Characterizing the complexity of enzymes on the basis of their
... active site. Cofactors, both metal ions and small organic molecules, offer an extension of the catalytic power of enzymes. Recently, we have extended the MACiE database to include Metal-MACiE [7,31], in order to fully categorize and annotate the metal ions in MACiE, and their roles and functions. We ...
... active site. Cofactors, both metal ions and small organic molecules, offer an extension of the catalytic power of enzymes. Recently, we have extended the MACiE database to include Metal-MACiE [7,31], in order to fully categorize and annotate the metal ions in MACiE, and their roles and functions. We ...
Homework Solutions
... Use Figure 21.10 to determine which types of intermolecular forces occur between each amino acid pair. a. isoleucine and valine: London dispersion forces of the nonpolar side chains b. threonine and phenylalanine: London dispersion forces. Since the side chain of phenylalanine has no O or N atom, no ...
... Use Figure 21.10 to determine which types of intermolecular forces occur between each amino acid pair. a. isoleucine and valine: London dispersion forces of the nonpolar side chains b. threonine and phenylalanine: London dispersion forces. Since the side chain of phenylalanine has no O or N atom, no ...
Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism
... • Short term: Carbamoyl‐P synthetase is allosterically activated by N‐ acetylglutamate, which is made from glutamate + acetyl‐CoA. • Glutamate level is representative of cell’s ammonia level, as the one of the first steps of amino acid degradation is transamination to glutamate. • Carbamoyl‐P synt ...
... • Short term: Carbamoyl‐P synthetase is allosterically activated by N‐ acetylglutamate, which is made from glutamate + acetyl‐CoA. • Glutamate level is representative of cell’s ammonia level, as the one of the first steps of amino acid degradation is transamination to glutamate. • Carbamoyl‐P synt ...
Lesson 2 - The George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences
... Orthologs – 2 homologs from different species ...
... Orthologs – 2 homologs from different species ...
HOW TO USE BAD: A BRIEF PRESENTATION
... because of its widespread use. The relationship between the empirically measured contact angle and surface tension has been also described. When the original publication does not report the contact angle, its value is assumed to be equal to that reported by the same author(s) in a related paper; or ...
... because of its widespread use. The relationship between the empirically measured contact angle and surface tension has been also described. When the original publication does not report the contact angle, its value is assumed to be equal to that reported by the same author(s) in a related paper; or ...
IL-13 - York College of Pennsylvania
... IL-13 ligand has been experimentally attached to other proteins to produce a new fusion or ‘chimera’ protein. By successfully developing a fused protein consisting of more than one active part, researchers have been able to successfully develop a single protein with multiple functions and potential ...
... IL-13 ligand has been experimentally attached to other proteins to produce a new fusion or ‘chimera’ protein. By successfully developing a fused protein consisting of more than one active part, researchers have been able to successfully develop a single protein with multiple functions and potential ...
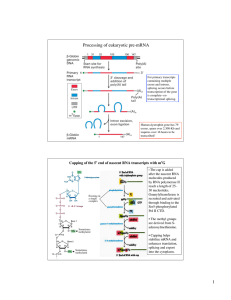
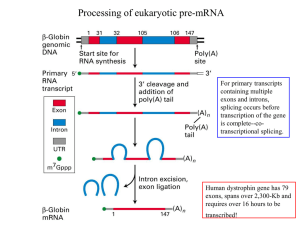
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
Genes Dev - The Jenny Lab
... Z68297) and finally to a putative Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein (40% identity, 60.5% similarity; YPR107c, GenBank accession no. U32445). As shown in Figure 1A, all these proteins share the same five C3-H repeats and highly conserved spacing between the single zinc fingers. The zinc knuckle domain ...
... Z68297) and finally to a putative Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein (40% identity, 60.5% similarity; YPR107c, GenBank accession no. U32445). As shown in Figure 1A, all these proteins share the same five C3-H repeats and highly conserved spacing between the single zinc fingers. The zinc knuckle domain ...
Mitochondrial quality control by the ubiquitin
... of both nuclear- and mitochondrially encoded proteins. The double membrane structure of mitochondria results in several distinct mitochondrial compartments, the matrix, the inner membrane, the intermembrane space and the outer membrane. Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins must be translocated fro ...
