Review Process - Molecular Systems Biology
... Action: As suggested, we have added a figure to the supplement (Suppl. Fig. 7) to show the relation between rank and q-value more clearly. d: Some statement of how likely it is that they would come up with an example with that association Q-value, given their additional filters for Novelty or other ...
... Action: As suggested, we have added a figure to the supplement (Suppl. Fig. 7) to show the relation between rank and q-value more clearly. d: Some statement of how likely it is that they would come up with an example with that association Q-value, given their additional filters for Novelty or other ...
A new subfamily of fungal subtilases: structural and functional
... prokaryotic subtilases, many members of this superfamily have been identified in eukaryotes such as fungi, plants, insects and mammals. Pleurotus ostreatus and Phanerochaete chrysosporium are white-rot basidiomycetes, which belong to different subclasses of ligninolytic micro-organisms, producing di ...
... prokaryotic subtilases, many members of this superfamily have been identified in eukaryotes such as fungi, plants, insects and mammals. Pleurotus ostreatus and Phanerochaete chrysosporium are white-rot basidiomycetes, which belong to different subclasses of ligninolytic micro-organisms, producing di ...
Dynamin and the Actin Cytoskeleton Cooperatively Regulate
... These observations prompted us to carry out a more systematic comparison between BAR domain- and FCH domain-containing proteins. Sequence comparisons and structural predictions suggested that the FCH domain, together with the CC region that typically follows this domain, define a protein module simi ...
... These observations prompted us to carry out a more systematic comparison between BAR domain- and FCH domain-containing proteins. Sequence comparisons and structural predictions suggested that the FCH domain, together with the CC region that typically follows this domain, define a protein module simi ...
Polypeptide Composition of Envelopes of Spinach Chloroplasts
... Preparation of intact chloroplasts—Spinach was purchased from a local farmer. Intact chloroplasts were prepared according to Siegenthaler and Dumont (1990) with some modifications. Leaves were homogenized for 10 s in the grinding medium containing 350 mM sorbitol, 25 mM 3-(/V-morpholino)propanesufon ...
... Preparation of intact chloroplasts—Spinach was purchased from a local farmer. Intact chloroplasts were prepared according to Siegenthaler and Dumont (1990) with some modifications. Leaves were homogenized for 10 s in the grinding medium containing 350 mM sorbitol, 25 mM 3-(/V-morpholino)propanesufon ...
Adaptation and Protein Quality Control Under Metalloid
... having ecological consequences as well as being linked to a broad range of degenerative conditions in animals, plants and humans. While the toxicity of several metalloids is well established, the underlying molecular mechanisms are often not clear. Several human degenerative diseases are linked to m ...
... having ecological consequences as well as being linked to a broad range of degenerative conditions in animals, plants and humans. While the toxicity of several metalloids is well established, the underlying molecular mechanisms are often not clear. Several human degenerative diseases are linked to m ...
Evolution of the eukaryotic membrane
... (vesicular, tubular or otherwise) that export material from a particular organelle for delivery to another compartment in a highly specific manner (McMahon and Mills, 2004; Robinson, 2004). Protein factors including SNAREs, tethering complexes, syntaxin-binding proteins [also known as Sec1/Munc18 (S ...
... (vesicular, tubular or otherwise) that export material from a particular organelle for delivery to another compartment in a highly specific manner (McMahon and Mills, 2004; Robinson, 2004). Protein factors including SNAREs, tethering complexes, syntaxin-binding proteins [also known as Sec1/Munc18 (S ...
Overexpression of yeast karyopherin Pse1p/Kap121p stimulates the
... The majority of mitochondrial proteins are encoded by the nuclear genome, translated in the cytoplasm, and translocated into the organelle. However, all the mitochondrial genomes known so far always contain two genes, coding for apocytochrome b and for the subunit I of cytochrome oxidase. This speci ...
... The majority of mitochondrial proteins are encoded by the nuclear genome, translated in the cytoplasm, and translocated into the organelle. However, all the mitochondrial genomes known so far always contain two genes, coding for apocytochrome b and for the subunit I of cytochrome oxidase. This speci ...
