Enzymatic Protein Deglycosylation Kit (EDEGLY)
... sugars because of their limited specificities and because they leave one N-acetylglucosamine residue attached to the asparagine.6,7 There is no enzyme comparable to PNGase F for removing intact O-linked sugars. Monosaccharides must be removed by a series of exoglycosidases until only the Gal-β(1→3)- ...
... sugars because of their limited specificities and because they leave one N-acetylglucosamine residue attached to the asparagine.6,7 There is no enzyme comparable to PNGase F for removing intact O-linked sugars. Monosaccharides must be removed by a series of exoglycosidases until only the Gal-β(1→3)- ...
Lecture 6
... Protein structure: Amino acids • Essential vs non-essential – Essential: NOT made by body – Nonessential: made by the body ...
... Protein structure: Amino acids • Essential vs non-essential – Essential: NOT made by body – Nonessential: made by the body ...
Recognition Specificity for the Bacterial Avirulence Protein AvrPto Is
... is required for maximal kinase activity and substrate binding (Johnson et al., 1996). The activation domain in PKA is thought to be stabilized, and substrate binding facilitated, by the formation of hydrogen bonds between phosphate oxygens on phospho-T197 and the charged side chains of R165, K189, a ...
... is required for maximal kinase activity and substrate binding (Johnson et al., 1996). The activation domain in PKA is thought to be stabilized, and substrate binding facilitated, by the formation of hydrogen bonds between phosphate oxygens on phospho-T197 and the charged side chains of R165, K189, a ...
Additional Methods_Office2004
... 561 nm diode laser from an Agilent (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, California) MLC400B monolithic laser combiner. Activation was performed using a 405 nm diode laser from the MLC400B, and applied as needed to ensure enough emitters were consistently being identified for the software drift correc ...
... 561 nm diode laser from an Agilent (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, California) MLC400B monolithic laser combiner. Activation was performed using a 405 nm diode laser from the MLC400B, and applied as needed to ensure enough emitters were consistently being identified for the software drift correc ...
Computational Methods for Exploration and Analysis of
... of biology and other fields that model dynamic systems. Macromolecules move, and their movements are needed for a complete picture of life. Computational biology, with concepts imported from physics and chemistry, increasingly plays a major role, which has recently been recognized by the Nobel Commi ...
... of biology and other fields that model dynamic systems. Macromolecules move, and their movements are needed for a complete picture of life. Computational biology, with concepts imported from physics and chemistry, increasingly plays a major role, which has recently been recognized by the Nobel Commi ...
"Genetic Methods of Polymer Synthesis". In: Encyclopedia of
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
Systemic Delivery of siRNA by a Plant PHLOEM SMALL RNA
... (a) and (b) Total proteins were extracted from infected tissues (A) and phloem exudate (B) of pumpkin plants in which c-Myc4-His8 tagged rbcS, GFP, CmPSRP1 WT, Qm and ∆C were expressed using a ZYMV vector. Total proteins extracted from infected tissues (10 µg) and phloem exudate (40 µg) were separa ...
... (a) and (b) Total proteins were extracted from infected tissues (A) and phloem exudate (B) of pumpkin plants in which c-Myc4-His8 tagged rbcS, GFP, CmPSRP1 WT, Qm and ∆C were expressed using a ZYMV vector. Total proteins extracted from infected tissues (10 µg) and phloem exudate (40 µg) were separa ...
669 Salmonella typhimurium - Journal of General Virology
... Immediately after binding, the tail proteins begin to cleave the O antigen. As the rhamnosylgalactose linkages are cleaved, the proteins apparently migrate down the chain. This is based on the fact that when unattached tail protein is bound to ceils, it is not found free in the medium until some tim ...
... Immediately after binding, the tail proteins begin to cleave the O antigen. As the rhamnosylgalactose linkages are cleaved, the proteins apparently migrate down the chain. This is based on the fact that when unattached tail protein is bound to ceils, it is not found free in the medium until some tim ...
pH - TeacherWeb
... – Dissolves and dissociates ionic substances – Forms layers around large charged molecules, e.g., proteins (colloid formation) – Body’s major transport medium – Most biological molecules are happy in it (uhm, dissolve!) ...
... – Dissolves and dissociates ionic substances – Forms layers around large charged molecules, e.g., proteins (colloid formation) – Body’s major transport medium – Most biological molecules are happy in it (uhm, dissolve!) ...
Role of the ubiquitinselective CDC48UFD1/NPL4 chaperone
... Sigurd Braun1, Kai Matuschewski2,3, Michael Rape1, Sven Thoms2,4 and ...
... Sigurd Braun1, Kai Matuschewski2,3, Michael Rape1, Sven Thoms2,4 and ...
Ion homeostasis, channels, and transporters: an update on cellular
... that these effects of PTX on erythrocyte ion homeostasis were substantially attenuated by the presence of ouabain, the classical and highly selective inhibitor of the Na⫹-K⫹-ATPase. Subsequent biochemical and physiological analyses over the past 20 years have identified the Na⫹-K⫹-ATPase as the majo ...