... of both nuclear- and mitochondrially encoded proteins. The double membrane structure of mitochondria results in several distinct mitochondrial compartments, the matrix, the inner membrane, the intermembrane space and the outer membrane. Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins must be translocated fro ...
alignment-2005
... can be more informative than DNA • protein is more informative (20 vs 4 characters); many amino acids share related biophysical properties • codons are degenerate: changes in the third position often do not alter the amino acid that is specified CGX codes for ARG (Arginine) where X is one of AGCT • ...
... can be more informative than DNA • protein is more informative (20 vs 4 characters); many amino acids share related biophysical properties • codons are degenerate: changes in the third position often do not alter the amino acid that is specified CGX codes for ARG (Arginine) where X is one of AGCT • ...
ppt - Vanderbilt University
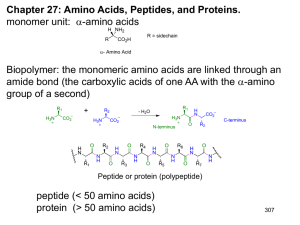
... 27.8: Introduction to Peptide Structure Determination. Protein Structure: primary (1°) structure: the amino acid sequence secondary (2°): frequently occurring substructures or folds tertiary (3°): three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain quaternary (4°): overall orga ...
... 27.8: Introduction to Peptide Structure Determination. Protein Structure: primary (1°) structure: the amino acid sequence secondary (2°): frequently occurring substructures or folds tertiary (3°): three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain quaternary (4°): overall orga ...
Plant hormone receptors: new perceptions
... The TIR1 and AFB proteins are nuclear localized and exhibit typical F-box protein architecture, having an Nterminal F-box domain that mediates interactions with the SKP1 SCF subunit, followed by a series of leucinerich repeats (LRRs) that comprise the substrate-binding domain. Crucial insight into h ...
... The TIR1 and AFB proteins are nuclear localized and exhibit typical F-box protein architecture, having an Nterminal F-box domain that mediates interactions with the SKP1 SCF subunit, followed by a series of leucinerich repeats (LRRs) that comprise the substrate-binding domain. Crucial insight into h ...
2-Oxoacid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes
... 1984 ; Pratt et al., 1989). The only known function of DHLipDH is as the third enzyme component of the ODHCs along with the glycine cleavage system, the activity of which has also not been reported in the Archaea (reviewed by Danson, 1988, 1993). The gene encoding DHLipDH from Haloferax volcanii has ...
... 1984 ; Pratt et al., 1989). The only known function of DHLipDH is as the third enzyme component of the ODHCs along with the glycine cleavage system, the activity of which has also not been reported in the Archaea (reviewed by Danson, 1988, 1993). The gene encoding DHLipDH from Haloferax volcanii has ...
Stress puts TIA on TOP
... 59TOP mRNAs are regulated in a tissue- and cell typespecific manner. For example, eEF2 mRNA confers growthdependent regulation in cells of hematopoietic, but not in cells of nonhematopoietic, origins, while translation of b1-tubulin mRNA, which possesses all classical features of TOP mRNAs, is absol ...
... 59TOP mRNAs are regulated in a tissue- and cell typespecific manner. For example, eEF2 mRNA confers growthdependent regulation in cells of hematopoietic, but not in cells of nonhematopoietic, origins, while translation of b1-tubulin mRNA, which possesses all classical features of TOP mRNAs, is absol ...
Capabilities and limitations of gel electrophoresis for elemental
... concentration, V is transported by transferrin, forming one of the most labile metal complexes of this protein. However, if transferrin, previously incubated with 48V as vanadate, was submitted to native gel electrophoresis, V was detected at the anode and was hence no longer bound to transferrin, a ...
... concentration, V is transported by transferrin, forming one of the most labile metal complexes of this protein. However, if transferrin, previously incubated with 48V as vanadate, was submitted to native gel electrophoresis, V was detected at the anode and was hence no longer bound to transferrin, a ...
投影片 1
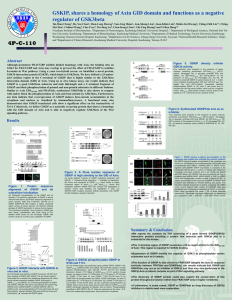
... Figure 7. GSKIP causes b-catenin accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus and activates the reporter systems. (A) GSKIP induces b-catenin accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus as visualized by immunofluorescence. HeLa cells were co-transfected with GSKIP, GSKIP(L130P) or pIRES vector, together ...