Chem ppt for lecture, part 2 File
... acids together are broken when water is added to the bond. Figure 2.18 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... acids together are broken when water is added to the bond. Figure 2.18 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Amino acid Catabolism
... the synthesis of urea, which is quantitatively the most important route for disposing of nitrogen from the body. • In the second phase of amino acid catabolism, the carbon skeletons of the α-ketoacids are converted to common intermediates of energy producing, metabolic pathways. These compounds can ...
... the synthesis of urea, which is quantitatively the most important route for disposing of nitrogen from the body. • In the second phase of amino acid catabolism, the carbon skeletons of the α-ketoacids are converted to common intermediates of energy producing, metabolic pathways. These compounds can ...
Nucleic Acid and Protein Quantitation Methods
... detection. For dsDNA, the common methods include Hoechst, and Invitrogen Quant-iT PicoGreen®, Broad Range, and High Sensitivity dsDNA kits. These dyes have different excitation/emission profiles (Table 1) which may be more or less convenient depending on the individual application. Hoechst can be le ...
... detection. For dsDNA, the common methods include Hoechst, and Invitrogen Quant-iT PicoGreen®, Broad Range, and High Sensitivity dsDNA kits. These dyes have different excitation/emission profiles (Table 1) which may be more or less convenient depending on the individual application. Hoechst can be le ...
Biological electron-transfer reactions
... Electron-transfer reactions are characteristic features of a variety of fundamental biological processes that include energy metabolism (photosynthesis, respiration, nitrogen fixation), hormone (steroids, prostaglandins) biosynthesis and xenobiotic detoxification. For most of the proteins involved i ...
... Electron-transfer reactions are characteristic features of a variety of fundamental biological processes that include energy metabolism (photosynthesis, respiration, nitrogen fixation), hormone (steroids, prostaglandins) biosynthesis and xenobiotic detoxification. For most of the proteins involved i ...
Chapter 5 - Red Hook Central Schools
... Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, defense against foreign substances, and organic catalysts ...
... Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, defense against foreign substances, and organic catalysts ...
Optimal Dietary Protein Levels in Juvenile Electric Blue Cichlid
... A feeding trial was conducted to determine the dietary protein requirement of juvenile electric blue cichlids (Sciaenochromis fryeri). Groups of fish (0.50±0.01 g) were fed one of four isocaloric diets containing protein levels ranging 35-50% for 12 weeks. According to the broken-line model, the die ...
... A feeding trial was conducted to determine the dietary protein requirement of juvenile electric blue cichlids (Sciaenochromis fryeri). Groups of fish (0.50±0.01 g) were fed one of four isocaloric diets containing protein levels ranging 35-50% for 12 weeks. According to the broken-line model, the die ...
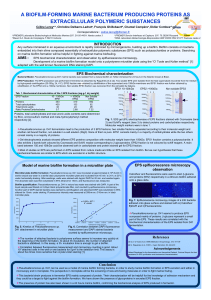
A biofilm-forming marine bacterium producing proteins
... another cell bound fraction, non soluble in a salt solution (36g/l). None of them is pure. EPS1 consists mainly in a majority of carbohydrates while the two others consist mainly in a majority of proteins. Gel electrophoresis analysis showed different EPS proteins composition with molecular weight ...
... another cell bound fraction, non soluble in a salt solution (36g/l). None of them is pure. EPS1 consists mainly in a majority of carbohydrates while the two others consist mainly in a majority of proteins. Gel electrophoresis analysis showed different EPS proteins composition with molecular weight ...
File
... • Consists of a single RNA strand that is only about 80 nucleotides long • Each carries a specific amino acid on one end and has an anticodon on the other end • A special group of enzymes pairs up the proper tRNA molecules with their corresponding amino acids. • tRNA brings the amino acids to the ri ...
... • Consists of a single RNA strand that is only about 80 nucleotides long • Each carries a specific amino acid on one end and has an anticodon on the other end • A special group of enzymes pairs up the proper tRNA molecules with their corresponding amino acids. • tRNA brings the amino acids to the ri ...
