“Ancient” Viruses
... Complementation Wild type function in a mutant defective virus restored by a gene provided from outside the virus. Helper virus, helper plasmid or engineered gene can be the source. Effective in trans only. ...
... Complementation Wild type function in a mutant defective virus restored by a gene provided from outside the virus. Helper virus, helper plasmid or engineered gene can be the source. Effective in trans only. ...
DNA
... • Exons are sections of coding DNA – i.e. they contain instructions for making proteins. • Introns are sections of non-coding DNA (once called "junk DNA") – i.e. they do not contain instructions for making proteins but are now believed to serve other important ...
... • Exons are sections of coding DNA – i.e. they contain instructions for making proteins. • Introns are sections of non-coding DNA (once called "junk DNA") – i.e. they do not contain instructions for making proteins but are now believed to serve other important ...
All in one Groups
... • Once a gene is cloned, its nucleotide sequence can be determined. • Today sequencing is carried out by sequencing machines (automated). • The first automated procedure was called the “dideeoxyribonucleotide Chain termination method.” ...
... • Once a gene is cloned, its nucleotide sequence can be determined. • Today sequencing is carried out by sequencing machines (automated). • The first automated procedure was called the “dideeoxyribonucleotide Chain termination method.” ...
Ribosome and Introduction to DNA Forensics
... 1. Ionic bonds are formed by ________________of electrons by an atom. Covalent bonds form by ________________ of electrons. the sharing 2. Cells contain four major families of small organic molecules, what are they? 1.____________ 2. nucleotides __________________3. ________________4. __________ Sug ...
... 1. Ionic bonds are formed by ________________of electrons by an atom. Covalent bonds form by ________________ of electrons. the sharing 2. Cells contain four major families of small organic molecules, what are they? 1.____________ 2. nucleotides __________________3. ________________4. __________ Sug ...
The Genetic Code
... amino acid this codon codes for! – Each code always starts with AUG (start) and ends with a stop codon! ...
... amino acid this codon codes for! – Each code always starts with AUG (start) and ends with a stop codon! ...
Jan 19
... 2) label primers with fluorescent dyes Primer for each base is a different color! A CGT 3) Load reactions in one lane 4) machine detects with laser & records order of elution ...
... 2) label primers with fluorescent dyes Primer for each base is a different color! A CGT 3) Load reactions in one lane 4) machine detects with laser & records order of elution ...
GMO lecture green slides only
... 35S promotor of the cauiliflower mosaic virus (CaMV 35s 221 bp -promoter element common in most transgenic plants. Its the “start” of a gene. Also indicates the plant is genetically ...
... 35S promotor of the cauiliflower mosaic virus (CaMV 35s 221 bp -promoter element common in most transgenic plants. Its the “start” of a gene. Also indicates the plant is genetically ...
PPT
... Each cell has a receptor on its cell surface that recognizes a specific part of a microbe. That receptor triggers a Signal transduction pathway. This triggers gene expression (transcription) that… …leads to protein synthesis (translation) that… …allows the cell to grow (duplicate all its proteins th ...
... Each cell has a receptor on its cell surface that recognizes a specific part of a microbe. That receptor triggers a Signal transduction pathway. This triggers gene expression (transcription) that… …leads to protein synthesis (translation) that… …allows the cell to grow (duplicate all its proteins th ...
DNA
... a. Complete the base sequence of the complementary strand of the hypothetical DNA molecule diagrammed below. b. Use dashed lines to indicate hydrogen bonding between paired bases. c. Show how this molecule would be replicated: o Draw the molecule partially “unzipped” while undergoing replication, fo ...
... a. Complete the base sequence of the complementary strand of the hypothetical DNA molecule diagrammed below. b. Use dashed lines to indicate hydrogen bonding between paired bases. c. Show how this molecule would be replicated: o Draw the molecule partially “unzipped” while undergoing replication, fo ...
Did you ever get a message from a friend that was in code
... E a. DNA unwinds in many separate areas. b. Many areas of replication are occurring along the large eukaryotic chromosome at the same time. -appears 2. Prokaryotic DNA replication a. b. replication occurs in two directions ...
... E a. DNA unwinds in many separate areas. b. Many areas of replication are occurring along the large eukaryotic chromosome at the same time. -appears 2. Prokaryotic DNA replication a. b. replication occurs in two directions ...
Karyn Sykes January 24, 2009 LLOG 1: Immortal Genes: Running in
... diagnostics. Finally, scientists found that there are pieces of DNA coding that not only exist in humans and all eukaryotes but also in archaean genes. This discovery was profound because it gives more insight into the theory of evolution. By finding these codes, many scientists believe that an arch ...
