www.d3technologies.co.uk
... Typical SERS spectra for the Alanine, Phenylanine and Cysteine are shown in Figure.4 (a), (b) and (c) respectively. The main vibrational modes of each analyte are clearly identifiable. The typical skeleton torsional and stretching modes of L-Alanine in the 400-1000 cm-1 range is shown in Figure. 4 ( ...
... Typical SERS spectra for the Alanine, Phenylanine and Cysteine are shown in Figure.4 (a), (b) and (c) respectively. The main vibrational modes of each analyte are clearly identifiable. The typical skeleton torsional and stretching modes of L-Alanine in the 400-1000 cm-1 range is shown in Figure. 4 ( ...
1 - Wikispaces
... © Methanoic is produced when the ester, methyl ethanoate reacts with sodium hydroxide solution. CH3COOCH3 + NaOH ...
... © Methanoic is produced when the ester, methyl ethanoate reacts with sodium hydroxide solution. CH3COOCH3 + NaOH ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, _ ...
... and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, _ ...
AP Protein synthesis
... • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA: – A site- holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain – P site- holds the tRNA that carries the growing ...
... • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA: – A site- holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain – P site- holds the tRNA that carries the growing ...
Engineering the Genetic Code. Expanding the Amino Acid Repertoire for... Design of Novel Proteins Brochure
... The researchers and students are provided with a comprehensive coverage of important new principles of different methods and strategies to incorporate new or modified amino acids into proteins including a lot of practical advice for first–time users of these powerful approaches. Numerous examples, m ...
... The researchers and students are provided with a comprehensive coverage of important new principles of different methods and strategies to incorporate new or modified amino acids into proteins including a lot of practical advice for first–time users of these powerful approaches. Numerous examples, m ...
Monomers are atoms or small molecules that bond together to form
... Amino Acids: The building blocks of protein. Amino acids are the monomers that build a polymer called protein. There are 20 amino acid monomers but they all have a general structure of: à A Central Carbon (C) à An Amino group (NH3) à A carboxyl or acid (COO-) à A Hydrogen (H à The R group (20 diff ...
... Amino Acids: The building blocks of protein. Amino acids are the monomers that build a polymer called protein. There are 20 amino acid monomers but they all have a general structure of: à A Central Carbon (C) à An Amino group (NH3) à A carboxyl or acid (COO-) à A Hydrogen (H à The R group (20 diff ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... DNA Structure and Replication In the mid-1900s, scientists knew that chromosomes, made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and proteins, contained genetic information. However, they did not know whether the DNA or the protein was the actual genetic material. ...
... DNA Structure and Replication In the mid-1900s, scientists knew that chromosomes, made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and proteins, contained genetic information. However, they did not know whether the DNA or the protein was the actual genetic material. ...
No Slide Title
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
Answer Key for Final Exam
... 11. Consider all the data shown below, and determine the structure of the unknown molecule. Assign every peak in the 1H NMR and 13C NMR to atoms in the molecule. Also identify key peak(s) in the IR spectrum and MS spectrum (20 points). Molecular formula: C11H14O2 ...
... 11. Consider all the data shown below, and determine the structure of the unknown molecule. Assign every peak in the 1H NMR and 13C NMR to atoms in the molecule. Also identify key peak(s) in the IR spectrum and MS spectrum (20 points). Molecular formula: C11H14O2 ...
13-2 PowerPoint
... The Molecular Basis of Heredity One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the near-universal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the sam ...
... The Molecular Basis of Heredity One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the near-universal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the sam ...
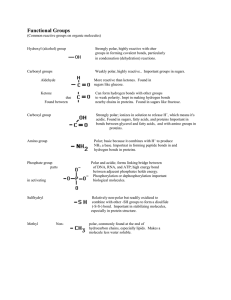
Functional Groups List
... Strongly polar, highly reactive with oher groups in forming covalent bonds, particularly in condensation (dehydration) reactions. ...
... Strongly polar, highly reactive with oher groups in forming covalent bonds, particularly in condensation (dehydration) reactions. ...
Unit 1 Objectives 2015
... 4. What function does nitrogen serve in proteins? In nucleic acids? 5. What function does phosphorus serve in nucleic acids? In phospholipids? 6. Why do biological systems need water? 7. How does the structure of a water molecule relate to its function(s)? 8. How does the polarity of water lead to t ...
... 4. What function does nitrogen serve in proteins? In nucleic acids? 5. What function does phosphorus serve in nucleic acids? In phospholipids? 6. Why do biological systems need water? 7. How does the structure of a water molecule relate to its function(s)? 8. How does the polarity of water lead to t ...
Transcription and Translation
... • Ribosomal RNAs – (rRNA) makes us the ribosome. Each ribosome consists of about 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein. • Messenger RNAs – (mRNA) "record" information from DNA in the cell nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. • Transfer RNAs- (tRNA) delivers amino acids one by one to protein chains gro ...
... • Ribosomal RNAs – (rRNA) makes us the ribosome. Each ribosome consists of about 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein. • Messenger RNAs – (mRNA) "record" information from DNA in the cell nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. • Transfer RNAs- (tRNA) delivers amino acids one by one to protein chains gro ...
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA - Tenafly Public Schools
... P. 185 – mRNA gets “read” at ribosome and “translated” into an amino acid sequence ...
... P. 185 – mRNA gets “read” at ribosome and “translated” into an amino acid sequence ...
Document
... • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siRNA or miRNA component and either: - cleaves the mRNA (leading to degradation or mRNA) or - represses transla ...
... • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siRNA or miRNA component and either: - cleaves the mRNA (leading to degradation or mRNA) or - represses transla ...
Objectives • Explain the "one gene–one polypeptide" hypothesis
... There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. This same genetic coding system is shared by almost all organisms. In experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after being transferred from one species to another, even when t ...
... There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. This same genetic coding system is shared by almost all organisms. In experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after being transferred from one species to another, even when t ...
Terminator
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS What is a gene?
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
NOTES: 13.1-13.2 - Protein Synthesis (powerpoint)
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
Asymptotics of RNA Shapes: secondary structure
... Computational molecular biology is concerned with the development of mathematical models and novel algorithms to solve fundamental problems of molecular biology in the post-genome era. A central problem of structural biology concerns the algorithmic prediction of the structure of RNA and protein fro ...
... Computational molecular biology is concerned with the development of mathematical models and novel algorithms to solve fundamental problems of molecular biology in the post-genome era. A central problem of structural biology concerns the algorithmic prediction of the structure of RNA and protein fro ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.