... that these effects of PTX on erythrocyte ion homeostasis were substantially attenuated by the presence of ouabain, the classical and highly selective inhibitor of the Na⫹-K⫹-ATPase. Subsequent biochemical and physiological analyses over the past 20 years have identified the Na⫹-K⫹-ATPase as the majo ...
The Origin of the Genetic Code
... represent more than one amino acid. Of course, it is known that mutations can produce errors in the translation mechanism and so make certain codons ambiguous, but it is not known whether ambiguity occurs "normally". Again in what follows I shall assume that this is not usually the case for present- ...
... represent more than one amino acid. Of course, it is known that mutations can produce errors in the translation mechanism and so make certain codons ambiguous, but it is not known whether ambiguity occurs "normally". Again in what follows I shall assume that this is not usually the case for present- ...
Phylogeny of Geminiviruses - Journal of General Virology
... whitefly- and leafhopper-transmitted geminiviruses (Thomas et al., 1986). These observations, together with the fact that coat protein is the only protein that has been purified from most geminiviruses, limits the usefulness of a serological approach in a comparative study. We have overcome these pr ...
... whitefly- and leafhopper-transmitted geminiviruses (Thomas et al., 1986). These observations, together with the fact that coat protein is the only protein that has been purified from most geminiviruses, limits the usefulness of a serological approach in a comparative study. We have overcome these pr ...
Document
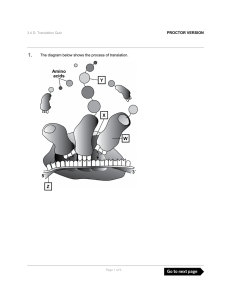
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
Study of the arginine repressor in different organisms
... stearothermophilus (ArgRBst, Fig. 1) [3] and Bacillus subtilis (AhrCBsu) [4] have been solved. Notwithstanding the low amino acid sequence identity they all have the same fold: a N-terminal DNA binding domain is connected via a short linker to a C-terminal domain involved in binding of arginine and ...
... stearothermophilus (ArgRBst, Fig. 1) [3] and Bacillus subtilis (AhrCBsu) [4] have been solved. Notwithstanding the low amino acid sequence identity they all have the same fold: a N-terminal DNA binding domain is connected via a short linker to a C-terminal domain involved in binding of arginine and ...
PLoS Pathogens
... pathogenic bacteria, but also influence symbiotic interactions between nitrogen-fixing nodule bacteria (rhizobia) and leguminous host plants. In this study, we characterized NopM (nodulation outer protein M) of Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, which shows sequence similarities with novel E3 ubiquitin li ...
... pathogenic bacteria, but also influence symbiotic interactions between nitrogen-fixing nodule bacteria (rhizobia) and leguminous host plants. In this study, we characterized NopM (nodulation outer protein M) of Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, which shows sequence similarities with novel E3 ubiquitin li ...
the incorporation of c from sodium acetate- 2
... Text-fig. 1. Tracing of chromatogram of C. briggsae amino acids (Exp. 2). ...
... Text-fig. 1. Tracing of chromatogram of C. briggsae amino acids (Exp. 2). ...
CDPKs – a kinase for every Ca signal?
... Fig. 2. Unrooted phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between the CDPK superfamily, plant SNF1-like kinases, and the most closely related animal kinases, the calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs). Calcium and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CcaMKs) and the single plant CaMK (No. 7 ...
... Fig. 2. Unrooted phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between the CDPK superfamily, plant SNF1-like kinases, and the most closely related animal kinases, the calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs). Calcium and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CcaMKs) and the single plant CaMK (No. 7 ...
characterization of proteins from the cytoskeleton of giardia lamblia
... running buffer, the absorbance profile at 280 nm had four close protein peaks followed by a complex salt peak. When column fractions were individually concentrated and analysed by SDS/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, it was apparent that proteins had eluted in the order corresponding to their mon ...
... running buffer, the absorbance profile at 280 nm had four close protein peaks followed by a complex salt peak. When column fractions were individually concentrated and analysed by SDS/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, it was apparent that proteins had eluted in the order corresponding to their mon ...
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... Overview of Amino Acid Biosynthesis Arginine is listed as an essential amino acid because humans require arginine in their diet to support rapid growth during childhood and pregnancy. However, arginine is actually generated from argininosuccinate in the urea cycle, which means that a small amount o ...
... Overview of Amino Acid Biosynthesis Arginine is listed as an essential amino acid because humans require arginine in their diet to support rapid growth during childhood and pregnancy. However, arginine is actually generated from argininosuccinate in the urea cycle, which means that a small amount o ...
(From The Rockefdler Institute) Experimental
... The amino acid composition of twice recrystallized pepsin (Worthington Biochemical Corporation) has been determined chromatographicaUy on columns of Amberlite IF, 120 resin. The results of the analyses obtained on four different preparations indicate a close agreement in their amino acid composition ...
... The amino acid composition of twice recrystallized pepsin (Worthington Biochemical Corporation) has been determined chromatographicaUy on columns of Amberlite IF, 120 resin. The results of the analyses obtained on four different preparations indicate a close agreement in their amino acid composition ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.