Signaling - Mr. Moore`s Web Page
... How does a nerve work • Watch each of the videos that follow. Use the videos to describe the process of depolarization. Try to do it in a series of steps. You can also use other web sites to help you in this process. You might want to use the picture on slide 9 to help you describe the process. Wri ...
... How does a nerve work • Watch each of the videos that follow. Use the videos to describe the process of depolarization. Try to do it in a series of steps. You can also use other web sites to help you in this process. You might want to use the picture on slide 9 to help you describe the process. Wri ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.