DNA Functions
... Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA mol ...
... Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA mol ...
Transcription and Translation
... • The first tRNA detaches and leaves it’s amino acid. • Two new tRNA with their amino acids move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
... • The first tRNA detaches and leaves it’s amino acid. • Two new tRNA with their amino acids move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
Carbohydrates
... Cholesterol = Helps maintain the fluidity of the membrane Protein Remove the water from our cells and what’s left is mostly protein! Determines the structure and function of an organism. STRUCTURE 20 different amino acids - Functional groups - carboxyl group at one end (C terminus); amino ...
... Cholesterol = Helps maintain the fluidity of the membrane Protein Remove the water from our cells and what’s left is mostly protein! Determines the structure and function of an organism. STRUCTURE 20 different amino acids - Functional groups - carboxyl group at one end (C terminus); amino ...
Document
... quite high. • Two anhydride bonds in ATP are cleaved on activation of each amino acid and synthesis of an aminoacyl-tRNA. • One GTP is required for entry of each amino acid into the ribosomal unit. ...
... quite high. • Two anhydride bonds in ATP are cleaved on activation of each amino acid and synthesis of an aminoacyl-tRNA. • One GTP is required for entry of each amino acid into the ribosomal unit. ...
Formative 3.5 2014
... Any ester with 6 carbons. Any 6 carbon carboxylic acid. (c) (i) Butan-1-ol reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to form but-1-ene and water. This is an elimination reaction. Since this is a primary alcohol with the –OH group at the end of the carbon chain there is only one possible product. Butan-2-ol is ...
... Any ester with 6 carbons. Any 6 carbon carboxylic acid. (c) (i) Butan-1-ol reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to form but-1-ene and water. This is an elimination reaction. Since this is a primary alcohol with the –OH group at the end of the carbon chain there is only one possible product. Butan-2-ol is ...
Biochemistry - Science Geek
... Proteins are large molecules that may consist of hundreds, or even thousands of amino acids. Proteins are important in cell structure, as enzymes, which speed up reactions in the body, and as antibodies which fight infection ...
... Proteins are large molecules that may consist of hundreds, or even thousands of amino acids. Proteins are important in cell structure, as enzymes, which speed up reactions in the body, and as antibodies which fight infection ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... brought by tRNA and attached to the 1st amino acid. 5.) This continues until the “Stop” codon is reached. ...
... brought by tRNA and attached to the 1st amino acid. 5.) This continues until the “Stop” codon is reached. ...
Ch. 11 - Gene Action and protein synthesis
... When two tRNA molecules are adjacent to each other, the larger subunit of the ribosome is able to form a peptide bond between the two amino acids that they carry, releasing the first of the tRNA molecules With each formation of a peptide bond, the mRNA moves along the ribosome and the next tRNA mole ...
... When two tRNA molecules are adjacent to each other, the larger subunit of the ribosome is able to form a peptide bond between the two amino acids that they carry, releasing the first of the tRNA molecules With each formation of a peptide bond, the mRNA moves along the ribosome and the next tRNA mole ...
Unit 2.1.1a - Biological Molecules
... would be TOO easy now wouldn’t it! I mean something we’ve done in Biology recently!) o ____________ ___________ also contain a carboxyl group ...
... would be TOO easy now wouldn’t it! I mean something we’ve done in Biology recently!) o ____________ ___________ also contain a carboxyl group ...
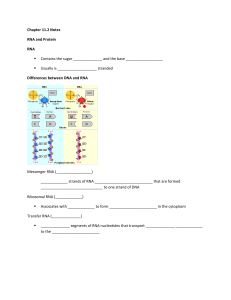
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
Name: ____________ Protein Synthesis Children`s Book Due
... Protein synthesis is one of the most important processes in an organism. As you’ve learned, it creates proteins needed for an organism to function. It is also a multi-step process that some students find difficult to remember. You, however, are going to have no problem mastering it! To simplify the ...
... Protein synthesis is one of the most important processes in an organism. As you’ve learned, it creates proteins needed for an organism to function. It is also a multi-step process that some students find difficult to remember. You, however, are going to have no problem mastering it! To simplify the ...