... diagnostics. Finally, scientists found that there are pieces of DNA coding that not only exist in humans and all eukaryotes but also in archaean genes. This discovery was profound because it gives more insight into the theory of evolution. By finding these codes, many scientists believe that an arch ...
Phenotypic effects and variations in the genetic material (part 2)
... After a point deletion, the new sequence might be ATG-AGCGTA-TAT-AA. In this case, a T has been deleted. The new amino acid sequence is methionine, serine, valine, tyrosine, and then the final AA doesn't code for anything. ...
... After a point deletion, the new sequence might be ATG-AGCGTA-TAT-AA. In this case, a T has been deleted. The new amino acid sequence is methionine, serine, valine, tyrosine, and then the final AA doesn't code for anything. ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
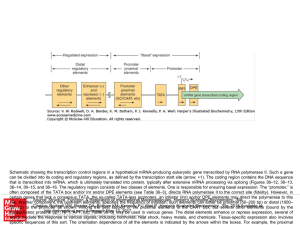
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
... chromosome of >20 Mb interstitially or >10 Mb telomerically (15 and 8 Mb, respectively, for imprinted chromosomes). * Contiguous homozygosity of >8 Mb within multiple chromosomes suggests common descent. These regions of potential recessive allele risk are designated. * A high level of allele homozy ...
File
... (1) starch necessary for ribosome synthesis in the cytoplasm (2) organic substance that is broken down into molecules B, C, and D (3) proteins that form the ribosome in the cytoplasm (4) directions for the synthesis of molecules B, C, and D 4. Molecules B, C, and D are similar in that they are usual ...
... (1) starch necessary for ribosome synthesis in the cytoplasm (2) organic substance that is broken down into molecules B, C, and D (3) proteins that form the ribosome in the cytoplasm (4) directions for the synthesis of molecules B, C, and D 4. Molecules B, C, and D are similar in that they are usual ...
dnachap12_12-3
... Mendel/flower images from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html Blood cell by Riedell ...
... Mendel/flower images from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html Blood cell by Riedell ...
Transcription, Translation and Mutations
... Models in science are used to describe ideas, understand biological processes and make predictions. Objective: Build a model to learn about transcription In groups, work to build a model of transcription. The magnets and safety pins will serve as the hydrogen and phosphodiester bonds, respectively. ...
... Models in science are used to describe ideas, understand biological processes and make predictions. Objective: Build a model to learn about transcription In groups, work to build a model of transcription. The magnets and safety pins will serve as the hydrogen and phosphodiester bonds, respectively. ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 4 of 14
... the amino acid in the P site and A site by peptidyl transferase and the amino acid it transferred to the tRNA in the A site and the tRNAs move through like a conveyer belt. Translocation: when the A site meets a stop codon a release factor not carrying an amino acid is called to the site which ly ...
... the amino acid in the P site and A site by peptidyl transferase and the amino acid it transferred to the tRNA in the A site and the tRNAs move through like a conveyer belt. Translocation: when the A site meets a stop codon a release factor not carrying an amino acid is called to the site which ly ...
Mutation
... Here a base is removed from the DNA sequence and similarly upsets the coding for every amino acid from the deletion onwards. Base additions and deletions always have larger effects because they cause a ‘frame shift’ in the code. Instead of a single amino acid being affected, every amino acid after t ...
... Here a base is removed from the DNA sequence and similarly upsets the coding for every amino acid from the deletion onwards. Base additions and deletions always have larger effects because they cause a ‘frame shift’ in the code. Instead of a single amino acid being affected, every amino acid after t ...
Unit B2, B2.7 Mark scheme
... gametes – 1 F1 genotypes corresponding to ‘lines’ – 1 lines must be correct Albino (aa) identified – 1 (lower case) ...
... gametes – 1 F1 genotypes corresponding to ‘lines’ – 1 lines must be correct Albino (aa) identified – 1 (lower case) ...
Why Do Names Keep Changing
... Proteins are strings of amino acids. There are 24 amino acids coded by DNA plus a start and stop signal (total 26) and 4 different types of base. 1 base / codon codes for 4 amino acids 2 bases / codon codes for 16 amino acids 3 bases / codon codes for 64 amino acids Enough! This is the called the tr ...
... Proteins are strings of amino acids. There are 24 amino acids coded by DNA plus a start and stop signal (total 26) and 4 different types of base. 1 base / codon codes for 4 amino acids 2 bases / codon codes for 16 amino acids 3 bases / codon codes for 64 amino acids Enough! This is the called the tr ...
Transduction
... • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the culture medium. • Bacteria show horizonta ...
... • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the culture medium. • Bacteria show horizonta ...