The Use of Multiple Transcription Starts Causes the Dual Targeting
... Fig. 2 RT-PCR experiments showing the existence of two mRNAs originating from a PMDAR gene. (A) Genome sequence of the 5¢ region corresponding to PMDAR-L and PMDAR-S mRNAs. Protein-coding sequences are underlined and their corresponding amino acid sequences are described below them. Start codons, AT ...
... Fig. 2 RT-PCR experiments showing the existence of two mRNAs originating from a PMDAR gene. (A) Genome sequence of the 5¢ region corresponding to PMDAR-L and PMDAR-S mRNAs. Protein-coding sequences are underlined and their corresponding amino acid sequences are described below them. Start codons, AT ...
Protein 4.1, a component of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton and
... Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Wroc³aw, Wroc³aw, Poland Abstract: The review is focused on the domain structure and function of protein 4.1, one of the proteins belonging to the membrane skeleton. The protein 4.1 of the red blood cells (4.1R) is a multifunctional protein that localizes to t ...
... Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Wroc³aw, Wroc³aw, Poland Abstract: The review is focused on the domain structure and function of protein 4.1, one of the proteins belonging to the membrane skeleton. The protein 4.1 of the red blood cells (4.1R) is a multifunctional protein that localizes to t ...
Chemistry in living systems
... chemoselective drug assembly in the presence of living cells53, 54, 55. They reported that decanal and octyl aminoguanidine—both independently harmless to cells—react selectively to form a hydrazone-linked detergent capable of lysing cultured erythrocytes. This same strategy was used to generate inh ...
... chemoselective drug assembly in the presence of living cells53, 54, 55. They reported that decanal and octyl aminoguanidine—both independently harmless to cells—react selectively to form a hydrazone-linked detergent capable of lysing cultured erythrocytes. This same strategy was used to generate inh ...
Enzyme changes in malnutrition - Journal of Clinical Pathology
... This work was entirely empirical; later work was at least guided by some more definite objective or hypothesis. For example, our studies of oxidative phosphorylation in the liver (Waterlow, 1961) were based on the idea that protein deficiency might interfere with an overall reaction which depended u ...
... This work was entirely empirical; later work was at least guided by some more definite objective or hypothesis. For example, our studies of oxidative phosphorylation in the liver (Waterlow, 1961) were based on the idea that protein deficiency might interfere with an overall reaction which depended u ...
Identification of Antigenic Regions of Duck Hepatitis B Virus Core
... The induction of humoral response in ducks by DNA-based immunization against duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) core protein (DHBc) was investigated. In addition, the amino acid specificity of the induced response was compared by using peptide scanning to that elicited either by protein immunization or d ...
... The induction of humoral response in ducks by DNA-based immunization against duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) core protein (DHBc) was investigated. In addition, the amino acid specificity of the induced response was compared by using peptide scanning to that elicited either by protein immunization or d ...
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ
... 1.2 Course short description Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solv ...
... 1.2 Course short description Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solv ...
`Hybrid Protein Model`for optimally defining 3D protein structure
... Protein prediction is based first and foremost on an accurate knowledge of the available protein structures. These structures may be studied at different levels: (i) local, on the basis of its classical secondary structures (3state coding) or of a ‘structural alphabet’ (n-state coding, n > 3); (ii) ...
... Protein prediction is based first and foremost on an accurate knowledge of the available protein structures. These structures may be studied at different levels: (i) local, on the basis of its classical secondary structures (3state coding) or of a ‘structural alphabet’ (n-state coding, n > 3); (ii) ...
Evolutionary Relationships and Protein Domain Architecture in an
... lower eukaryotes. Genetic evidence shows that many of these atypical calpains are, like conventional calpains, involved in signal transduction cascades, tissue differentiation, and sex determination. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the calpain-like protein TRA-3 is involved in a pathway leading to female ...
... lower eukaryotes. Genetic evidence shows that many of these atypical calpains are, like conventional calpains, involved in signal transduction cascades, tissue differentiation, and sex determination. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the calpain-like protein TRA-3 is involved in a pathway leading to female ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.