Transduction
... • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the culture medium. • Bacteria show horizonta ...
... • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the culture medium. • Bacteria show horizonta ...
Why Do Names Keep Changing
... Proteins are strings of amino acids. There are 24 amino acids coded by DNA plus a start and stop signal (total 26) and 4 different types of base. 1 base / codon codes for 4 amino acids 2 bases / codon codes for 16 amino acids 3 bases / codon codes for 64 amino acids Enough! This is the called the tr ...
... Proteins are strings of amino acids. There are 24 amino acids coded by DNA plus a start and stop signal (total 26) and 4 different types of base. 1 base / codon codes for 4 amino acids 2 bases / codon codes for 16 amino acids 3 bases / codon codes for 64 amino acids Enough! This is the called the tr ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
Genetic Disorder Oral Presentation Requirements
... recessive gene cause the genetic disorder? Or is there some other type of inheritance or mutation? Is the genetic disorder caused by fewer or extra chromosomes, or extra or missing pieces of chromosomes? 2. You should include any other information regarding the cause of the genetic disorder. This co ...
... recessive gene cause the genetic disorder? Or is there some other type of inheritance or mutation? Is the genetic disorder caused by fewer or extra chromosomes, or extra or missing pieces of chromosomes? 2. You should include any other information regarding the cause of the genetic disorder. This co ...
REVIEW for EXAM4-May 12th
... To reiterate, the sequence of events in Central Dogma as follow: first transcription > posttranscription> translation > post-translation. Transcriptional control is the most important step in this process because it is the first step and determines whether the gene will be transcribed in the first p ...
... To reiterate, the sequence of events in Central Dogma as follow: first transcription > posttranscription> translation > post-translation. Transcriptional control is the most important step in this process because it is the first step and determines whether the gene will be transcribed in the first p ...
Techniques
... • Extract mRNA (cDNA) from a tissue of interest • The mRNA is then tagged with a fluorescent dye and incubated overnight with the microarray. • mRNA hybridize to spots on the microarray that contain complementary DNA sequences. • Microarray is washed and scanned by a laser that cause the mRNA hybrid ...
... • Extract mRNA (cDNA) from a tissue of interest • The mRNA is then tagged with a fluorescent dye and incubated overnight with the microarray. • mRNA hybridize to spots on the microarray that contain complementary DNA sequences. • Microarray is washed and scanned by a laser that cause the mRNA hybrid ...
Lecture #15 - Suraj @ LUMS
... • A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germline mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells (germ cells) and can be passed from generation to generation, from parent to newborn. Moreover ...
... • A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germline mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells (germ cells) and can be passed from generation to generation, from parent to newborn. Moreover ...
Non-viral Transfection
... Liposomes were first introduced in 1987 by Felgner and coworkers (9). The liposomes currently in use typically contain a mixture of cationic and neutral lipids organized into lipid bilayer structures. Transfection-complex formation is based on the interaction of the positively charged liposome with ...
... Liposomes were first introduced in 1987 by Felgner and coworkers (9). The liposomes currently in use typically contain a mixture of cationic and neutral lipids organized into lipid bilayer structures. Transfection-complex formation is based on the interaction of the positively charged liposome with ...
Teaching Evolution Without Conflict or “THE
... • Any one of thousands of possible mutations in the several genes for a biochemical pathway could explain why a particular species fails to make a particular enzyme. • What does this suggest about the fact that Vitamin C production is blocked in several similar species by the exact same mutation in ...
... • Any one of thousands of possible mutations in the several genes for a biochemical pathway could explain why a particular species fails to make a particular enzyme. • What does this suggest about the fact that Vitamin C production is blocked in several similar species by the exact same mutation in ...
Glossary of terms related to Neuromuscular Conditions
... A clinical sign named after the English physician who first described it in 1879. Whenever there is a weakness in the muscles around the hips, rising from the floor becomes increasingly difficult. The person has to press on his thighs and then climbs up them in order to extend the hips and straighte ...
... A clinical sign named after the English physician who first described it in 1879. Whenever there is a weakness in the muscles around the hips, rising from the floor becomes increasingly difficult. The person has to press on his thighs and then climbs up them in order to extend the hips and straighte ...
Gene Section WFDC1 (WAP four-disulfide core domain 1) in Oncology and Haematology
... The rat homologue of ps20 was originally identified as a secreted growth inhibitor. These growth regulatory effects and the cell phenotypic properties in vitro, suggest that ps20 may function as a mediator of stromal-epithelial interactions and contribute to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Th ...
... The rat homologue of ps20 was originally identified as a secreted growth inhibitor. These growth regulatory effects and the cell phenotypic properties in vitro, suggest that ps20 may function as a mediator of stromal-epithelial interactions and contribute to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Th ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
Chapter 15 Review Questions
... part and a positively charged one), disulfide linkages (covalent bonds involving 2 sulfurs), and dispersion forces (temporary bonds between non-polar side-chains). The quaternary structure of a protein takes multiple tertiary structures and bonds them together (i.e. several amino acid chains, folded ...
