HW Questions on Lipids and Proteins
... 11. Where & when in your body might this reaction (mentioned above) take place? • Digestion of food in the mouth, stomach & small intestine (in digestive syst.) • During Cell Respiration in the breakdown of glucose to release energy 12. How are the concept of monomer and polymer related to monosacch ...
... 11. Where & when in your body might this reaction (mentioned above) take place? • Digestion of food in the mouth, stomach & small intestine (in digestive syst.) • During Cell Respiration in the breakdown of glucose to release energy 12. How are the concept of monomer and polymer related to monosacch ...
Drag and Drop Protein Synthesis Name Period Type in the following
... 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nucleotides, how many mRNA codons will there be? 4. The enzyme that creates mRNA from a DNA sequence is called: 5. Each codon of mRNA (hence each triplet in DNA) codes for one: 6. The specific amino acid carried by a tRNA is determined it's: 7. True or False? When ...
... 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nucleotides, how many mRNA codons will there be? 4. The enzyme that creates mRNA from a DNA sequence is called: 5. Each codon of mRNA (hence each triplet in DNA) codes for one: 6. The specific amino acid carried by a tRNA is determined it's: 7. True or False? When ...
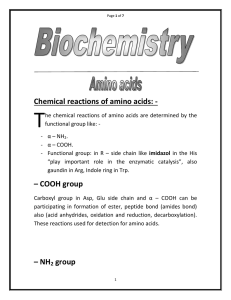
Chemical reactions of amino acids:
... Rupture and formation salts bonds accompany oxygenation and deoxygenation of Hb. The most important reaction of amino acids is peptide bond formation. The reactions involve removal of water molecule between α – NH3+ group of amino acid and COO- group of second amino acid. H ...
... Rupture and formation salts bonds accompany oxygenation and deoxygenation of Hb. The most important reaction of amino acids is peptide bond formation. The reactions involve removal of water molecule between α – NH3+ group of amino acid and COO- group of second amino acid. H ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Amides
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
Chap 3
... 1. Transcription: the RNA molecule is synthesized on a DNA template by an enzymatic process that involves several distinct events. (1) Transcription starts at a specific site to which the appropriate enzyme binds. (2) Then polymerization is initiated, followed by chain elongation. (3) Finally, chain ...
... 1. Transcription: the RNA molecule is synthesized on a DNA template by an enzymatic process that involves several distinct events. (1) Transcription starts at a specific site to which the appropriate enzyme binds. (2) Then polymerization is initiated, followed by chain elongation. (3) Finally, chain ...
Proteins
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
CH 17_ From Gene to Protein
... • Base analogs: chemicals that are similar to normal DNA bases but that pair incorrectly • Chemicals that interfere with correct DNA replication by inserting themselves into the double helix and distorting the ...
... • Base analogs: chemicals that are similar to normal DNA bases but that pair incorrectly • Chemicals that interfere with correct DNA replication by inserting themselves into the double helix and distorting the ...
DNA
... 260 nm The concentration of nucleotides and nucleic acids thus often is expressed in terms of “ABSORBANCE AT 260 nm.” ...
... 260 nm The concentration of nucleotides and nucleic acids thus often is expressed in terms of “ABSORBANCE AT 260 nm.” ...
Chapter 11 DNA and Genes
... • When m-RNA enters the cytoplasm, it has instructions for how to build proteins. These instructions are written in a (11) nitrogen base language and must be translated into a language that proteins ...
... • When m-RNA enters the cytoplasm, it has instructions for how to build proteins. These instructions are written in a (11) nitrogen base language and must be translated into a language that proteins ...
Welcome to Mrs. Gomez-Buckley General Biology Class (Room 615)
... mRNA is edited – some parts taken out (introns) mRNA goes out of nucleus to ribosome mRNA attaches to ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up an amino acid tRNA attaches to mRNA matching complementary base pairs at opposite end from amino acid Amino acid is attached to other amino acids he ...
... mRNA is edited – some parts taken out (introns) mRNA goes out of nucleus to ribosome mRNA attaches to ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up an amino acid tRNA attaches to mRNA matching complementary base pairs at opposite end from amino acid Amino acid is attached to other amino acids he ...
Lecture 9
... Sometime between 4 billion years ago and 3.5 billion years ago, the first organisms came into being. What was their origin? We don’t have fossils or other evidence to explain what the earliest life was like, therefore much of what I will present today is hypothetical. Experiments can be done that pr ...
... Sometime between 4 billion years ago and 3.5 billion years ago, the first organisms came into being. What was their origin? We don’t have fossils or other evidence to explain what the earliest life was like, therefore much of what I will present today is hypothetical. Experiments can be done that pr ...
enzymes catalysts - World of Teaching
... Synthesis reactions phosphorylase Glucose-1-phosphate Starch (Substrate) (enzyme) (product) ...
... Synthesis reactions phosphorylase Glucose-1-phosphate Starch (Substrate) (enzyme) (product) ...
Organic Chemistry (I) chapter 3 alkanes
... E. 3-butyl-5,6-dimethyloctane 3. Choose the correct IUPAC name for the following molecule. ...
... E. 3-butyl-5,6-dimethyloctane 3. Choose the correct IUPAC name for the following molecule. ...
Proteins Synthesis
... Stop codons do not code for any amino acid Reaching stop sequence causes a release factor or bind to the A-site of the ribosome and facilitates the release of the polypeptide. Small and large ribosomal units separate Polypeptide is now ready for further processing and folding! Recall, A pr ...
... Stop codons do not code for any amino acid Reaching stop sequence causes a release factor or bind to the A-site of the ribosome and facilitates the release of the polypeptide. Small and large ribosomal units separate Polypeptide is now ready for further processing and folding! Recall, A pr ...
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
... • Introns ; non coding sequence . , transcribed but not translated .also vary in sequence , number and length from one gene to anther but they are sharing the base sequence GT in the 5` end and AG in the 3` end of all introns . Promoters ; sequence of DNA nucleotides up-stream of the initial base o ...
... • Introns ; non coding sequence . , transcribed but not translated .also vary in sequence , number and length from one gene to anther but they are sharing the base sequence GT in the 5` end and AG in the 3` end of all introns . Promoters ; sequence of DNA nucleotides up-stream of the initial base o ...
a more thorough description of current interests.
... However, designing new and useful Fig. 2. Functional metallopeptides: (Path A) Proximity-driven catalytic reactivity and catalytic function remains protein modification; (Path B) Cooperative inhibition of protein– a daunting challenge. We have focused protein interactions with a hybrid organic-inorg ...
... However, designing new and useful Fig. 2. Functional metallopeptides: (Path A) Proximity-driven catalytic reactivity and catalytic function remains protein modification; (Path B) Cooperative inhibition of protein– a daunting challenge. We have focused protein interactions with a hybrid organic-inorg ...
3.5 Transcription and translation – summary of
... meaning more than one codon can code for a particular amino acid; the genetic code is universal; meaning it is the same in almost all organisms; (AUG is the) start codon; some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation; ...
... meaning more than one codon can code for a particular amino acid; the genetic code is universal; meaning it is the same in almost all organisms; (AUG is the) start codon; some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation; ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA): decodes the information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA): decodes the information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
Chemistry O`Life Notes ChemOLifenotes_2
... enzymes, regulatory, etc.) This is how enzymes work to speed up chemical reactionsjust one example... ...
... enzymes, regulatory, etc.) This is how enzymes work to speed up chemical reactionsjust one example... ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.