... Figure 7. GSKIP causes b-catenin accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus and activates the reporter systems. (A) GSKIP induces b-catenin accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus as visualized by immunofluorescence. HeLa cells were co-transfected with GSKIP, GSKIP(L130P) or pIRES vector, together ...
Plant mitochondria contain the protein translocase subunits TatB
... It has been known for more than 20 years that the Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondrial genome contains a gene encoding for a TatC like protein (although it is also known as either orfX or Mttb) (Sunkel et al., 1994, Unseld et al., 1997). However, no functional data has ever been ascribed to it. One of ...
... It has been known for more than 20 years that the Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondrial genome contains a gene encoding for a TatC like protein (although it is also known as either orfX or Mttb) (Sunkel et al., 1994, Unseld et al., 1997). However, no functional data has ever been ascribed to it. One of ...
The Strategic Use of Ruminally Protected Amino Acids in Dairy
... by weight. We (Patton et al., 2003) found in a meta-analysis of experiments that neither MET or LYS as a percent of MP were correlated with milk protein percent (Figures 1 and 2). Further, longer term experiments attempting to increase the milk protein by increasing MET and LYS as a % of MP with rum ...
... by weight. We (Patton et al., 2003) found in a meta-analysis of experiments that neither MET or LYS as a percent of MP were correlated with milk protein percent (Figures 1 and 2). Further, longer term experiments attempting to increase the milk protein by increasing MET and LYS as a % of MP with rum ...
Lecture 15: Processing of viral pre-mRNA
... – Can encode 5’ genes, e.g. gag-pol of retroviruses Can be used as ‘genomes’ for packaging inside of nascent viral particles (e.g. retroviruses) ...
... – Can encode 5’ genes, e.g. gag-pol of retroviruses Can be used as ‘genomes’ for packaging inside of nascent viral particles (e.g. retroviruses) ...
Scavenging of 14-3-3 proteins reveals their involvement in the cell
... al., 2003). Thus, we next asked whether 14-3-3 scavenging only affected the cell-surface transport of KATP channels when Arg-based signals are present in the channel complex. For these experiments, we used a SUR1-Kir6.2 fusion protein, in which the C-terminus of SUR1 was linked to the N-terminus of ...
... al., 2003). Thus, we next asked whether 14-3-3 scavenging only affected the cell-surface transport of KATP channels when Arg-based signals are present in the channel complex. For these experiments, we used a SUR1-Kir6.2 fusion protein, in which the C-terminus of SUR1 was linked to the N-terminus of ...
EVALUATION OF ANTIOXIDANT AND ANTI-ARTHRITIC ACTIVITIES OF SOME 2-ARYLAMINOTHIAZOLE DERIVATIVES
... minimum side effects [2]. It has been established that in many inflammatory disorders, there is excessive activation of phagocytes, production of reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide (O2.), hydroxyl (OH.) and peroxyl (OOH., ROO.) radicals as well as non‐free radical species (H2O2) which can h ...
... minimum side effects [2]. It has been established that in many inflammatory disorders, there is excessive activation of phagocytes, production of reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide (O2.), hydroxyl (OH.) and peroxyl (OOH., ROO.) radicals as well as non‐free radical species (H2O2) which can h ...
“Nice” plotting of proteins
... get a much smoother and better views of protein structures? Polynomial fits are sound if higher order derivatives of the “true” function (beyond the order of the polynomial) do not contribute significantly to the description of the function. However, the reverse is also true… If high order derivativ ...
... get a much smoother and better views of protein structures? Polynomial fits are sound if higher order derivatives of the “true” function (beyond the order of the polynomial) do not contribute significantly to the description of the function. However, the reverse is also true… If high order derivativ ...
Review Process - Molecular Systems Biology
... Action: As suggested, we have added a figure to the supplement (Suppl. Fig. 7) to show the relation between rank and q-value more clearly. d: Some statement of how likely it is that they would come up with an example with that association Q-value, given their additional filters for Novelty or other ...
... Action: As suggested, we have added a figure to the supplement (Suppl. Fig. 7) to show the relation between rank and q-value more clearly. d: Some statement of how likely it is that they would come up with an example with that association Q-value, given their additional filters for Novelty or other ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.