Three scientists who revealed the structure and workings of the
... of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) into the 20 or so amino acid members of the protein alphabet (see top box p44). For this reason, Ramakrishnan explains, ribosomes have been of central importance in biology ever since their discovery in the 1950s. ‘Virtually every molecule in the cell was either made b ...
... of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) into the 20 or so amino acid members of the protein alphabet (see top box p44). For this reason, Ramakrishnan explains, ribosomes have been of central importance in biology ever since their discovery in the 1950s. ‘Virtually every molecule in the cell was either made b ...
CYP450 Protein Assay – Human Induction Kit Extended Panel
... bound proteins that function as a major metabolizing enzyme in the human body. Quantification of CYP induction is critical in determining the disposition, safety and efficacy of drugs. It is advantageous to measure actual protein levels when performing such studies, however traditional Western blot ...
... bound proteins that function as a major metabolizing enzyme in the human body. Quantification of CYP induction is critical in determining the disposition, safety and efficacy of drugs. It is advantageous to measure actual protein levels when performing such studies, however traditional Western blot ...
Anti-MRF antibody - Oligodendrocyte Marker ab85464 Product datasheet 1 Image
... A transmembrane region is predicted by sequence analysis tools. However, the protein is nuclear and probably acts as a transcription factor. It is therefore unclear whether the predicted transmembrane region is a hydrophobic region that does not insert into membranes or whether it is a real transmem ...
... A transmembrane region is predicted by sequence analysis tools. However, the protein is nuclear and probably acts as a transcription factor. It is therefore unclear whether the predicted transmembrane region is a hydrophobic region that does not insert into membranes or whether it is a real transmem ...
overview rna, transcription, translation
... During translation, a small ribosomal subunit attaches to a mRNA molecule. At the same time, an initiator tRNA molecule recognizes and binds to a specific codon sequence on the same mRNA molecule. A large ribosomal subunit then joins the newly formed complex. The initiator tRNA resides in one bindin ...
... During translation, a small ribosomal subunit attaches to a mRNA molecule. At the same time, an initiator tRNA molecule recognizes and binds to a specific codon sequence on the same mRNA molecule. A large ribosomal subunit then joins the newly formed complex. The initiator tRNA resides in one bindin ...
DNA & THE GENETIC CODE (protein synthesis)
... • Translation involves decoding/reading the triplet message on mRNA. • Each codon, 3 bases, has a natural complementary sequence of 3 bases, called the anticodon. • This set of 3 bases is attached to a specific tRNA molecule that carries and transfers a specific amino acid. • The specific amino aci ...
... • Translation involves decoding/reading the triplet message on mRNA. • Each codon, 3 bases, has a natural complementary sequence of 3 bases, called the anticodon. • This set of 3 bases is attached to a specific tRNA molecule that carries and transfers a specific amino acid. • The specific amino aci ...
NMR experiment-driven modeling of biological macromolecules
... biomacromolecules at atomic resolution, whether these are proteins, RNA, DNA, and their complexes. Knowledge of the 3D structure is vital for understanding functions and mechanisms of action of macromolecules, and for rationalizing the effect of mutations. 3D structures are also important as guides ...
... biomacromolecules at atomic resolution, whether these are proteins, RNA, DNA, and their complexes. Knowledge of the 3D structure is vital for understanding functions and mechanisms of action of macromolecules, and for rationalizing the effect of mutations. 3D structures are also important as guides ...
DNA - California State University, Stanislaus
... • Natural sources: cosmic rays from the sun and outer space, radioactive elements in soil and terrestrial products (wood, stone) and in the atmosphere (radon) • Artificial sources of radiation which contribute to our radiation exposure. Among these are ...
... • Natural sources: cosmic rays from the sun and outer space, radioactive elements in soil and terrestrial products (wood, stone) and in the atmosphere (radon) • Artificial sources of radiation which contribute to our radiation exposure. Among these are ...
File
... - hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas that reduces the blood glucose levels by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood to the skeletal muscles and tissue - Insulin binds reversibly to receptors in the cell membrane to promote uptake - these are also known as “antibodies” - ...
... - hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas that reduces the blood glucose levels by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood to the skeletal muscles and tissue - Insulin binds reversibly to receptors in the cell membrane to promote uptake - these are also known as “antibodies” - ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.