... part and a positively charged one), disulfide linkages (covalent bonds involving 2 sulfurs), and dispersion forces (temporary bonds between non-polar side-chains). The quaternary structure of a protein takes multiple tertiary structures and bonds them together (i.e. several amino acid chains, folded ...
Gene Technology
... now have the same sticky ends (plasmid should also be resistant to antibiotic like ampicillin) 3. Mix the foreign DNA with the plasmids 4. Apply DNA ligase ...
... now have the same sticky ends (plasmid should also be resistant to antibiotic like ampicillin) 3. Mix the foreign DNA with the plasmids 4. Apply DNA ligase ...
mutation and recombination as one nucleotide pair
... pages, which opens with a discussion of the relationship between genotype and phenotype for quantitative characters. The author then disposes of the notoriously difficult problem of scales and scaling tests in one page. The partitioning of variation between additive and dominance components using a ...
... pages, which opens with a discussion of the relationship between genotype and phenotype for quantitative characters. The author then disposes of the notoriously difficult problem of scales and scaling tests in one page. The partitioning of variation between additive and dominance components using a ...
`Genes` Like That, Who Needs an Environment?
... ‘environment’ for any gene is composed of (1) regulatory and intronic sequences that are targeted by transcription and splicing factors (proteins and noncoding RNAs) that bind to them and (2) the specific environmental signals that cue these factors or otherwise influence the gene’s expression. I un ...
... ‘environment’ for any gene is composed of (1) regulatory and intronic sequences that are targeted by transcription and splicing factors (proteins and noncoding RNAs) that bind to them and (2) the specific environmental signals that cue these factors or otherwise influence the gene’s expression. I un ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
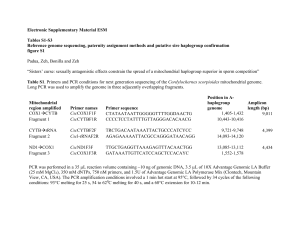
... CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in two fragments of similar length. In order to span the entire genome, 35 primer pairs were designed, with ~ 100-bp overlap between con ...
... CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in two fragments of similar length. In order to span the entire genome, 35 primer pairs were designed, with ~ 100-bp overlap between con ...
DNA vaccination
... gene of interest such as SV40 promoter, Rous Sarcoma Virus (RSV) promoter The most recent one is cytomegalovirus (CMV). ...
... gene of interest such as SV40 promoter, Rous Sarcoma Virus (RSV) promoter The most recent one is cytomegalovirus (CMV). ...
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE
... Later in development, the X encoded factor is not produced. sxl is now transcribed from a different promoter producing a longer pre mRNA. For this pre mRNA to form mRNA encoding a functional Sxl protein, an exon containing a stop codon must be spliced out. Sxl represses splicing at the site that wou ...
... Later in development, the X encoded factor is not produced. sxl is now transcribed from a different promoter producing a longer pre mRNA. For this pre mRNA to form mRNA encoding a functional Sxl protein, an exon containing a stop codon must be spliced out. Sxl represses splicing at the site that wou ...
I. Mutations: primary tools of genetic analysis
... A. Mutations are heritable changes in base sequence that modify the information content of DNA ð one way geneticists classify mutations is by their effect on the DNA molecule B. Spontaneous mutations affecting genes occur at a very low rate 1. The mutation rate varies from gene to gene 2. Forward mu ...
... A. Mutations are heritable changes in base sequence that modify the information content of DNA ð one way geneticists classify mutations is by their effect on the DNA molecule B. Spontaneous mutations affecting genes occur at a very low rate 1. The mutation rate varies from gene to gene 2. Forward mu ...
How Proteins are Made - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... – Not two to one either—there are only 16 possible combinations of two bases of DNA (AA, AT, AC, AG, CA, etc.). – Sydney Brenner suggested it worked as a triplet code—three nucleotides (called a codon) signifying one amino acid. There are 64 different possible combinations of the four nucleotides, m ...
... – Not two to one either—there are only 16 possible combinations of two bases of DNA (AA, AT, AC, AG, CA, etc.). – Sydney Brenner suggested it worked as a triplet code—three nucleotides (called a codon) signifying one amino acid. There are 64 different possible combinations of the four nucleotides, m ...
DNA: Structure and Function
... • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is complimentary to T • G is ...
... • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is complimentary to T • G is ...
Genetics - Cobb Learning
... Who is Gregor Mendel? “Father of Genetics” Principle of Independent Assortment – Inheritance of one trait has no effect on the inheritance of another trait ...
... Who is Gregor Mendel? “Father of Genetics” Principle of Independent Assortment – Inheritance of one trait has no effect on the inheritance of another trait ...