DNA to Protein Synthesis
... The rRNA strand is the same as the DNA strand except Us have replaced Ts ...
... The rRNA strand is the same as the DNA strand except Us have replaced Ts ...
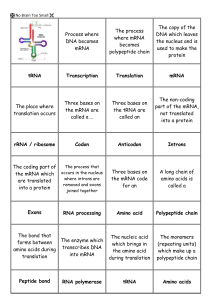
Gene expression flash cards
... The process which relates to the Which RNA is fact that more read to determine than one codon, the amino acid codes for an amino acid mRNA ...
... The process which relates to the Which RNA is fact that more read to determine than one codon, the amino acid codes for an amino acid mRNA ...
Name: :______ Genetic Mutations—Online Model Go to: http
... 2. A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the exposed codon, bringing its amino acid close to the first amino acid. 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the bond between the first tRNA molecule and it’s amino acid. 4. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the ...
... 2. A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the exposed codon, bringing its amino acid close to the first amino acid. 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the bond between the first tRNA molecule and it’s amino acid. 4. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the ...
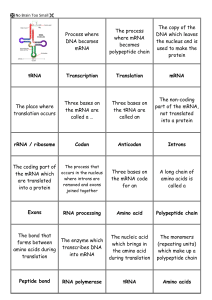
Gene expression flash cards
... The process which relates to the Which RNA is fact that more read to determine than one codon, the amino acid codes for an amino acid mRNA ...
... The process which relates to the Which RNA is fact that more read to determine than one codon, the amino acid codes for an amino acid mRNA ...
Chapter 12
... Particular base sequences in the DNA specify termination – the signal that the end of the gene has been reached and transcription can terminate. ...
... Particular base sequences in the DNA specify termination – the signal that the end of the gene has been reached and transcription can terminate. ...
Protocol S1.
... on their proximity (in this case within 4.5 Å) within the resulting folds. The amino acid contact map yielded by this process can then be used to determine the degree of fold disruption expected in any conceivable chimaera of the parental amino acid sequences. For all the amino acid residues that ar ...
... on their proximity (in this case within 4.5 Å) within the resulting folds. The amino acid contact map yielded by this process can then be used to determine the degree of fold disruption expected in any conceivable chimaera of the parental amino acid sequences. For all the amino acid residues that ar ...
4. Transcription in Detail
... The first tRNA that is brought into the P site carries _________________ because the start code is ____________. The second tRNA enters the _________ site A ____________________ bond forms between methionine and alanine. The ribosome ________________________the mRNA and adds another amino acid ...
... The first tRNA that is brought into the P site carries _________________ because the start code is ____________. The second tRNA enters the _________ site A ____________________ bond forms between methionine and alanine. The ribosome ________________________the mRNA and adds another amino acid ...
Biochemistry Outline MS Word
... b. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide used to supply energy for synthetic reactions and other energy-requiring metabolic activities in the cell. Structure of DNA and RNA 1. Nucleotides are a molecular complex of three types of molecules: a phosphate (phosphoric acid), a pentose sugar, and ...
... b. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide used to supply energy for synthetic reactions and other energy-requiring metabolic activities in the cell. Structure of DNA and RNA 1. Nucleotides are a molecular complex of three types of molecules: a phosphate (phosphoric acid), a pentose sugar, and ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
Chapter 17: Gene Expression Gene Expression DNA houses all
... o Changing introns/exons during splicing can yield different proteins o One gene = multiple products o About 20k genes & 175-200k proteins Different exons often different domains Prokaryote mRNA translated immediately ...
... o Changing introns/exons during splicing can yield different proteins o One gene = multiple products o About 20k genes & 175-200k proteins Different exons often different domains Prokaryote mRNA translated immediately ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... New nucleotides are placed in the fork and link to the corresponding parental nucleotide already there (A with T, C with G). ...
... New nucleotides are placed in the fork and link to the corresponding parental nucleotide already there (A with T, C with G). ...
Class Notes 1 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • 20 different side chains, corresponding to 20 amino acids • Divided into 3 classes: – Hydrophobic (non-polar) – Charged (weak acid or weak base) – Polar (hydrophilic) ...
... • 20 different side chains, corresponding to 20 amino acids • Divided into 3 classes: – Hydrophobic (non-polar) – Charged (weak acid or weak base) – Polar (hydrophilic) ...
Model Description Sheet
... two loops (L10 and the highly flexible L3) and two zinc ions. These zinc ions are held in place by three histidine amino acids (H120, H122, H189) on L3 and a triplet of amino acids on L10. The zinc ions bind to and sever the ß-lactam ring on carbapenems, inhibiting its antibiotic properties. It’s th ...
... two loops (L10 and the highly flexible L3) and two zinc ions. These zinc ions are held in place by three histidine amino acids (H120, H122, H189) on L3 and a triplet of amino acids on L10. The zinc ions bind to and sever the ß-lactam ring on carbapenems, inhibiting its antibiotic properties. It’s th ...
Chapter08_Outline
... • This creates a binding site for a charged tRNAMet (an initiator tRNA), bound with elongation factor eIF2, and a small 40S ribosomal subunit together with eIF3 and ...
... • This creates a binding site for a charged tRNAMet (an initiator tRNA), bound with elongation factor eIF2, and a small 40S ribosomal subunit together with eIF3 and ...
1. Overview of Gene Expression Overview of Gene Expression Chapter 10B:
... • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small percentage of genes are special types of RNA molecules) ...
... • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small percentage of genes are special types of RNA molecules) ...
Protein synthesis - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Missense mutations occur when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon (a code for a specific amino acid), resulting in the wrong amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. This can lead to disease, like sickle cell anemia. Nonsense mutations occur when a change in the DNA sequence ...
... Missense mutations occur when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon (a code for a specific amino acid), resulting in the wrong amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. This can lead to disease, like sickle cell anemia. Nonsense mutations occur when a change in the DNA sequence ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.